Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Economic Growth
Uploaded by
ximenaliza6Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Economic Growth
Uploaded by
ximenaliza6Copyright:
Available Formats
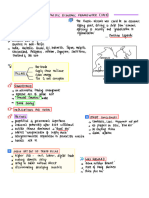
* RGDP : of national output
value an
economy's
Sig S
that has been adjusted for inflation.
I concept , diagrams , example
China Pem , Venezuela ,
,
Argentina
Refers to an increase in a
country's real gross domestic (RGDP) over time
. (For two consecutive quarters)
↳ sustained increase in the potential productive capacity of the economy
. J quality andlor quantity of Fop
of economic activity declines Crecession or slump in .c)
B
↳ Negative economic growth : Economic downturn
, level
MASONS of Differences
between GROWTH rates
MostImportant in
Factor Ereforments Size and Skills of Labour force
↳ most practical
for people to
way
have a
higher standard of
Highly skilled workforce contributes to
Living
Quantity or quality of a country's FoP .
economic . For
growth instance large
supply)
,
(USA , Saudi Arabia endowed in oil
Labour force in China =
economic growth .
the
The more factor resources a country has
Discovery
economic growth
.
of Raw Materials
more likely to achieve
Investment Expenditure Discovery of any tradable commodities
Coil , metals , etc)
. PPC outwards
↳ In capital a human resources
,
country's
Mobility of Laboyn
boosts productive capacity
.
Greater proportion of GDP in FDI
stimulates economic growth and development . Extent : workers willing and able to
change jobs and locations for employment.
Labour Productivity ↓ (occupationally and geographically able)
= economic growth
Output produced in a given time period
Factors : experience , training skills Investment , .
in education and
training = economic growth
.
Representing
enomic growth is RGDP increases Current Level/Actual
level of national income
growth)
Economy operates below its full employment but moves towards its potential
short-run
CDP
-
level of by using more resources
efficiently
.
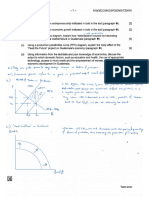
④ AD-AS diagram ② Business cycle ③ Production possibility
curve
DL E SRAS Potential
n
capacity
good
maximum
RGDP f -to
? Output
/lapape
the
produce by
f
·
-o
B economy
O A * using previously
D
time
Ye Y2 REDP unemployed
Boom and recovery
resources
DL E
SRAS Services
------------
Pr SRASS Increase quantity Fop
quality of in the long
1/
in or run .
P2 Long-run
(employment , economic
-
growth)
&
Ye Y REDP ④ AD-AS diagram ② Business cycle ③ Production possibility
curve
PL *
LRAS
* Rightwards of AD LRAS2 RODP A * Outwards shift
curve and SRAS curve
reduce pot 2 Good (discovery)
stime
costs of
output 1
PPC 2
Living
AD
PPC
PREDD ,
* Increase in labour supply , > Services
in
improvement technology.
MEASUREMENT 3
Need to establish a base year of analysis
nominal GDP-inflation effect = Real GDP
Final-Initial 2nd year- 1st
RATE =%
-
year
Real GDP GROWTH >
-
- - 100 (percentage)
Initial 1st year
Takes account of fluctuations -
Example
·
:
in
prices (inflation) RGDP
Formula :
STEP 1
RGDP
formula
Adjusted for inflation by using GDP deflator
STEP 2
practice
Growth
rate
-
formula
zo
=>
oe
Nominal GR %
-nezoxnoogonaReaooo2sNoma a
both (positive and negative)
consequences
④ Impact on
living standards
to meet their needs and wants
to spend more
>
-
Higher real income enables people
Impacts
· Reduction or elimination of poverty , as more
people able to purchase basic goods
.
and encourages investment
Creation
·
of new jobs and lower unemployment ,
raise
consumption
fund + ment and services (in long run = economic growth)
·
Increased tax revenues , enables government to goods
↳ (expenditure & income) + enomic activity
Increased greater profits increase capital stock to
expand productive capacity.
consumer
spending , higher
·
sales revenue and ,
POV : firms
· Increased income levels , tend to a rise in dement goods (tobaco , alcohol)
POV : consumers
· Risk of inflation, owing to excessive aggregate demand, danger of demand-pull inflation , rising prices (decline of
economy)
② Impact on the environment >
- Create regative externalities
road congestion , climate change ,
land erosion , loss of biodiversity
·
Problems : air pollution ,
equities
·
Creation of market failures : resource depletion (deforestation) - threatening intergenerational
through environmentally sustainable methods
=
green
GDP (taking account environmental damage)
③ Impact on income distribution is Creates greater disparities in the distributions of income and wealth
·
Widens the gap between poor and rich
·
Howers with tax
revenues, government can use to redistribute income and wealth in the economy
.
You might also like
- Judging: The Value IndustrialDocument1 pageJudging: The Value IndustrialSheie WiseNo ratings yet
- 44040.raheel 20tariq - LiteraturereviewDocument3 pages44040.raheel 20tariq - LiteraturereviewDaim AliNo ratings yet
- Ratio (3 Marks)Document4 pagesRatio (3 Marks)mehtaharshit0709No ratings yet
- Indian EconomyDocument4 pagesIndian Economyvengurlekarsiddhi08No ratings yet
- Mindmap Returns Management XPODocument1 pageMindmap Returns Management XPONgoc PhamNo ratings yet
- (Package 2 - Pec-Dcsm) NSRP Daily Progress Report - 201910 - 23Document21 pages(Package 2 - Pec-Dcsm) NSRP Daily Progress Report - 201910 - 23duyanhNo ratings yet
- Research WorkDocument24 pagesResearch WorkBamba GNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Design of Goods and Services OpmDocument1 pageChapter 5 Design of Goods and Services Opmnurfarhana6789No ratings yet
- Brochure UYC EnglishDocument8 pagesBrochure UYC EnglishAndra SerbanNo ratings yet
- Economic DevelopmentDocument16 pagesEconomic DevelopmentJake MempinNo ratings yet
- Autism ENGDocument1 pageAutism ENGWillem HeesbeenNo ratings yet
- Economic ModelsDocument3 pagesEconomic ModelsX ZNo ratings yet
- October 2022 eDocument20 pagesOctober 2022 eEng Clive KabelengaNo ratings yet
- MGT 320Document2 pagesMGT 320Anfal KankouniNo ratings yet
- Editorial 29.11.2022Document9 pagesEditorial 29.11.2022Sandeep MittalNo ratings yet
- Topic 3Document2 pagesTopic 3sofianasery28No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 28-Nov-2023Document10 pagesAdobe Scan 28-Nov-2023rushikesh huleNo ratings yet
- Summary - Cost AccountingDocument43 pagesSummary - Cost AccountingNESIBE ERBASNo ratings yet
- Stragies GerstleDocument28 pagesStragies GerstleasitarekNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2019Document27 pagesAnnual Report 2019Dan p.No ratings yet
- D Articles SnapshotDocument3 pagesD Articles Snapshotfantastic worldNo ratings yet
- CH 16Document1 pageCH 16陳郁茗No ratings yet
- Cpi Metadata.2016 PDFDocument132 pagesCpi Metadata.2016 PDFurbam zarateNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument1 page1 PDFSim Pei YingNo ratings yet
- Mindmap Supply Chain Network Redesign Chainalytics 2020Document1 pageMindmap Supply Chain Network Redesign Chainalytics 2020Ngoc PhamNo ratings yet
- 393608551 Barry Cockcroft Rock Me萨克斯独奏 PDFDocument8 pages393608551 Barry Cockcroft Rock Me萨克斯独奏 PDFPedro Filipe Ribeiro67% (3)
- Project Was: 32 To Ina Ina StatedDocument1 pageProject Was: 32 To Ina Ina StatedSheie WiseNo ratings yet
- Sample Expense ReportDocument1 pageSample Expense Reportmharaynel.afableNo ratings yet
- Mapa Conceptual Análisis FinancieroDocument4 pagesMapa Conceptual Análisis FinancieroRoberto SantosNo ratings yet
- Line With Situa Con: of ImportingDocument1 pageLine With Situa Con: of ImportingSheie WiseNo ratings yet
- 22 - 9 IpefDocument1 page22 - 9 IpefAadesh kumar Soni nayakNo ratings yet
- Lower Lower-More of More More - Mar Keting Project Not Well The Market It Which of Interrelation Follows Dynamic Industrial byDocument1 pageLower Lower-More of More More - Mar Keting Project Not Well The Market It Which of Interrelation Follows Dynamic Industrial bySheie WiseNo ratings yet
- Design WeldDocument1 pageDesign WeldPabloScurraNo ratings yet
- CFA Reading NotesDocument1 pageCFA Reading Noteshwykvycjs8No ratings yet
- IB Economics Notes - Market FailureDocument43 pagesIB Economics Notes - Market FailureAnindya WardhanaNo ratings yet
- TQM 2021HB79113Document1 pageTQM 2021HB79113chirag sharmaNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument1 page4 PDFSim Pei YingNo ratings yet
- Transportation: A Global Supply Chain Perspective (8e) : Coyle, Novack, and GibsonDocument4 pagesTransportation: A Global Supply Chain Perspective (8e) : Coyle, Novack, and Gibson熊No ratings yet
- Real Estate: Presented By: Bansal (5) Pankaj Jain (13) ANUPAM KASUHIK (16) Nimish ShinghatwadiaDocument13 pagesReal Estate: Presented By: Bansal (5) Pankaj Jain (13) ANUPAM KASUHIK (16) Nimish Shinghatwadiamanjul2010No ratings yet
- 20240219econ Paper 2 PracticeDocument2 pages20240219econ Paper 2 PracticeCHAN KWOK KING G9G-01No ratings yet
- Case Study 1 Part 1: The StoryDocument5 pagesCase Study 1 Part 1: The StoryMary Jane InsigneNo ratings yet
- Rural DevelopmentDocument1 pageRural DevelopmentKhushi SatwaniNo ratings yet
- Mindmap For Operational Transparency in SAP: Supply Chain MindmappingDocument1 pageMindmap For Operational Transparency in SAP: Supply Chain MindmappingobNo ratings yet
- Eq FD RoadmapDocument1 pageEq FD RoadmapWilmer E. Cumbicus JiménezNo ratings yet
- Proforma 2Document1 pageProforma 2Wrishi BiswasNo ratings yet
- Vĩ Mô Chap 10-1Document1 pageVĩ Mô Chap 10-1Tâm Bùi Thị ThanhNo ratings yet
- Macro I CH 2 Basic Concepts in MacroeconomicsDocument89 pagesMacro I CH 2 Basic Concepts in MacroeconomicsHaftom YitbarekNo ratings yet
- Schlumberger Role in Commercial Integration: Gabriela Prete, Country Manager Schlumberger ArgentinaDocument6 pagesSchlumberger Role in Commercial Integration: Gabriela Prete, Country Manager Schlumberger ArgentinaFranz Gutierrez VegaNo ratings yet
- Coming Up On The Downside: Tear Up Those Old TracksDocument1 pageComing Up On The Downside: Tear Up Those Old TracksnagendraNo ratings yet
- Case Study 2 Part 1: The StoryDocument5 pagesCase Study 2 Part 1: The StoryMary Jane InsigneNo ratings yet
- 04b Economic Risk Capital (2011)Document13 pages04b Economic Risk Capital (2011)apluNo ratings yet
- Product With: For The ExportsDocument1 pageProduct With: For The ExportsSheie WiseNo ratings yet
- UNIT 2 - Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument2 pagesUNIT 2 - Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesSean Michael TanChuaNo ratings yet
- Us CB Consumer Products Industry Outlook InfographicDocument1 pageUs CB Consumer Products Industry Outlook InfographicS NNo ratings yet
- All Editorials PDFDocument18 pagesAll Editorials PDFMD NADEEM ASGARNo ratings yet
- EconDocument11 pagesEconSamaira IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Jps Rate Schedules 2018-2019 Jps Rate Schedules 2018-2019: The Electricity Licence, 2016Document2 pagesJps Rate Schedules 2018-2019 Jps Rate Schedules 2018-2019: The Electricity Licence, 2016csf571No ratings yet
- AI in The Fashion Industry - PosterDocument2 pagesAI in The Fashion Industry - PosterjesusantelicesNo ratings yet
- Teacher Thought For InterviewDocument37 pagesTeacher Thought For InterviewMahaprasad JenaNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior Exam 2 Practice QuestionsDocument1 pageOrganizational Behavior Exam 2 Practice QuestionsSydney EverettNo ratings yet
- Instability of Slender Concrete Deep BeamDocument12 pagesInstability of Slender Concrete Deep BeamFrederick TanNo ratings yet
- Henry's Bench: Keyes Ky-040 Arduino Rotary Encoder User ManualDocument4 pagesHenry's Bench: Keyes Ky-040 Arduino Rotary Encoder User ManualIsrael ZavalaNo ratings yet
- Cement Grouted Rock BoltsDocument28 pagesCement Grouted Rock BoltsBhaskar ReddyNo ratings yet
- GW1101-1DI (3IN1) DatasheetDocument6 pagesGW1101-1DI (3IN1) DatasheetGina HuachoNo ratings yet
- Short Stories Planet Earth AnswersDocument2 pagesShort Stories Planet Earth AnswersLina Vasquez Vasquez100% (2)
- Dharmakirti On Pratyaksa PDFDocument14 pagesDharmakirti On Pratyaksa PDFonlineyyk100% (1)
- Teacher Survey - Outdoor Classroom Feedback: Please Circle All That ApplyDocument3 pagesTeacher Survey - Outdoor Classroom Feedback: Please Circle All That ApplyBrooke Doran RoeNo ratings yet
- John Deere CaseDocument2 pagesJohn Deere CaseAldo ReynaNo ratings yet
- Am Jetstream Pre-Int Unit 8 Lesson 2Document2 pagesAm Jetstream Pre-Int Unit 8 Lesson 2Jennyfer Guevara50% (2)
- Analysis and Design of Suspended Buildings: Creative and Innovative Report-1Document14 pagesAnalysis and Design of Suspended Buildings: Creative and Innovative Report-1Nirmal RaviNo ratings yet
- Tahmina Ferdousy Jhumu: HND Btec Unit 15 Psychology For Health and Social CareDocument29 pagesTahmina Ferdousy Jhumu: HND Btec Unit 15 Psychology For Health and Social CareNabi BoxNo ratings yet
- BarDocument1 pageBarJoannalyn Libo-onNo ratings yet
- 12 - Chepter 5Document11 pages12 - Chepter 5KhaireddineNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Double Award Science BiologyDocument9 pagesMark Scheme: Double Award Science BiologyDaniel LoughreyNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Industrial Engineering: Part - B (10 Marks) : Answer All The QuestionsDocument4 pagesNational Institute of Industrial Engineering: Part - B (10 Marks) : Answer All The QuestionsTulasi PatleNo ratings yet
- The Explanatory GapDocument2 pagesThe Explanatory GapPapuna ChivadzeNo ratings yet
- Certified Vendors As of 6 17 22Document18 pagesCertified Vendors As of 6 17 22Harry ConnerNo ratings yet
- Mesa Quirurgica Opt 70 Ec 02 PDFDocument36 pagesMesa Quirurgica Opt 70 Ec 02 PDFTEYLER BARBOZANo ratings yet
- Zero Voltage Switching Active Clamp Buck-BoostDocument10 pagesZero Voltage Switching Active Clamp Buck-Boostranjitheee1292No ratings yet
- Management From RamayanaDocument14 pagesManagement From Ramayanasaaket batchuNo ratings yet
- Easy BuyDocument14 pagesEasy BuyChinmaya BeheraNo ratings yet
- UNIABROAD PitchdeckDocument21 pagesUNIABROAD PitchdeckVikas MurulidharaNo ratings yet
- 6 Best Chainsaw Under 300: A Complete Buying Guide: What We LikeDocument5 pages6 Best Chainsaw Under 300: A Complete Buying Guide: What We LikeFahim WatsonNo ratings yet
- M7Ge-Iiib-1: Renante Tillo JosolDocument3 pagesM7Ge-Iiib-1: Renante Tillo JosolRenante T. JosolNo ratings yet
- ART Threaded Fastener Design and AnalysisDocument40 pagesART Threaded Fastener Design and AnalysisAarón Escorza MistránNo ratings yet
- Āyāt Al-Aḥkām, Ayat Al-AhkamDocument6 pagesĀyāt Al-Aḥkām, Ayat Al-AhkamRasoul NamaziNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Pakistani English Language LearnersDocument19 pagesFactors Affecting Pakistani English Language LearnersSaima Bint e KarimNo ratings yet
- Predicates and ArgumentsDocument4 pagesPredicates and ArgumentsOanh NguyễnNo ratings yet