Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Topic 3
Uploaded by
sofianasery28Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Topic 3
Uploaded by
sofianasery28Copyright:
Available Formats
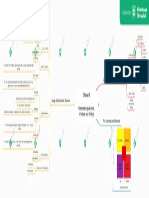
TOPIC 3 : NEW PUBLIC MANAGEMENT (NPM)
Introduction to NPM Characteristics/Elements Comparison between Bureaucratic
model (BM) & NPM
.
MANTRA ·
Aimed at improving efficiency Hood (1995) Pollitt (2003) Hughes (2003)
:
public sector ,
, ↑
f Zu Y
and performance in the
delivery of services .
1 change in management's focus from inputs
major emphases/values Actors Strategies
and
·
ensuring the effectiveness and efficiency and processes to output cresult) & outcomes core objectives
↳ focu from
ending BM : rational & efficient organizational BM : hierarchical control , clear lines BM : Public bureaucracy
in public services I
delivery
. beginning to
.
NPM ideology
2)
change towards measurement and model for the pursuit of goals
. of responsibility , accountability ,
hierarchies
·
existing structures and policies of the government quantification .
PM : Enhance
efficiency & quality in continuity
, probity ·
M :
Markets and
are primary causes of inefficiency & poor performance . 3) Restructuring public sector .
NM :
Downsize government , contract ,
incentives
.
·
It claims that changing the structure of governmental ↳ downsizing public sector through regulation and competition , flexibility
.
agencies alone will not fix the government's problems Privatization & Commercialization
since they are so widespread and complex. 4) Preference :
more specialized ,
I can & Advantages of NPM
·
Hence , a number of drastic reforms and market-based flat autonomous organizational forms 1) Promotes individualism
5) substitution of ↳ leads
fixes are provided by PM proponents ,
formal hierarchical to efficiency & effectiveness in
delivery of good & services
-
example :
relationship to contracts and contract -
2) New public management
>
-
downsizing the public sector through privatization & like relationship improves product delivery
deregulation. b) shift to greater competition in public 3) Makes bureaucratic system to be more efficient and cost benefit .
>
-
enhanced role of private sector sector . 4)
Improves structures of public sector
> introduction
-
of private management principles 7) Empharis on private sector-style ↳ reducing the cost &
spending
.
into the public sector .
management & flexibility ,
cost recovery
So
·
, NPM advocates maximising the role of the private sector and entrepreneurship
. Disadvantages of NPM
in governance and service delivery since it views the 'market ·) shift towards a management culture 1) Blurred lines between policymaking & providing services
as a remedy for an expansive and inefficient governmental sector .
↳
customer orientation I due to regulation can be .
bend
Three integrating themes of NPM (Dunleavy et al . (2006) ↳ accountability for results -
2) Questions have been raised about
~ ↓ -
> ↳ potential politicization of the
public service
↳ executives
Disaggregation competition incentivization are hired on contract under pay-for-performance systems
·
splitting up large
·
purchaser -
provider split ·
linking incentives to 3) will be a challenge for citizen to effectively choose the appropriate government services they need .
Provider public servant
:
public sector ·
competition among performance. H) There are concerns that public managers more away from trying to meet citizens' needs & limitations
hierarchies . providers ↳ 'money reward' on accountability to the public .
↳ task will be divided ↳
bagus 5) Question integrity for
orang Kerja nya & compliance when dealing with incentives public managers .
↳ award
less responsibility , diberk e .
: managers being more
g or less faithful arise.
increase performance.
6)
Public interest is at risk & could undermine the trust in government·
"Government must be accountable larger public interest , not individual immediate
to the
only to
customers or consumers of government services .
Public Sector Reformation
Introduction to New (NPS)
Public Service Characteristics of New Public Service CNPS] 4) Serve citizens ,
not customers.
·
The NPS approach' is a concept that describes how According to Denhardt et. al (2000) and Kusnadar (2019) -
Instead of the accumulation of individual self-interests , the public interest comes from a
administered & provided 1) serve , rather than steer
discussion about shared values
public services are ·
·
This
strategy places strong emphasis working Instead of trying Consequently
-
a on to dominate or reshape society , public -
,
rather than just attending to the needs of their 'customers' , public servants
together , getting involved and using technology to servants are playing a more and more crucial role concentrate on
building relationships of trust and collaboration to and
among citizens ..
increase productivity transparency
,
and citizen satisfaction- in assisting citizens in expressing and achieving their 5) Accountability is not simple .
·
Traditionally
, Public Services been provided by common interests-
hierarchical , bureaucratic structures that prioritize rules 2) The public interest is the aim , not the by-product
and regulations over and innovation.
flexibility Building collective
-
common
a ,
understanding of the public
·
There has been realization in recent yearss public interest
an
increasing interest of the is a
responsibility of
that this traditional method is insufficient to meet the public administrators.
needs of 21st-century citizens
. -
The goal is not to achieve quick solutions driven by
. Rather ,
individual choices it is the creation of shared
interests and shared responsibility
.
3) Think strategically act democratically
.
,
The most efficient and ethical ways to develop policies
and programs that address public needs are through
teamwork and cooperative methods
.
&
You might also like
- Operations Management Process EvaluationDocument1 pageOperations Management Process EvaluationQuang HữuNo ratings yet
- Data Governance Cheat SheetDocument1 pageData Governance Cheat SheetFernando HernandezNo ratings yet
- Danfoss at a Glance: Core & Clear Digital Transformation JourneyDocument1 pageDanfoss at a Glance: Core & Clear Digital Transformation JourneyAvronNo ratings yet
- CRM Dashboard Team Whiteboard in Pink Black Tactile 3D StyleDocument1 pageCRM Dashboard Team Whiteboard in Pink Black Tactile 3D Stylewalidkadfi72No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Formulation and Verification of Accounting TheoryDocument1 pageChapter 2 Formulation and Verification of Accounting Theoryammar beatlesNo ratings yet
- Mop Bicycle Heny PortmanDocument1 pageMop Bicycle Heny Portmanamir sedighiNo ratings yet
- Summary - Cost AccountingDocument43 pagesSummary - Cost AccountingNESIBE ERBASNo ratings yet
- CO Template Office Learning PlanDocument2 pagesCO Template Office Learning PlanMIGNONETTE ERIM DULAYNo ratings yet
- RCK Programme Methods Intro Deck 0522 V1.0Document8 pagesRCK Programme Methods Intro Deck 0522 V1.0grecnNo ratings yet
- Biggest operational challenges in meeting strategic goals for metals companiesDocument1 pageBiggest operational challenges in meeting strategic goals for metals companiesÆdzitØn EstradaNo ratings yet
- 14 - Integration Management - 2013 V5Document5 pages14 - Integration Management - 2013 V5DougNo ratings yet
- Zusammenfassung FIBDocument14 pagesZusammenfassung FIBHanna MichaelNo ratings yet
- Driving Electric Distribution ExcellenceDocument15 pagesDriving Electric Distribution Excellencekashifbutty2kNo ratings yet
- Itsm Chart V2.0 PDFDocument1 pageItsm Chart V2.0 PDFleslewis65100% (1)
- Careers 3Document1 pageCareers 3CityPressNo ratings yet
- October AccomplishmentDocument17 pagesOctober AccomplishmentReyma GalingganaNo ratings yet
- Value Chain Map ITIL4Document2 pagesValue Chain Map ITIL4Belem PianaNo ratings yet
- Central Finance 1709Document38 pagesCentral Finance 1709Romain DepNo ratings yet
- PM One Page FlowchartDocument1 pagePM One Page FlowchartbenNo ratings yet
- HR Strategy Focuses on Recruiting and Developing Diverse TalentDocument2 pagesHR Strategy Focuses on Recruiting and Developing Diverse TalentSimaSenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Design of Goods and Services OpmDocument1 pageChapter 5 Design of Goods and Services Opmnurfarhana6789No ratings yet
- A Financial Statement Analysis Project FDocument2 pagesA Financial Statement Analysis Project FAliNo ratings yet
- Poster Process Map Itil PDFDocument1 pagePoster Process Map Itil PDFdeba8012No ratings yet
- 9 - Human Resource Management - 2013 - V5Document4 pages9 - Human Resource Management - 2013 - V5DougNo ratings yet
- Business Organisation, Structure and Strategy: Corporate-Level Strategy (Companywide)Document1 pageBusiness Organisation, Structure and Strategy: Corporate-Level Strategy (Companywide)Minhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- ManAccCHAPTER 1 PDFDocument8 pagesManAccCHAPTER 1 PDFsaralimanuyag8_25539No ratings yet
- Balanced BSCDocument23 pagesBalanced BSCRenato GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management: Attractive Opportunity Implementation PlanDocument2 pagesStrategic Management: Attractive Opportunity Implementation PlanKatrizia FauniNo ratings yet
- IT4IT Reference Card2Document1 pageIT4IT Reference Card2GuillermoVillalonNo ratings yet
- Environmental Scanning The Basic Model: - 30/11/2011 - Prepared by Carl Olav Staff / Rune Fjellvang Page 1 of 1Document1 pageEnvironmental Scanning The Basic Model: - 30/11/2011 - Prepared by Carl Olav Staff / Rune Fjellvang Page 1 of 1Baher WilliamNo ratings yet
- Logistic Support Analysis (LSA) : TitleDocument26 pagesLogistic Support Analysis (LSA) : Titlenebodepa lyftNo ratings yet
- WFP2023Document36 pagesWFP2023Fallucky SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Untt-Y: Coanned With FamcrannarDocument12 pagesUntt-Y: Coanned With FamcrannarRoy mrunalNo ratings yet
- 1699611082master Web Ad - TV 14112023Document11 pages1699611082master Web Ad - TV 14112023javedNo ratings yet
- Dixon 1QFY22 Result Update - OthersDocument14 pagesDixon 1QFY22 Result Update - OthersjoycoolNo ratings yet
- Annex G Work Program - Osec Fms Form No. 3 As of .141 Lamitan CityDocument3 pagesAnnex G Work Program - Osec Fms Form No. 3 As of .141 Lamitan CityGayeGabriel100% (1)
- Low-cost strategy and value chain activitiesDocument1 pageLow-cost strategy and value chain activitiesMinhh KhanggNo ratings yet
- Mindmap European Operations FootprintDocument1 pageMindmap European Operations FootprintJoão Pedro Correia BorgaNo ratings yet
- Memba 2022 Web Brochure - SpreadsDocument8 pagesMemba 2022 Web Brochure - SpreadsNimit AnandNo ratings yet
- Embedded Project WorksheetDocument4 pagesEmbedded Project WorksheetcammanderNo ratings yet
- Deloitte - Anaplan-CoE-whitepaperDocument11 pagesDeloitte - Anaplan-CoE-whitepapersnowboardhollandNo ratings yet
- Scan 0001Document2 pagesScan 0001jimcccNo ratings yet
- Domestic Auto Parts Strategy MapDocument1 pageDomestic Auto Parts Strategy MapMacarena Bahamondes ArroyoNo ratings yet
- IF 07C Special Instruction Form Form - 07 03 January 2022 4Document2 pagesIF 07C Special Instruction Form Form - 07 03 January 2022 4chqaiserNo ratings yet
- Bachelor in Management Studies (BMS)Document99 pagesBachelor in Management Studies (BMS)Amit AmitNo ratings yet
- Finding the right title for a service sector documentDocument4 pagesFinding the right title for a service sector documentriya penkar0% (1)
- 2013 + Federal EA Framework (V2, U.S. Federal Government)Document436 pages2013 + Federal EA Framework (V2, U.S. Federal Government)Đào Duy AnhNo ratings yet
- Responsibility Matrix PDFDocument1 pageResponsibility Matrix PDFNour MerjaniNo ratings yet
- MotivationMeans IPDA LCI ReportDocument255 pagesMotivationMeans IPDA LCI Reportsuman samratNo ratings yet
- Payroll (HR) RCM 2022-2023Document1 pagePayroll (HR) RCM 2022-2023Aman ParchaniNo ratings yet
- LeanIX - An Agile Framework To Implement TOGAF With LeanIX - ENDocument1 pageLeanIX - An Agile Framework To Implement TOGAF With LeanIX - ENPaul Vintimilla CarrascoNo ratings yet
- LeanIX An Agile Framework To Implement TOGAF With LeanIX enDocument1 pageLeanIX An Agile Framework To Implement TOGAF With LeanIX enLarry LarsNo ratings yet
- Managing People: Theories and ConceptsDocument1 pageManaging People: Theories and ConceptsmiaNo ratings yet
- Value Stream Improvement Plan TemplateDocument4 pagesValue Stream Improvement Plan TemplatemilandivacNo ratings yet
- Education: Project: Develop The Supply Chain Model For Adhesives (Incl. Stationary) and Wood Finishes CategoriesDocument1 pageEducation: Project: Develop The Supply Chain Model For Adhesives (Incl. Stationary) and Wood Finishes CategoriesVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development Standards JAN2023Document97 pagesSustainable Development Standards JAN2023lirepi8208No ratings yet
- Ekatm CRMDocument2 pagesEkatm CRMVritti iMediaNo ratings yet
- China Suzhou Office Q1 2021 ENDocument2 pagesChina Suzhou Office Q1 2021 ENsangoi_vipulNo ratings yet
- Base Enterprise Value Map PDFDocument1 pageBase Enterprise Value Map PDFjvr001100% (1)
- Scientific ManagementDocument24 pagesScientific Managementdipti30No ratings yet
- College Entrepreneurship Homework GuideDocument5 pagesCollege Entrepreneurship Homework GuideH MNo ratings yet
- Differences Between A Limited Liability Partnership and A General PartnershipDocument1 pageDifferences Between A Limited Liability Partnership and A General PartnershipHanenFamNo ratings yet
- Union Bank 1Document12 pagesUnion Bank 1bindu mathaiNo ratings yet
- Monopoly: Imba Nccu Managerial Economics Jack WuDocument26 pagesMonopoly: Imba Nccu Managerial Economics Jack WuMelina KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Consol MBDocument1,216 pagesConsol MBSancho HoNo ratings yet
- Compound AmountDocument68 pagesCompound AmountKEYDAVE ARNADONo ratings yet
- Loan Account Statement 019763997Document2 pagesLoan Account Statement 019763997Nikhil JadonNo ratings yet
- Sales Report: Philippine Seven CorporationDocument2 pagesSales Report: Philippine Seven CorporationGreyNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Laboratory BudgetDocument27 pagesLesson 7 - Laboratory BudgetFranzil Shannen PastorNo ratings yet
- Course Overview: CME Group Courses Module 3Document8 pagesCourse Overview: CME Group Courses Module 3Darren FNo ratings yet
- Privatisation of RailwaysDocument2 pagesPrivatisation of RailwaysRajnish PrakashNo ratings yet
- Business Law ExamDocument3 pagesBusiness Law ExamBarzala CarcarNo ratings yet
- PO GCWS G85012 To MIDocument6 pagesPO GCWS G85012 To MIandika bukopinNo ratings yet
- Accounting of DepreciationDocument9 pagesAccounting of DepreciationPrasad BhanageNo ratings yet
- Abm TermsDocument2 pagesAbm TermsAxeliaNo ratings yet
- Final Black Book GST in ResturentsDocument66 pagesFinal Black Book GST in Resturentsirfan khan100% (2)
- Amazon Takes On Future Over Deal With Reliance: TCS Beats Street Estimates On Faster Demand RecoveryDocument17 pagesAmazon Takes On Future Over Deal With Reliance: TCS Beats Street Estimates On Faster Demand RecoveryAmit SemwalNo ratings yet
- GST Notes-CA Inter-May 23 1 Lyst8910 PDFDocument172 pagesGST Notes-CA Inter-May 23 1 Lyst8910 PDFMaheshkumar PerlaNo ratings yet
- Taxguru - in-GST Audit GSTR-9C Practical Checklist Alongwith Audit ProcessDocument3 pagesTaxguru - in-GST Audit GSTR-9C Practical Checklist Alongwith Audit ProcesschetudaveNo ratings yet
- Business Studies Topical QuestionsDocument64 pagesBusiness Studies Topical Questionsnyabinge silvesterNo ratings yet
- Tax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash MemoDocument1 pageTax Invoice/Bill of Supply/Cash MemoPrem ChanderNo ratings yet
- The Investment Setting: Key Factors That Impact Required ReturnsDocument45 pagesThe Investment Setting: Key Factors That Impact Required ReturnsTorun SoktyNo ratings yet
- Yard Fencing KSEB 2Document6 pagesYard Fencing KSEB 2isan.structural TjsvgalavanNo ratings yet
- Money (Rupiahs)Document5 pagesMoney (Rupiahs)Indarwati Siska PertiwiNo ratings yet
- Lease Contract for Residential PropertyDocument2 pagesLease Contract for Residential PropertyMichael Angelo PalmaNo ratings yet
- Recording Process Strengths and WeaknessesDocument2 pagesRecording Process Strengths and WeaknessesSUSILAWATI ISMAILNo ratings yet
- CMHA Presentation - January 19, 2022Document47 pagesCMHA Presentation - January 19, 2022WVXU NewsNo ratings yet
- Medalleo Low Rise - 01-Mar-2023 - 1Document2 pagesMedalleo Low Rise - 01-Mar-2023 - 1Karan PhoolwaniNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering ME8094-Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems Unit I - MCQ BankDocument10 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering ME8094-Computer Integrated Manufacturing Systems Unit I - MCQ BankSanjayVaghelaNo ratings yet