Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Math Important Identities and Concepts
Uploaded by
patelrohil2006Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Math Important Identities and Concepts
Uploaded by
patelrohil2006Copyright:
Available Formats
Trigonometry Identities
Addition and subtraction identities Sum identities
sin(a + b) = sin(a) cos(b) + cos(a) sin(b) sin(a) + sin(b) = 2 sin ( a+b a−b
2 ) cos ( 2 )
sin(a − b) = sin(a) cos(b) − cos(a) sin(b) sin(a) − sin(b) = 2 cos ( a+b a−b
2 ) sin ( 2 )
cos(a + b) = cos(a) cos(b) − sin(a) sin(b) cos(a) + cos(b) = 2 cos ( a+b a−b
2 ) cos ( 2 )
cos(a + b) = cos(a) cos(b) + cos(a) cos(b) cos(a) − cos(b) = − 2 sin ( a+b a−b
2 ) sin ( 2 )
tan(a) + tan(b)
tan(a + b) = 1−tan(a) tan(b)
tan(a) − tan(b)
tan(a + b) = 1 + tan(a) tan(b)
Double Angle Identities Double Angle Identities
sin(2a) = 2 sin(a) cos(a) sin(2a) = 2 sin(a) cos(a)
cos(2a) = cos2 (a) − sin2 (a) cos(2a) = cos2 (a) − sin2 (a)
= 2 cos2 (a) − 1 = 2 cos2 (a) − 1
= 1 − 2sin2 (a) = 1 − 2sin2 (a)
2 tan(a) 2 tan(a)
tan(2a) = 1 − tan2 (a) tan(2a) = 1 − tan2 (a)
Product identities Pythagorean Identities
cos(a) cos(b) = 12 (cos(a + b) + cos(a − b)) sin2 a + cos2 a = 1
sin(a) sin(b) = 12 (cos(a − b) − cos(a + b)) sin2 a = 1 − cos2 a
cos2 a = 1 − sin2 a
sin(a) cos(b) = 12 (sin(a + b) + sin(a − b))
cos(a) sin(b) = 12 (sin(a + b) − sin(a − b))
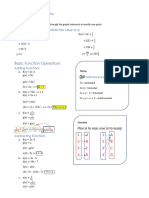
Differentiation rules
“Nice to know” Category Product Rule
I f h(x) = g(x) f (x),
T he derivative of f (x) * k is always f ′(x) * k h′(x) = g ′(x) f (x) + g(x) f ′(x)
Quotient Rules Chain Rule
I f h(x) = g(x)
f (x)
,
g ′(x) f (x) − g(x) f ′(x) Replace differentiable part of function
h′(x) = f (x)2 with “m”, calculate the derivative and
then multiply the value of m’.
1
I f h(x) = f (x)
,
f ′(x) Example:
h′(x) =− f (x)2
h(x) = (3x2 + 1)5
a
I f h(x) = f (x)
, (where a is a constant)
a * f ′(x) let 3x2 + 1 = m
h′(x) =− f (x)2
h′(x) = m5
= 5m4 * m′
= 5(3x2 + 1)4 * (3x2 + 1)′
= 30x(3x2 + 1)4
You might also like
- SdraftDocument7 pagesSdraftnbgNo ratings yet
- MATHS Rappels Formulaire: Institut National Polytechnique de ToulouseDocument6 pagesMATHS Rappels Formulaire: Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouselina meriemNo ratings yet
- AMA1110 Tutorial - 2sDocument3 pagesAMA1110 Tutorial - 2sBrian LiNo ratings yet
- For MulesDocument2 pagesFor MulesOuma ImaNo ratings yet
- ENG1001 Tutorial 7 (Differentiation)Document2 pagesENG1001 Tutorial 7 (Differentiation)raleyNo ratings yet
- Gen MathDocument3 pagesGen MathDaniel SolicitoNo ratings yet
- MTH 125 - Mathematics II (Final - Exam Preperation)Document20 pagesMTH 125 - Mathematics II (Final - Exam Preperation)FajerNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument7 pagesUntitledChetan GargNo ratings yet
- Exercises 1 - DifferentiationDocument9 pagesExercises 1 - DifferentiationLexNo ratings yet
- Calculus Demystified Muya PDFDocument354 pagesCalculus Demystified Muya PDFMazé Santos Lima100% (3)
- Step Formula Booklet PDFDocument24 pagesStep Formula Booklet PDFA FryNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivatives 22Document10 pagesApplication of Derivatives 22Pawan KumarNo ratings yet
- AP EAMCET 2019 Previous Year Question Papers With Solutions - 21st April 2019 Morning Shift-1-83Document83 pagesAP EAMCET 2019 Previous Year Question Papers With Solutions - 21st April 2019 Morning Shift-1-83Chandana InguvaNo ratings yet
- AP EAMCET 2019 Previous Year Question Papers With Solutions - 21st April 2019 Morning ShiftDocument239 pagesAP EAMCET 2019 Previous Year Question Papers With Solutions - 21st April 2019 Morning Shiftyashwanthkumarmannava18No ratings yet
- Queatufyfgo 1: SolutionDocument7 pagesQueatufyfgo 1: SolutionAlhajiNo ratings yet
- Question7 - Differential CalculusDocument4 pagesQuestion7 - Differential CalculusSnehasish DasNo ratings yet
- Math 126: Calculus IiDocument1 pageMath 126: Calculus IinarasimhacharibabuNo ratings yet
- Formula CompilationDocument6 pagesFormula CompilationKirstie Alley San JoseNo ratings yet
- Partial Fractions PDFDocument36 pagesPartial Fractions PDFlakkaraju prasanna100% (1)
- FactrizacinDocument1 pageFactrizacinReik Luiz DiazNo ratings yet
- Gabarito - Prova 1 Área 2 UFPE 2019.1Document1 pageGabarito - Prova 1 Área 2 UFPE 2019.1André SilvaNo ratings yet
- paperII SolnDocument11 pagespaperII Solnapi-19834738No ratings yet
- Itf 1Document3 pagesItf 1shriteshNo ratings yet
- Functions SPMDocument4 pagesFunctions SPMAyu NajatNo ratings yet
- Maths QP Set-1Document6 pagesMaths QP Set-1Zam NaizamNo ratings yet
- Maths QP Set-1Document6 pagesMaths QP Set-1Furan FluxNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 2 Evaluating FunctionsDocument2 pagesActivity No. 2 Evaluating FunctionsRossel Jane CampilloNo ratings yet
- 24 Trig Identity ProblemsDocument4 pages24 Trig Identity ProblemsAldrean TinayaNo ratings yet
- Inverse TrigonometryDocument7 pagesInverse TrigonometryAbhiNo ratings yet
- Commonly Used FunctionsDocument2 pagesCommonly Used FunctionsIvan Kristiawan ZegaNo ratings yet
- Lista 1Document2 pagesLista 1SkaylayerNo ratings yet
- MATH 131 Tutorial 2 2024Document2 pagesMATH 131 Tutorial 2 2024jamakonke8No ratings yet
- Combined TutorialDocument8 pagesCombined TutorialVongNo ratings yet
- L-09 Pride Practice Session: For Unacademy Subscription Use Code - Join For UpdatesDocument4 pagesL-09 Pride Practice Session: For Unacademy Subscription Use Code - Join For UpdatesMOHD SARFARAZNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Prove IdentitiesDocument1 pageTrigonometry Prove Identitiesadhi adhNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument3 pagesTrigonometric IdentitiesAndrea BucciNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-04-16 at 2.26.24 PMDocument2 pagesScreenshot 2023-04-16 at 2.26.24 PMt6cqcr2qx7No ratings yet
- Exercise 2 B New ModuleDocument2 pagesExercise 2 B New ModuleEddieLohNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics Test 1: Directions For Questions 1 To 25: Select The Correct AlternaDocument6 pagesEngineering Mathematics Test 1: Directions For Questions 1 To 25: Select The Correct AlternaAKASH PALNo ratings yet
- Maths Formulas For Class 11 - All Important 11th Class Math FormulaeDocument9 pagesMaths Formulas For Class 11 - All Important 11th Class Math FormulaerajnishNo ratings yet
- Worksheet A: Artial RactionsDocument13 pagesWorksheet A: Artial RactionsBryan YeohNo ratings yet
- 2 Trigonometric Identities 2Document4 pages2 Trigonometric Identities 2alothman mahmoudNo ratings yet
- QUADRATICS SolutionsDocument9 pagesQUADRATICS SolutionsAna Clara Maria Ramirez FleumerNo ratings yet
- ENG1001 Tutorial 6 (Differentiation)Document6 pagesENG1001 Tutorial 6 (Differentiation)raleyNo ratings yet
- Développements Limités en 0 Des Fonctions Usuelles: A Savoir Par CoeurDocument4 pagesDéveloppements Limités en 0 Des Fonctions Usuelles: A Savoir Par CoeurchanezNo ratings yet
- TEST 2 Functions, Transformations, Logarithms, Financial - SOLUTIONSDocument7 pagesTEST 2 Functions, Transformations, Logarithms, Financial - SOLUTIONSShaniel PinoboocNo ratings yet
- MATH 175 Calculus I - 2020-2021 Fall Worksheet 7: Differentiation RulesDocument3 pagesMATH 175 Calculus I - 2020-2021 Fall Worksheet 7: Differentiation RulesmalafikokamilNo ratings yet
- XII ClassDocument3 pagesXII ClasspremsempireNo ratings yet
- Soalan Klon SM015 Set BDocument12 pagesSoalan Klon SM015 Set BNUR FAHIRA ELIANA BINTI MOHD ZULKIFLI KM-PelajarNo ratings yet
- Functions Adv SheetDocument27 pagesFunctions Adv Sheetvasukushal2006No ratings yet
- National Level Science Talent Search Examination-Un472: Math e M AticsDocument9 pagesNational Level Science Talent Search Examination-Un472: Math e M AticsMOMI MALA BORANo ratings yet
- Basic Trigonometric FormulaDocument1 pageBasic Trigonometric Formulakotekatbasil0000No ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics FormulasDocument5 pagesEngineering Mathematics Formulasvenkata sridhar DhulipalaNo ratings yet
- Ecuaciones Sustituir B en Ecuación 2 Sustituir Cy B en La Ecuación 3Document2 pagesEcuaciones Sustituir B en Ecuación 2 Sustituir Cy B en La Ecuación 3ClaudiaEspinosaNo ratings yet
- hw7 DiffDocument8 pageshw7 DiffYONGCHENG LIUNo ratings yet
- 2022 Advanced PaperDocument16 pages2022 Advanced PaperEVIN S MANOJNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 SolutionsDocument8 pagesQuiz 3 SolutionsevilgamerspgNo ratings yet
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesFrom EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesRating: 1.5 out of 5 stars1.5/5 (2)
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Ten Reasons To Oppose The Death PenaltyDocument5 pagesTen Reasons To Oppose The Death PenaltyAlvin ArellanoNo ratings yet
- Assignment OSDocument11 pagesAssignment OSJunaidArshadNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan TemplateJeffrey GagoNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Online Games To The AcademicDocument20 pagesThe Impact of Online Games To The AcademicJessica BacaniNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Week 3-4Document2 pagesMath 10 Week 3-4Rustom Torio QuilloyNo ratings yet
- ZEROPAY WhitepaperDocument15 pagesZEROPAY WhitepaperIlham NurrohimNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa Inggris: ButterflyDocument4 pagesTugas Bahasa Inggris: ButterflyRiyadi TeguhNo ratings yet
- Norm ANSI PDFDocument1 pageNorm ANSI PDFAbdul Quddus Mat IsaNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper Pre Board Xii Biology 2023-24-1Document6 pagesPractice Paper Pre Board Xii Biology 2023-24-1salamnaseema14No ratings yet
- Angles, Bearings and AzimuthDocument10 pagesAngles, Bearings and AzimuthMarc Dared CagaoanNo ratings yet
- Subtotal Gastrectomy For Gastric CancerDocument15 pagesSubtotal Gastrectomy For Gastric CancerRUBEN DARIO AGRESOTTNo ratings yet
- Electron LayoutDocument14 pagesElectron LayoutSaswat MohantyNo ratings yet
- Permeability PropertiesDocument12 pagesPermeability Propertieskiwi27_87No ratings yet
- Operation Manual-KINGSTONE SDP-ENG-20120205 PDFDocument49 pagesOperation Manual-KINGSTONE SDP-ENG-20120205 PDFJiménezNo ratings yet
- Heart Attack Detection ReportDocument67 pagesHeart Attack Detection ReportAkhil TejaNo ratings yet
- The Life Cycle of Brent FieldDocument21 pagesThe Life Cycle of Brent FieldMalayan AjumovicNo ratings yet
- ShotcreteDocument7 pagesShotcreteafuhcivNo ratings yet
- Lords of ChaosDocument249 pagesLords of ChaosBill Anderson67% (3)
- ESG Conundrum PDFDocument30 pagesESG Conundrum PDFVijay Kumar SwamiNo ratings yet
- Case Study On "Unilever in Brazil-Marketing Strategies For Low Income Consumers "Document15 pagesCase Study On "Unilever in Brazil-Marketing Strategies For Low Income Consumers "Deepak BajpaiNo ratings yet
- 60 Plan of DepopulationDocument32 pages60 Plan of DepopulationMorena Eresh100% (1)
- Addpac AP1000 DSDocument2 pagesAddpac AP1000 DSEnrique RamosNo ratings yet
- Sullivan's Interpersonal TheoryDocument27 pagesSullivan's Interpersonal TheoryJezalen GonestoNo ratings yet
- Substitution Reactions - PMDocument64 pagesSubstitution Reactions - PMprasoon jhaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Course Syllabus (2023) - SignedDocument3 pagesStatistics and Probability Course Syllabus (2023) - SignedDarence Fujihoshi De AngelNo ratings yet
- Centric WhitepaperDocument25 pagesCentric WhitepaperFadhil ArsadNo ratings yet
- Exchange 2010 UnderstandDocument493 pagesExchange 2010 UnderstandSeKoFieNo ratings yet
- Enter Absence APIDocument45 pagesEnter Absence APIEngOsamaHelalNo ratings yet
- MATLAB For Data VisualizationDocument63 pagesMATLAB For Data Visualizationfahmi fawjiNo ratings yet
- OSX ExpoDocument13 pagesOSX ExpoxolilevNo ratings yet