Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Serumuricacid
Uploaded by
editing visualsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Serumuricacid
Uploaded by
editing visualsCopyright:
Available Formats
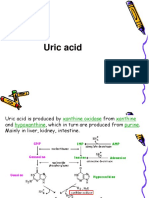
PRACTICAL 5: ESTIMATION OF SERUM URIC ACID
INTRODUCTION
The estimation of serum uric acid is typically done through a blood test called a
serum uric acid test. This test measures the amount of uric acid in the blood and is
often used to diagnose conditions such as gout or kidney stones. It's important to
consult with a healthcare professional for accurate interpretation of the results and
proper medical advice.
The estimation of serum uric acid is important for several reasons:
• Diagnosis of Gout: Elevated levels of serum uric acid are associated with
gout, a type of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the
joints. Measuring serum uric acid levels can aid in the diagnosis of gout.
• Monitoring Uric Acid Levels: Monitoring serum uric acid levels helps in
managing conditions such as gout and hyperuricemia (high levels of uric
acid in the blood). It allows healthcare providers to track changes in uric
acid levels over time and adjust treatment accordingly.
• Prevention of Complications: High levels of uric acid in the blood can lead
to complications such as kidney stones, kidney disease, and cardiovascular
disease. Regular monitoring of serum uric acid levels can help identify
individuals at risk and take preventive measures.
• Assessment of Treatment Efficacy: For individuals undergoing treatment for
conditions related to uric acid, such as gout, measuring serum uric acid
levels helps assess the effectiveness of treatment. It allows healthcare
providers to determine if treatment needs to be adjusted or continued.
• Identification of Underlying Health Issues: Abnormal serum uric acid levels
may indicate underlying health issues such as kidney dysfunction or
metabolic disorders. Monitoring these levels can aid in the early detection
and management of such conditions. Overal, the estimation of serum uric
acid is crucial for diagnosing, monitoring, and managing various health
conditions associated with abnormal uric acid levels, ultimately helping to
improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
METHODS TO ESTIMATE SERUM URIC ACID LEVELS
There are several methods to estimate serum uric acid levels:
• Colorimetric Method: This method involves the use of a reagent that reacts
with uric acid to produce a colored compound. The intensity of the color is
proportional to the concentration of uric acid, which can be measured
spectrophotometrically.
• Enzymatic Method: Enzymes such as uricase can be used to catalyze the
oxidation of uric acid, producing a compound that can be measured
spectrophotometrically. This method is highly specific for uric acid and is
commonly used in clinical laboratories.
• High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC): HPLC is a
chromatographic technique that separates components of a mixture based on
their interactions with a stationary phase. It can be used to quantify uric acid
levels in serum samples with high sensitivity and specificity.
• Electrochemical Method: This method involves the use of electrodes to
measure the oxidation or reduction of uric acid in a sample. It is often used
in point-of-care testing devices for rapid and accurate estimation of serum
uric acid levels.
• Automated Analyzers: Modern clinical laboratories often use automated
analyzers that employ various methods, such as enzymatic assays or ion-
selective electrodes, to measure serum uric acid levels. These analyzers
provide high throughput and accuracy, making them suitable for routine
clinical testing.
REFERENCE RANGES OF SERUM URIC ACID LEVELS
The reference range for serum uric acid levels can vary slightly depending on the
laboratory and the method of analysis used. However, generally accepted reference
ranges are as follows:
Men: 3.4 to 7.0 mg/dL (200 to 420 µmol/L)
Women: 2.4 to 6.0 mg/dL (140 to 360 µmol/L)
CLINICAL IMPORTANCE OF SERUM URIC ACID
Serum uric acid levels have clinical importance for several reasons:
• Diagnosis and Management of Gout: Elevated serum uric acid levels are a
hallmark of gout, a painful form of arthritis caused by the deposition of urate
crystals in the joints. Monitoring serum uric acid levels helps diagnose gout
and guide treatment decisions, such as lifestyle changes, medications to
lower uric acid levels, and management of acute flares.
• Risk Assessment for Gout and Related Conditions: High serum uric acid
levels are associated with an increased risk of developing gout, as well as
other health conditions such as kidney stones, kidney disease, and
cardiovascular disease. Measuring serum uric acid levels helps identify
individuals at higher risk for these conditions and implement preventive
strategies.
• Monitoring Kidney Function: Uric acid is excreted by the kidneys, so serum
uric acid levels can reflect kidney function. Elevated uric acid levels may
indicate impaired kidney function or an increased risk of developing kidney
disease. Monitoring serum uric acid levels can aid in the assessment and
management of kidney function.
• Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Risk: High serum uric acid levels
have been associated with metabolic syndrome, a cluster of conditions
including obesity, high blood pressure, and insulin resistance, which
increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Monitoring uric acid levels may
help identify individuals at higher risk for cardiovascular events and guide
preventive interventions. Response to Treatment: For individuals undergoing
treatment for conditions related to uric acid, such as gout or hyperuricemia,
monitoring serum uric acid levels helps assess the effectiveness of treatment.
Adjustments to medications or lifestyle interventions can be made based on
changes in uric acid levels over time.
You might also like
- What To Know About Uric Acid TestsDocument64 pagesWhat To Know About Uric Acid Testsmusembijosef2011No ratings yet
- Biochemistry Techniques and Their Use in Diagnosis RMAUDocument35 pagesBiochemistry Techniques and Their Use in Diagnosis RMAUKellyNo ratings yet
- The Essential Guide to Routine Blood Tests for General Health: Health, #2From EverandThe Essential Guide to Routine Blood Tests for General Health: Health, #2No ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry AssignmentDocument5 pagesClinical Chemistry AssignmentAsiaNo ratings yet
- CP Acute Renal Failure Chap7Document128 pagesCP Acute Renal Failure Chap7Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudNo ratings yet
- RapidTest Instructions 2019 PrintDocument2 pagesRapidTest Instructions 2019 Printmrvictor008No ratings yet
- Lectur 09 Measurement of MetabolitesDocument38 pagesLectur 09 Measurement of MetabolitesNavoda ThathsaraniNo ratings yet
- Rheumatoid ArthritisDocument21 pagesRheumatoid ArthritisDianne BernardoNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Tests and Their SignificanceDocument66 pagesBiochemical Tests and Their Significancet sNo ratings yet
- Uric AcidDocument30 pagesUric AcidKesavanVeeraNo ratings yet
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument18 pagesChronic Renal FailureJoan Carla BocoNo ratings yet
- Joanalain C. Cortez, RN Clinical InstructorDocument179 pagesJoanalain C. Cortez, RN Clinical InstructorMark CadaNo ratings yet
- 6 Hypertension Nursing Care - Arif Setyo UpoyoDocument40 pages6 Hypertension Nursing Care - Arif Setyo UpoyoRizka Nur AgustinNo ratings yet
- Proteinuria and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument34 pagesProteinuria and Chronic Kidney DiseaseВалерий ГаврилуцаNo ratings yet
- Urine AlbuminDocument14 pagesUrine Albuminbalen.shiwani04No ratings yet
- FrancesFranciscoCC2 1Document6 pagesFrancesFranciscoCC2 1Frances FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Abordaje de PX Con Enf RenalDocument12 pagesAbordaje de PX Con Enf Renalcleooatra mairenaNo ratings yet
- Serum Uric Acid In: HypertensiveDocument6 pagesSerum Uric Acid In: HypertensivesyifaNo ratings yet
- Hiperuricemia AsintomaticaDocument1 pageHiperuricemia AsintomaticaElizabethNo ratings yet
- Indications and Interpretation of Renal Function Tests Medicine.1Document26 pagesIndications and Interpretation of Renal Function Tests Medicine.1sangeet75No ratings yet
- Diabetic NephropathyDocument38 pagesDiabetic NephropathyMade Widiastika100% (1)
- Chronic Liver Disease, - 082829Document21 pagesChronic Liver Disease, - 082829Syed Yusuf SyedNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome + ArfDocument64 pagesNephrotic Syndrome + ArfkrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On: Acute Kidney InjuryDocument52 pagesGuidelines On: Acute Kidney InjuryWilsonne ChuaNo ratings yet
- Non-Protein Nitrogen CompoundsDocument6 pagesNon-Protein Nitrogen CompoundspixiedustNo ratings yet
- Uric AcidDocument13 pagesUric Acidphoto copyhemnNo ratings yet
- NPNDocument42 pagesNPNreynanrolleNo ratings yet
- Acute PancreatitisDocument7 pagesAcute PancreatitisVytheeshwaran Vedagiri100% (9)
- URINE PHDocument2 pagesURINE PHediting visualsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Hospital Pharmacy Notes Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Document5 pagesChapter 9 Hospital Pharmacy Notes Complete Notes by Noteskarts Acc To ER20Mobeen AhmedNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic and LabDocument2 pagesDiagnostic and LabShiehan Mae ForroNo ratings yet
- Algoritma CKD PDFDocument2 pagesAlgoritma CKD PDFDesla Citra100% (1)
- Intro To Medtech Clinical Chemistry ReviewerDocument11 pagesIntro To Medtech Clinical Chemistry Reviewerjesanndei100% (1)
- Normal Levels of Uric Acid and GOUTDocument55 pagesNormal Levels of Uric Acid and GOUTmail2winagNo ratings yet
- NICE 2011 SlidesetDocument25 pagesNICE 2011 SlidesetMocanu Cristina-VioricaNo ratings yet
- Case Study For Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument4 pagesCase Study For Acute GlomerulonephritisGabbii Cinco100% (1)
- RMU Session 7 - Diagnostic Support and EBMDocument40 pagesRMU Session 7 - Diagnostic Support and EBMgatete samNo ratings yet
- CKD PDFDocument20 pagesCKD PDFReyhan TarisNo ratings yet
- Renal Function TestsDocument36 pagesRenal Function TestsLawal Bello DanchadiNo ratings yet
- Kidney DiseaseDocument3 pagesKidney DiseaseHariNo ratings yet
- Association of Serum Uric AcidDocument40 pagesAssociation of Serum Uric AcidWoro Hapsari WahyuningrumNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Chemical Pathology or Clinical Chemistry Laboratory - 032305Document24 pagesIntroduction - Chemical Pathology or Clinical Chemistry Laboratory - 032305Fru Dillon AnyeNo ratings yet
- DM Algorithm Urine Alb 508cDocument1 pageDM Algorithm Urine Alb 508cArjunaPamungkasNo ratings yet
- High Uric CidDocument3 pagesHigh Uric Cidsarup007No ratings yet
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument14 pagesChronic Kidney DiseaseJoel CanenciaNo ratings yet
- Pengkajian Status Gizi Atlit Secara BiokimiaDocument31 pagesPengkajian Status Gizi Atlit Secara Biokimiatrioni widyastutiNo ratings yet
- VIVASDocument8 pagesVIVASapi-3856245No ratings yet
- Pharmacy Skills Lecture 7Document25 pagesPharmacy Skills Lecture 7Rabab Hamed SayedNo ratings yet
- Pandya 2016Document5 pagesPandya 2016cynthiaNo ratings yet
- Dietary On HDDocument23 pagesDietary On HDKevin OwenNo ratings yet
- Renal EmergenciesDocument63 pagesRenal EmergenciesSandeepa WeerawarnaNo ratings yet
- EduardoDocument12 pagesEduardomufti dewantaraNo ratings yet
- Genitourinary Emergencies BSN 4 2. 2Document39 pagesGenitourinary Emergencies BSN 4 2. 2Justine Domingo PascualNo ratings yet
- As N 2015010022 Supplementary DataDocument20 pagesAs N 2015010022 Supplementary DataAndrie GunawanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory and Diagnostic TestsDocument48 pagesLaboratory and Diagnostic TestsPHARMACY 2021No ratings yet
- PHM423: Clinical Pharmacy (Lecture) Week 3: Laboratory and Diagnostic ProceduresDocument56 pagesPHM423: Clinical Pharmacy (Lecture) Week 3: Laboratory and Diagnostic ProceduresHadassah ReyesNo ratings yet
- Standarts of Medical CareDocument34 pagesStandarts of Medical CareLussiana Mercy MaramisNo ratings yet
- Pbl-Gin Urine Test (Feme)Document11 pagesPbl-Gin Urine Test (Feme)KarthigaRamanNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Nephropathy Diabetic NephropathyDocument12 pagesDiabetic Nephropathy Diabetic NephropathyKokoland KukusNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts for Patients and Supporters: Cholangiocarcinoma: A cancer of the bile duct and liver Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeFrom EverandFast Facts for Patients and Supporters: Cholangiocarcinoma: A cancer of the bile duct and liver Information + Taking Control = Best OutcomeNo ratings yet
- Test Plan TemplateDocument3 pagesTest Plan TemplateMurtazaNo ratings yet
- Accuracy of Transferring Analog Dental Casts To A Virtual ArticulatorDocument9 pagesAccuracy of Transferring Analog Dental Casts To A Virtual ArticulatorNetra TaleleNo ratings yet
- Heroic Tales Core Rules 1.1.0Document33 pagesHeroic Tales Core Rules 1.1.0Melobajoya MelobajoyaNo ratings yet
- EL2 - Raise Organic Small RuminantsDocument62 pagesEL2 - Raise Organic Small RuminantsButch Demayo100% (1)
- EASA Part-66 Module 17 QBDocument53 pagesEASA Part-66 Module 17 QBFaisal Ahmed Newon80% (5)
- Ostrich RacingDocument4 pagesOstrich RacingalexmadoareNo ratings yet
- RKS IFC 2015 Solar CellDocument23 pagesRKS IFC 2015 Solar CellAnugrah PangeranNo ratings yet
- PriceDoxy 09 September 2011Document56 pagesPriceDoxy 09 September 2011Elena OltuNo ratings yet
- Note 15-Feb-2023Document4 pagesNote 15-Feb-2023Oliver ScissorsNo ratings yet
- PQS Catalogue 4 2Document143 pagesPQS Catalogue 4 2sagarNo ratings yet
- Compuware DCRUM Intro 2012 Version 12.00Document142 pagesCompuware DCRUM Intro 2012 Version 12.00JanNo ratings yet
- Minuto hd8761Document64 pagesMinuto hd8761Eugen Vicentiu StricatuNo ratings yet
- 61-Article Text-180-1-10-20170303 PDFDocument25 pages61-Article Text-180-1-10-20170303 PDFSOUMYA GOPAVARAPUNo ratings yet
- ENG11H Realism 6-Outcasts of Poker FlatDocument3 pagesENG11H Realism 6-Outcasts of Poker FlatJosh Cauhorn100% (1)
- Lessons From The Humanitarian Disaster Logistics Management A Case Study of The Earthquake in HaitiDocument19 pagesLessons From The Humanitarian Disaster Logistics Management A Case Study of The Earthquake in HaitiM Irfan Kemal100% (1)
- EtchDocument2 pagesEtchlex bactolNo ratings yet
- Five Star Env Audit Specification Amp Pre Audit ChecklistDocument20 pagesFive Star Env Audit Specification Amp Pre Audit ChecklistMazhar ShaikhNo ratings yet
- MODULE-6 Human Person As Embodied SpiritDocument18 pagesMODULE-6 Human Person As Embodied SpiritRoyceNo ratings yet
- Holiday Assignment (Dussehra Vacation) - 2022-23Document3 pagesHoliday Assignment (Dussehra Vacation) - 2022-23yogeshNo ratings yet
- Youth and Moral ValuesDocument6 pagesYouth and Moral ValuesAlka SinghNo ratings yet
- A3 Report Template Checklist - SafetyCultureDocument4 pagesA3 Report Template Checklist - SafetyCulturewarriorninNo ratings yet
- Practical Econometrics Data Collection Analysis and Application 1st Edition Hilmer Test BankDocument27 pagesPractical Econometrics Data Collection Analysis and Application 1st Edition Hilmer Test Bankdavidhallwopkseimgc100% (28)
- A. Erfurth, P. Hoff. Mad Scenes in Early 19th-Century Opera PDFDocument4 pagesA. Erfurth, P. Hoff. Mad Scenes in Early 19th-Century Opera PDFbiarrodNo ratings yet
- Designing The Workplace For CollaborationDocument17 pagesDesigning The Workplace For Collaborationmas zak danielNo ratings yet
- Cosmology Questions and Answers - SanfoundryDocument9 pagesCosmology Questions and Answers - SanfoundryGopinathan MNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations For O&G IndustryDocument38 pagesAbbreviations For O&G IndustryMike George MeyerNo ratings yet
- Dispersion Relation of Electromagnetic WavesDocument2 pagesDispersion Relation of Electromagnetic WavesFidel SouzaNo ratings yet
- 311762en WDocument36 pages311762en WOprisor CostinNo ratings yet
- Edwards SVV HandoutDocument2 pagesEdwards SVV HandoutossinNo ratings yet
- The Necessary Art of PersuasionDocument14 pagesThe Necessary Art of PersuasionAnugragha SundarNo ratings yet