Professional Documents
Culture Documents
G9 Adverbs
G9 Adverbs
Uploaded by
beejay9999delCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
G9 Adverbs
G9 Adverbs
Uploaded by
beejay9999delCopyright:
Available Formats
Certainly!
Let's delve deeper into each type of adverb and provide more examples:
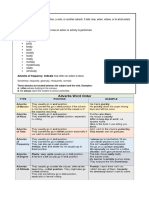
1. Adverb of Time:
- Adverbs of time answer the question "When?" They give information about the timing or frequency of an action.
- **Examples:**
- She will arrive tomorrow.
- We meet **weekly**.
- He finished the work **early**.
2. Adverb of Place:
- Adverbs of place answer the question "Where?" or "To where?" They describe the location or direction of the action.
- Examples:
- The kids played **outside**.
- They searched for the treasure **everywhere**.
- The train is arriving **here**.
3. Adverb of Manner:
- Adverbs of manner answer the question "How?" They describe the way in which an action is performed.
- Examples:
- She sings **beautifully**.
- He solved the problem **quickly**.
- The athlete ran **effortlessly**.
It's important to note that adverbs can sometimes be formed by adding the suffix "-ly" to adjectives. However, not all
adverbs follow this pattern. For instance:
Adjective: quick → Adverb: quickly
Adjective: careful → Adverb: carefully
In some cases, the same word can function as both an adjective and an adverb without any change:
- The food smells **good**. (adjective)
- She cooks **well**. (adverb)
Understanding adverbs and their various types can enhance the clarity and richness of language, providing more details
about the actions being described.
An adverb is a word that modifies or describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb. Adverbs typically provide
information about the manner, degree, frequency, time, or place of an action or the quality of an adjective.
They add more detail to a sentence and help convey how, when, where, or to what extent something occurs.
You might also like
- More Detailed About AdverbDocument2 pagesMore Detailed About AdverbenglishaungkokoNo ratings yet
- Verb & AdverbDocument5 pagesVerb & Adverbjaveriakhaliq89No ratings yet
- PEECDocument22 pagesPEECZenia Dwi KhairunisaNo ratings yet
- More Detailed About VerbsDocument1 pageMore Detailed About VerbsenglishaungkokoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Order of Adverbs?Document4 pagesWhat Is The Order of Adverbs?Tuấn Vũ VănNo ratings yet
- English Grammar GuideDocument3 pagesEnglish Grammar Guidedollybolpur23No ratings yet
- Adverb and Its TypesDocument10 pagesAdverb and Its TypesAlex LodelNo ratings yet
- Adverb: Adjective Verb Clause AdverbDocument5 pagesAdverb: Adjective Verb Clause AdverbHoang Thi Hai YenNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument22 pagesAdverbsDaisy Joyce TorresNo ratings yet
- Tugas Artikel AdverbsDocument11 pagesTugas Artikel AdverbsZul ZulpikalNo ratings yet
- English PPT ALSDocument28 pagesEnglish PPT ALSKatrina NalanganNo ratings yet
- Group 2: Adi Wiluyo (502211010003) MUHAMMAD YUSRIL (502211010011) Maulia Fadhila (502211010016)Document15 pagesGroup 2: Adi Wiluyo (502211010003) MUHAMMAD YUSRIL (502211010011) Maulia Fadhila (502211010016)Akiyo DwiNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of TimeDocument3 pagesAdverbs of Timemary aguirreNo ratings yet
- Adverbs Objectives: Identify Adverbs As Parts of Speech. Identify Forms of Adverbs. Identify Kinds of Adverbs. Fill in With The Correct AdverbDocument21 pagesAdverbs Objectives: Identify Adverbs As Parts of Speech. Identify Forms of Adverbs. Identify Kinds of Adverbs. Fill in With The Correct AdverbDania WazzeNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument22 pagesAdverbsAilljim Remolleno ComilleNo ratings yet
- Adverb: Adjective Verb Clause AdverbDocument3 pagesAdverb: Adjective Verb Clause AdverbLaura Andrea GomezNo ratings yet
- Grammar PPDocument4 pagesGrammar PPsammer30No ratings yet
- What Are ADVERBS and Its Uses - 20240221 - 115909 - 0000Document4 pagesWhat Are ADVERBS and Its Uses - 20240221 - 115909 - 0000laurenceheruela02No ratings yet
- The AdverbsDocument7 pagesThe Adverbssergeyka2004No ratings yet
- Adverb of Manner: These Adverbs Are Located Between The Subject and The Verb. ExamplesDocument4 pagesAdverb of Manner: These Adverbs Are Located Between The Subject and The Verb. ExamplesJan Arabella LabayNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 FUNCTIONAL ENGLISHDocument4 pagesUnit 1 FUNCTIONAL ENGLISHranjansmruti341No ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument4 pagesAdverbs20santiago11No ratings yet
- ADVERBS 2013.1 - Reading MaterialDocument7 pagesADVERBS 2013.1 - Reading MaterialMarina MouraNo ratings yet
- Adverb Spelling Notes: Give Me That Tape, PleaseDocument12 pagesAdverb Spelling Notes: Give Me That Tape, PleaseBeaux BambieNo ratings yet
- Forms and Classifications of AdverbsDocument25 pagesForms and Classifications of AdverbsBrenda PerezNo ratings yet
- ADVERBSDocument11 pagesADVERBSmillini772No ratings yet
- Adverbs-Kinds: Adverb AdjectiveDocument4 pagesAdverbs-Kinds: Adverb AdjectiveAngelus ElizabethNo ratings yet
- 4B07 VoNguyenThuyVy Adverbials in Vietnamese and EnglishDocument20 pages4B07 VoNguyenThuyVy Adverbials in Vietnamese and EnglishDerek Deleon100% (1)
- Module. AdverbsDocument6 pagesModule. AdverbsAditiya Nurul fatlyNo ratings yet
- Kayarian NG Filipino (Pang-Abay)Document7 pagesKayarian NG Filipino (Pang-Abay)Queency LozanoNo ratings yet
- College English Grammar 01 ReportDocument12 pagesCollege English Grammar 01 ReportWinston QuilatonNo ratings yet
- Adverbs of DegrDocument4 pagesAdverbs of DegrJoemarie Alfaras SongcuyaNo ratings yet
- English For Academic Purposes (EAPP)Document34 pagesEnglish For Academic Purposes (EAPP)Cherry Bee PapasNo ratings yet
- ADVERBSDocument17 pagesADVERBSjamelateoNo ratings yet
- Adverbs 1712936477Document14 pagesAdverbs 1712936477hmotwani430No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledRaahilNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument22 pagesAdverbsKeebeek S ArbasNo ratings yet
- AdverbulDocument7 pagesAdverbulToma Toma TomaNo ratings yet
- Adjetivos Compuestos en Inglã©s-Mesclado PDFDocument78 pagesAdjetivos Compuestos en Inglã©s-Mesclado PDFJason MaloneNo ratings yet
- The University of Chicago PressDocument18 pagesThe University of Chicago PressAraceli Enríquez OvandoNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument22 pagesAdverbslizete.capelas8130No ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument22 pagesAdverbsRiju DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Adverbul: Firstly, I Would Like To Welcome You Here. (ÎnDocument5 pagesAdverbul: Firstly, I Would Like To Welcome You Here. (ÎnOlteanu NicoletaNo ratings yet
- Adverb: Rules of Using AdverbsDocument3 pagesAdverb: Rules of Using AdverbsArsalan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Rules of Concord 2Document44 pagesRules of Concord 2oyetunji GideonNo ratings yet
- Enl 124 - 2024-03-31Document8 pagesEnl 124 - 2024-03-31Racheal IsikpojeNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument26 pagesTugas Bahasa InggrisMelly ShahabNo ratings yet
- Adverbs ReportDocument19 pagesAdverbs ReportAbegail Hingpis DanteNo ratings yet
- Adverbul in Engleza L4Document5 pagesAdverbul in Engleza L4trifu_mariusNo ratings yet
- E G E E G E: Nglish - Eneral Ducation Nglish - Eneral DucationDocument44 pagesE G E E G E: Nglish - Eneral Ducation Nglish - Eneral DucationKirito NajdNo ratings yet
- Lesson ThreeDocument7 pagesLesson ThreeIsabel RecaldeNo ratings yet
- Brown and Beige Simple English Reading and Writing Types of Discourse PresentationDocument47 pagesBrown and Beige Simple English Reading and Writing Types of Discourse PresentationNur AthirahNo ratings yet
- 1.categories of The VerbDocument7 pages1.categories of The Verbabril iñon rukavinaNo ratings yet
- AdverbsDocument30 pagesAdverbsVane SolisNo ratings yet
- 8 - AdverbsDocument21 pages8 - AdverbsKristine IvyNo ratings yet
- Adverbs: in Liinguistic PerspectiveDocument10 pagesAdverbs: in Liinguistic PerspectiveSalfinaz BarakbahNo ratings yet
- 12.07.2018 Thursday: Procedure FunctionDocument53 pages12.07.2018 Thursday: Procedure FunctionRaheel AliNo ratings yet
- Webster's Word Power Essential English Words: Learners' DictionaryFrom EverandWebster's Word Power Essential English Words: Learners' DictionaryNo ratings yet