Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Adverbs
Uploaded by
sergeyka20040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views7 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views7 pagesThe Adverbs
Uploaded by
sergeyka2004Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
THE ADVERBS
Abdykhalikova Aksunkar, Adilkhanova Madina, Baibala Meruert, Kartkozhak Nuray, Li
Sergey, Oken Kamila, Seitkereyeva Zhibek
Definition
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They
provide information about the manner, degree, frequency, or time of an
action or describe the intensity of an adjective. Examples include
"quickly," "very," and "often."
Adverbs play a crucial role in language by adding precision and detail to
expressions. They answer questions such as "how," "when," "where," or "to
what extent." Adverbs can range from those indicating time (e.g., "soon,"
"now") to manner (e.g., "carefully," "quickly"), frequency (e.g., "always,"
"sometimes"), or degree (e.g., "very," "too"). Their versatility allows them to
contribute nuance and specificity to sentences, making communication
more precise and vivid.
Degree of the
adverbs
Adverbs are an essential part of speech that modify or describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They
provide information about the manner, time, place, or degree of an action or state. Adverbs can also be
compared using degrees of comparison, similar to adjectives.
The positive degree is the basic form of the adverb, used to simply describe an action or state. For example,
the adverb "quickly" is in its positive degree when used in a sentence like "She ran quickly to catch the bus."
The comparative degree is used to compare two actions or states, indicating that one is done to a greater
extent than the other. To form the comparative degree of most adverbs, you add "more" before the adverb.
For example, the adverb "quickly" becomes "more quickly" in the comparative degree."She ran more quickly
than her friend."
The superlative degree is used to compare three or more actions or states, indicating that one is done to
the greatest extent. To form the superlative degree of most adverbs, you add "most" before the adverb. For
example, the adverb "quickly" becomes "most quickly" in the superlative degree."She ran most quickly out of
all the runners in the race."
It's important to note that some adverbs have irregular forms in their comparative and superlative degrees.
For example, the adverb "well" has the comparative form "better" and the superlative form "best." Another
example is the adverb "badly," which has the comparative form "worse" and the superlative form "worst."
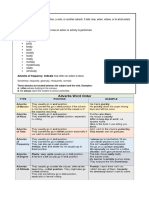
Classification
1) Adverbs of manner are words that describe how an action is performed or the way in which something
happens. These adverbs provide additional details about the manner or style in which a verb is carried out.
Examples include adverbs like quickly, smoothly, happily, and carefully. They answer the question "How?" in
relation to an action.
2) Adverbs of place are words that provide information about the location or direction of an action or the
position of an object. These adverbs help specify where the action is happening or where the subject is in
relation to something else. Examples of adverbs of place include words like here, there, nearby, and everywhere.
They answer the question "Where?" in the context of an action or situation.
3) Adverbs of frequency indicate how often an action occurs. These adverbs provide information about the
regularity or repetition of an action. Examples include words like always, often, rarely, and never. They answer
the question "How often?" in relation to the frequency of an action or event.
5) Adverbs of degree, measure, and quantity modify adjectives, verbs, or other adverbs to indicate the extent,
intensity, or amount of an action or quality. They provide additional information about the degree or extent of
something. Examples include words like very, too, almost, quite, much, and so. These adverbs answer questions
such as "To what extent?" or "How much?" in the context of an action or description.
6) Adverbs of time are words that provide information about when an action takes place. These adverbs
specify the timing, duration, or frequency of an event. Examples include words like yesterday, now, soon, and
always. Adverbs of time help answer questions such as "When?" or "How often?" in relation to a particular action
or situation.
Identify the Adverbs
Practic
Read the sentences given below and underline the adverbs.
1 The boy is too careless.
2 The winds are very strong.
3 The baby slept soundly.
4 The soldiers fought the war valiantly.
5 Joey always tries his best.
6 Surely you are mistaken.
7 The movie is to end soon.
8 Your friend messaged again.
9 I did my homework already.
10 I was rather busy.
Use the Right Adverbs
Complete the sentences by choosing the most appropriate adverb: Regularly, pretty, quickly, constantly, before.
The boy practiced his speech __
She _ makes the same mistake
He solved the problem _
We have met _
I know them _ well
Crossword
1. Refers to the place where an
action occurs.
2. Describes the frequency of an
action.
3. Indicates the manner in which
something is done.
4. Shows the duration of an
action.
5. Describes the degree to which
an action is performed.
6. Expresses the time when an
action happens.
7. A word that intensifies the
meaning of an adverb or
adjective.
QUIZ
https://quizizz.com/admin/quiz/6554d60aeda605aae5426979?source=quiz_share
You might also like
- Los AdverbiosDocument8 pagesLos AdverbiosAngelica Yaneth Abrego GuardadoNo ratings yet
- English PPT ALSDocument28 pagesEnglish PPT ALSKatrina NalanganNo ratings yet
- Tugas Bahasa InggrisDocument26 pagesTugas Bahasa InggrisMelly ShahabNo ratings yet
- Adverb: Rules of Using AdverbsDocument3 pagesAdverb: Rules of Using AdverbsArsalan QureshiNo ratings yet
- Seminarski RadDocument19 pagesSeminarski RadrifkonjaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs Describe VerbsDocument11 pagesAdverbs Describe Verbsjalebie talabangNo ratings yet
- All About AdverbsDocument18 pagesAll About AdverbsMazaya BtariNo ratings yet
- PEECDocument22 pagesPEECZenia Dwi KhairunisaNo ratings yet
- Brown and Beige Simple English Reading and Writing Types of Discourse PresentationDocument47 pagesBrown and Beige Simple English Reading and Writing Types of Discourse PresentationNur AthirahNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument11 pagesEnglishLino GemmaNo ratings yet
- B InggrisDocument9 pagesB Inggrisgrafada29No ratings yet
- Adverbs of DegrDocument4 pagesAdverbs of DegrJoemarie Alfaras SongcuyaNo ratings yet
- Adverb of Interrogative & Relative AdverbDocument10 pagesAdverb of Interrogative & Relative AdverbSonya Kasanova YusinNo ratings yet
- EngA Lesson 8 Sentence ExpansionDocument21 pagesEngA Lesson 8 Sentence ExpansionRei Deller TagiobonNo ratings yet
- Review Lessons - Language 5Document21 pagesReview Lessons - Language 5Mommy Joyee100% (1)
- 5 Types of Adverbs: Degree, Frequency, Manner, Place, TimeDocument18 pages5 Types of Adverbs: Degree, Frequency, Manner, Place, TimeJosé Emmanuel Martínez HernándezNo ratings yet
- AdverbDocument9 pagesAdverbPuja NurmalaNo ratings yet
- Adverbs-Kinds: Adverb AdjectiveDocument4 pagesAdverbs-Kinds: Adverb AdjectiveAngelus ElizabethNo ratings yet
- EB01PU4089921 Powerpoint PresentationDocument12 pagesEB01PU4089921 Powerpoint Presentationjaphetmaraga003No ratings yet
- 8 Parts of SpeechDocument5 pages8 Parts of SpeechMeliza ChocNo ratings yet
- Types of Adverbs As Part of Speech: Adverb: It Is A Word Used To Modify A Verb, An Adjective, Another Adverb or AnDocument9 pagesTypes of Adverbs As Part of Speech: Adverb: It Is A Word Used To Modify A Verb, An Adjective, Another Adverb or AnHammad Ali ShahzadNo ratings yet
- Rangkuman NayDocument8 pagesRangkuman Nayibaysubaei83No ratings yet
- Functional English 2Document21 pagesFunctional English 2Afzala YaseenNo ratings yet
- An AdverbDocument4 pagesAn AdverbBry AnNo ratings yet
- AderbsDocument3 pagesAderbsYassin Felix PereiraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 08Document4 pagesLecture 08sanamkhaan929No ratings yet
- Different Types of Adverbs With ExamplesDocument2 pagesDifferent Types of Adverbs With ExamplesRocio FernándezNo ratings yet
- Types of AdverbDocument2 pagesTypes of AdverbMonica Sario PolicinaNo ratings yet
- Composing Clear andDocument9 pagesComposing Clear andHaikara LorenzoNo ratings yet
- L1 Obtain and Convey Workplace InformationDocument37 pagesL1 Obtain and Convey Workplace InformationNarciso CardanaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To English AdverbsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To English AdverbsFrankie ArenolliNo ratings yet
- Group #3 English ReinforcementDocument2 pagesGroup #3 English ReinforcementDarlin EspinosaNo ratings yet
- New Vocab 508Document4 pagesNew Vocab 508api-588466161No ratings yet
- Basic Tenses Perfect TensesDocument5 pagesBasic Tenses Perfect TensesrheadistarNo ratings yet
- 5th D - ADVERB OF TIME AND PLACE-2Document17 pages5th D - ADVERB OF TIME AND PLACE-2Fely Mae Manlapas BelloNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 English Aspects of VerbDocument18 pagesGrade 5 English Aspects of VerbErnesto Cristo Jr TamayoNo ratings yet
- Remedial Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pagesRemedial Bahasa Inggrisllatipah294No ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English - AdverbDocument11 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English - AdverbPascual Denesse S.No ratings yet
- Фонетика емтиханDocument4 pagesФонетика емтиханАйжан СактапбергеноваNo ratings yet
- 4B07 VoNguyenThuyVy Adverbials in Vietnamese and EnglishDocument20 pages4B07 VoNguyenThuyVy Adverbials in Vietnamese and EnglishDerek Deleon100% (1)
- Blue Doodle Project Presentation 20240219 133719 0000Document17 pagesBlue Doodle Project Presentation 20240219 133719 0000alanNo ratings yet
- INGLES Actividad 1Document4 pagesINGLES Actividad 1Chiquinquira MorenoNo ratings yet
- Phrase StructureDocument3 pagesPhrase StructurePia DavesNo ratings yet
- Forms and Classifications of AdverbsDocument25 pagesForms and Classifications of AdverbsBrenda PerezNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledRaahilNo ratings yet
- Verbs & AdverbDocument33 pagesVerbs & AdverbAli Ali AneesNo ratings yet
- What Is Noun?Document4 pagesWhat Is Noun?Christian GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Verbs LessonDocument38 pagesLesson 5 Verbs LessonWane DavisNo ratings yet
- Adverb of Manner: These Adverbs Are Located Between The Subject and The Verb. ExamplesDocument4 pagesAdverb of Manner: These Adverbs Are Located Between The Subject and The Verb. ExamplesJan Arabella LabayNo ratings yet
- Adverbs: Mohammad Farhan Abid Eham ID: 171010101001, Department of English Batch 44, Prime UniversityDocument16 pagesAdverbs: Mohammad Farhan Abid Eham ID: 171010101001, Department of English Batch 44, Prime UniversityFarhan AbidNo ratings yet
- What Is Adverb?: Verbum ("Word", "Verb"), and The Nominal Suffix - Ium.. The Term 'Adverb' Itself MeansDocument5 pagesWhat Is Adverb?: Verbum ("Word", "Verb"), and The Nominal Suffix - Ium.. The Term 'Adverb' Itself MeansLejano JeffNo ratings yet
- SSC Hacks - EnglishDocument202 pagesSSC Hacks - EnglishArun Dominic100% (1)
- English TSKDocument8 pagesEnglish TSKSaGe MozNo ratings yet
- Rica B. Salon Bsed-English 1B. Reading Assignment 7Document6 pagesRica B. Salon Bsed-English 1B. Reading Assignment 7Charles Vincent PaniamoganNo ratings yet
- What Is The Progressive Verb Tense - Definition, Examples of The Continuous Tense - Writing ExplainedDocument31 pagesWhat Is The Progressive Verb Tense - Definition, Examples of The Continuous Tense - Writing ExplainedAroom AffandiNo ratings yet
- Module. AdverbsDocument6 pagesModule. AdverbsAditiya Nurul fatlyNo ratings yet
- Adjectives and Adverbs LessonDocument5 pagesAdjectives and Adverbs LessonRowena LinnumNo ratings yet
- Adverb FinalDocument24 pagesAdverb FinalMuhammad ArshadNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Subjectobjpron PDFDocument2 pagesWorksheet Subjectobjpron PDFChela PelotaNo ratings yet
- Grammar VI Chapter 3,4,5Document21 pagesGrammar VI Chapter 3,4,5mdirshad02031982No ratings yet
- Gateway b1+ 1st Edition WBDocument96 pagesGateway b1+ 1st Edition WBАнастасия МалушкоNo ratings yet
- Skripsi Bab 1,2,3, AmiDocument100 pagesSkripsi Bab 1,2,3, AmiAhlamiNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing I 05 29Document27 pagesAcademic Writing I 05 29Ngọc Lan HoàngNo ratings yet
- French SyllabusDocument2 pagesFrench SyllabusGAURAV KUMARNo ratings yet
- OUT Through UntilDocument20 pagesOUT Through UntilAnonymous NVe5TzNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument12 pagesTensesTieTiyWinnieNo ratings yet
- Easy Toeic. Unit 1Document26 pagesEasy Toeic. Unit 1Mã Thùy Vân QuýNo ratings yet
- 3-Minute Finnish #22 Ordering at A Restaurant: Lesson NotesDocument4 pages3-Minute Finnish #22 Ordering at A Restaurant: Lesson Notesfrank luisNo ratings yet
- English: Assessment FrameworkDocument3 pagesEnglish: Assessment FrameworkSGNo ratings yet
- Теоретическая грамматика госDocument10 pagesТеоретическая грамматика госДарья ОчманNo ratings yet
- StylisticsDocument12 pagesStylisticsOlya BragaNo ratings yet
- Languages - (eBook-PDF) Greek Language - AdjectivesDocument8 pagesLanguages - (eBook-PDF) Greek Language - Adjectivesdanutza277No ratings yet
- Articles With Words Beginning With H,' A or AnDocument3 pagesArticles With Words Beginning With H,' A or AnEdgar CorreaNo ratings yet
- Ingles 6 PrimariaDocument7 pagesIngles 6 PrimariaLoly Couceiro GonzálezNo ratings yet
- مراجعة شاملة انجلش وورلد 9Document48 pagesمراجعة شاملة انجلش وورلد 9AyazaNo ratings yet
- Passive in The Subordinate ClauseDocument4 pagesPassive in The Subordinate ClauseNash C. UsopNo ratings yet
- Notes of Reported Speech (Class 10 & 9)Document14 pagesNotes of Reported Speech (Class 10 & 9)Naren KumarNo ratings yet
- Verb To Be MiniDocument2 pagesVerb To Be MinizairiahothmanNo ratings yet
- Makalah Passive VoiceDocument13 pagesMakalah Passive VoiceSolehudin100% (1)
- Articles and Its Uses: Sadatun Nesa Lecturer, Department of English Port City International UniversityDocument16 pagesArticles and Its Uses: Sadatun Nesa Lecturer, Department of English Port City International UniversityPranta Dev NathNo ratings yet
- ESL/EFL Lesson Plan: Possessive PronounDocument3 pagesESL/EFL Lesson Plan: Possessive PronounJen91% (11)
- TU6 Diagnostic TestDocument2 pagesTU6 Diagnostic TestMANYI ARBOLEDA SOLORZANONo ratings yet
- Direct and Indirect Speech QuestionnaireDocument6 pagesDirect and Indirect Speech QuestionnaireSABARI R C1594No ratings yet
- Grammar Test 7Document1 pageGrammar Test 7Oscar MasindeNo ratings yet
- Class Discussion: Adjective Grammar Focus: Comparative and SuperlativeDocument9 pagesClass Discussion: Adjective Grammar Focus: Comparative and SuperlativeVito Mediandra 2034No ratings yet
- Verse (40:1) - Word by Word: Quranic Arabic CorpusDocument160 pagesVerse (40:1) - Word by Word: Quranic Arabic CorpusaminchatNo ratings yet
- Swedish IIIDocument14 pagesSwedish IIImende2010No ratings yet
- How To Improve Your Academic Writing PDFDocument24 pagesHow To Improve Your Academic Writing PDFipqtrNo ratings yet