Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Product Management
Uploaded by
nikki romero0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views6 pagesOriginal Title
product management
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views6 pagesProduct Management
Uploaded by
nikki romeroCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
CHAPTER 4 ● The NDP process is a sequential
The first part of Design phase is Stage 2; and conditional process
Build the Business Case: where ● The Go/No go evaluation
a formal market and financial process must be easy to use and
assessment are conducted. grounded in the day-to-day
operations of the corporation
Development Stage: The stage in the ● The process is characterized by
NPD (new product development) process uncertainty of information and the
where R&D and/or engineering is absence of solid financial data
conducted to develop the product/
service. The outcome of this stage is MUST-MEET CRITERIA
typically a product/ service ready for mass ● Strategic alignment
production. ● Favorable size of market
● Within technical capabilities or
Preliminary business plan to set a ability to acquire technology
roadmap to follow in the next stages of ● Significant product advantages
Development. compared to competition
● Environmental issues met:
Inputs for the Idea Screening Go/No government, economic, technical,
Go Gate Analysis sustainable, etc.
● List of potential ideas to take into ● Risk versus return hurdles of
product design organization met
● Market analysis of possible ● Profit potential hurdles met
segments
● Competitive analysis for segments SHOULD-MET CRITERIA
● Alignment with strategic direction ● Strategic importance of project to
of organization firm
● Probable investment needed to ● Unique product offering compared
capture profitable market share to competitors
● Need to acquire outside ● Adequate market size versus
expertise/technologies market growth
● Risk/ reward assessment ● Leverage core competencies of
firm-marketing, technical, and/or
Gate1: Idea screening manufacturing
The inputs would be the list of ideas ● Technically feasible with low risk
that have been generated through ● Certainty of return and/or profit or
Discovery process and the Identification sales
Assessment accumulated during the ● Favorable competitive situation
market evaluation. ● Index of attractiveness
requirement
Idea Screening Gate: The gate at which
product ideas are screened to determine
if they should advance to the scoping
stage.
Idea selection process: Avoiding two Voice of the customer (VOC): Strives to
errors: record in the customer’s own words the
1. Approving a potentially unprofitable benefits of a product or service
product and type.
2. Rejecting a potentially profitable INCORPORATING VOICE OF THE
product CUSTOMER IN THEIR DESIGN
PROCESS
Index of attractiveness: divides the
expected return by the development cost ● Capture voice of the customers
as a measure of how attractive the new ● Identify needs
product is compared to other potential ● Prioritize needs
new products ● Concept Development
● Design testing with customers
I= Index of attractiveness
T= Probability of successful technical BENEFIT CHAINS: Determine why
development customers have a particular need that is
C= probability of commercial success not yet addressed by existing products.
given that it is technically successful
D= Cost of development Preference model: A quantitative method
that gathers consumer’s preferences for
One explanation for overestimating features, benefits or attributes of a new
probability of success might be product/ service.
ENTREPRENEURIAL OPTIMISM
BIASNESS, where failure seems unlikely Zaltman’s metaphor elicitation
to those championing the idea. technique ( ZMET)- suggests that the
underlying values and meanings that
SCOPING STAGE: The NPD Stage in drive customers
which preliminary market assessment, a
preliminary technical assessment, and Laddering: Quantitative technique for
preliminary business/financial assessment finding the benefits an end user may see
are conducted. In this stage, opinions of in a new product.
the customers are collected.
Means- End Chain: it describes how a
Preliminary market assessment: product interacts with the customer
Consolidates all the findings that were through its attributes, benefits, to deliver
accumulated during the market definition values.
stage.
Scoring Models: A method of scoring an
individual project to determine its
attractiveness compared to other potential
products.
Attributes Problem Analysis workshop where the
- Concrete attributes main task is to brainstorm for new product
- Abstract attributes ideas.
Benefits
- Functional benefits Crowd Sourcing for new product Ideas
- Psycho- social benefits The practice of obtaining needed
Values services, ideas, or content by soliciting
- Instrumental values contributions from a large group of people
- Terminal values
Brainstorming- a technique developed in
CHAPTER 3 the 1950s and 1960s based on the belief
OPPORTUNITY IDENTIFICATION that randomized thoughts led to greater
● Idea Generation creativity.
● Opportunity Analysis
● Market Identification Attribute Listing- a method for
● Market Selection generating a new product idea where
● Concept development and attributes are listed for existing products
refinement
Individual creativity- the process where
IN-HOUSE IDEATION an individual, as opposed to a group,
● Engineering/Research identifies new product ideas.
● Sales
● Production Market profile analysis- procedure for
● Service Personnel matching a firm’s capabilities to market
● Marketing opportunities.
● Legal terms
● Top management Portfolio alignment- balancing the firm's
new product development strategy to
OUT-OF-HOUSE maximize return on investment in new
● Customers product development.
● Competitors
● Trade Partners Market identification- identify markets
● Design Firms that offer the best opportunities for the
● Suppliers organization.
Others
● Channels of Distribution Experience curve- this curve indicates
● Open Innovation that the unit cost of producing and
● The Global innovation grid distributing a product
Scenario generation- Brainstorming by Process Innovation- Innovation in the
developing scenarios of the future-best way a product or service is manufactured,
and worst cases as well as most likely created, or distributed,
Sleepy market- markets in which sales Proactive Innovation Process-
are stable and innovation has been Preempting competition by being first on
absent can represent an attractive the market
opportunity if they are penetrated
effectively. Reactive Innovation Process-
Addressing initiating pressures as they
Substitution- Observing or measuring occur, particularly in regards to new
directly which products substitute for one competitive offerings.
another is another method for market
segmentation. Fast Follower- imitative strategy the firm
will quickly develop an imitation to counter
CHAPTER 2 the attack on its market.
Innovation Arena- Focus on the firm’s
core competencies that have been Second But better- the firm does not just
identified in the corporate strategy. copy the competitive product, but
identifies ways to improve the product and
Market/Customers/Product Categories- its positioning.
Market size and profit margins can affect
the choice of development strategy. Defensive Strategy- protects the
profitability of existing products by
Technology- the innovation strategy encountering competitive new products.
cutting the edge of new technological
advances Customer ideation- is purposely reacting
to customer’s request and ideas.
Competition- The competitive
environment may be critical to selecting a PROACTIVE PROCESS
strategic posture. - An Alternative new product
strategy is for organizations to be
Channels- In many markets, middlemen proactive and initiate change.
serve a physical distribution, inventory,
selling, or servicing function. Innovative strategy- a proactive
innovation strategy where the focus is on
Resources- in the form of monetary research and development efforts
funding, man-hours, facilities,
management guidance outsource funding Offensive Strategy a proactive
innovation strategy that improves on a
Risk willingness to accept occasional product or service by leapfrogging the
failures should be a normal part of current technology
business.
Creative Destruction- a term coined by
Reward- given in recognition of one's Joseph Schumpeter a process of
service, effort, or achievement. industrial mutation that incessantly
revolutionizes
Disruptive Technology- Improving a Stage-gate innovation
product or service by leapfrogging the process-systematic, structured process
current technology for developing new products with gates
(stopping point)
Market/Customer Innovation– a
proactive innovation strategy where Gates- points in the stage-gate innovation
customer needs are identified process where the project’s viability is
assessed
Portfolio management for new products
is very similar to the concept of portfolio STEPS AS A FRAMEWORK
management in financial investment.
Discovery- another name for the
3 goals of portfolio Management opportunity identification stage.
● value maximization
● portfolio balance Scoping- a process design stage of the
● strategic alignment stage-gate process where screening of an
idea with a quick
Tools for portfolio Management
Economic Models include payback Building the Business Case- a process
period, break-even analysis in the Design stage of the stage-gate
process involving detailed investigation
Portfolio Maps also called (bubble with primary research-both
diagram) plot project against on two
criteria Development- is the go/no go decision
gate whether the project should be move
Strategic bucket a method for evaluating into expensive and resource heavy
a portfolio of products where the project
are allocated to buckets and then Testing- determines whether the product
resources are assigned to each class of as designed during the development
projects should be moved to testing and validation
Portfolio management is a mix of new Launch and post launch Review-
projects that as a combination seek to Process where the product/services that
maximize a firm’s profits. are being designed are tested prior to
launch.
CHAPTER 1
The “Frontline personnel “ are the face
of the company.
Employees’ close contact and potentially
long-term relationships with customers
Product Development Management
Association (PDMA)
Typical components include: ● Radical innovations: Innovations
● Engineering efforts/resources that introduce both market and
requirements technological discontinuities to the
● Marketing efforts/ resources marketplace.
requirements
● Manufacturing efforts/ resources THE PROACTIVE NEW PRODUCT
requirements DEVELOPMENT PROCESS
● Company synergies with existing New-to-the-firm products that take the
product platforms firm in a new direction
● Profitability and break even point.
Repositioning: Products that take on
Engineering issues addressed in the new uses, e.gLevi Jeans pants to fashion
product development phase may statement, aspirin for heart attacks. This
include: category accounts for about 7% of new
● Resources required products.
● Engineering operations planning
● Department scheduling Cost reductions- Products that replace
● Supplier collaboration existing products by providing similar
● Logistics planning performance at a lower cost
● Program review and monitoring
● Finalization of product attributes
and features
Testing and Validation Testing involves
tests or trials in the marketplace
Looping: A type of new product
development process commonly used in
Software design
Types of New Products and
Customizing the Development Process
● Incremental innovation:
Innovations that have small
incremental technology or small
marketing changes to an existing
product.
● Innovation: An iterative process
initiated by the perception of a
new market
● Really new innovations:
Innovations that introduce either a
new marketing or technological
innovation.
You might also like
- New Product Development ProcessDocument3 pagesNew Product Development ProcessDasari Chandra Kanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On Management of Depressive Disorders-1Document40 pagesCase Presentation On Management of Depressive Disorders-1Fatima MuhammadNo ratings yet
- New Product LaunchDocument43 pagesNew Product LaunchSB100% (1)
- New Product DevelopmentDocument12 pagesNew Product DevelopmentDiane ChakanzahNo ratings yet
- Product Design & DevelopmentDocument6 pagesProduct Design & Developmentdmjobs6369No ratings yet
- Idea Generation+Innovation+FunnelDocument29 pagesIdea Generation+Innovation+Funnelrajaryan13No ratings yet
- B2B Product Decisions, New Product DevelopmentDocument30 pagesB2B Product Decisions, New Product DevelopmentRohan KadamNo ratings yet
- Pricing Decisions: Course InstructorDocument239 pagesPricing Decisions: Course Instructormalibabu .gembaliNo ratings yet
- Sharp MX M283 363 453 503 PDFDocument404 pagesSharp MX M283 363 453 503 PDFAlejandro Barraza100% (2)
- Product ManagementDocument106 pagesProduct Managementvarunsharma8888100% (1)
- Product Creation and DevelopmentDocument3 pagesProduct Creation and DevelopmentleizlNo ratings yet
- The Promised Land PDFDocument12 pagesThe Promised Land PDFnazim2851No ratings yet
- New Product Development Essentials: Hands-on Help for Small Manufacturers and Smart Technical People: No Nonsence Manuals, #2From EverandNew Product Development Essentials: Hands-on Help for Small Manufacturers and Smart Technical People: No Nonsence Manuals, #2Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- R&D Productivity: How to Target It. How to Measure It. Why It Matters.From EverandR&D Productivity: How to Target It. How to Measure It. Why It Matters.No ratings yet
- Product Management Is An Organizational Lifecycle Function Within A Company Dealing With TheDocument20 pagesProduct Management Is An Organizational Lifecycle Function Within A Company Dealing With TheHarsh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - New Product DevelopmentDocument15 pagesChapter 10 - New Product Developmentkunal gargNo ratings yet
- Product Management ReviewerDocument8 pagesProduct Management ReviewerJm Almario BautistaNo ratings yet
- POMDocument5 pagesPOMSunil Kumar Singh100% (1)
- The Process: Business Engineering Product Product Design Marketing AnalysisDocument4 pagesThe Process: Business Engineering Product Product Design Marketing AnalysisShahzadyaqoob SagarNo ratings yet
- Compiled AnswersDocument20 pagesCompiled AnswersPKNo ratings yet
- New Product Development: A Dispersed and Integrated ProcessDocument7 pagesNew Product Development: A Dispersed and Integrated ProcesskashemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 KBTUDocument19 pagesChapter 7 KBTUFarhangaizNo ratings yet
- Product Kelompok 1 PresentasiDocument28 pagesProduct Kelompok 1 PresentasiIndah AbudimanNo ratings yet
- 2Q) Positioning of Ibm:: The Process of Product Development IncludesDocument5 pages2Q) Positioning of Ibm:: The Process of Product Development Includessurbhis_12No ratings yet
- Research On New Product Development: Prepared By: Priyega PremDocument21 pagesResearch On New Product Development: Prepared By: Priyega PremshrutiudayNo ratings yet
- Product DevelopmetDocument18 pagesProduct DevelopmetanishjohnaNo ratings yet
- New Product Development: Technology Entrepreneurship (ENT 600) Group 3 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering (FKM)Document29 pagesNew Product Development: Technology Entrepreneurship (ENT 600) Group 3 Faculty of Mechanical Engineering (FKM)duff_808No ratings yet
- Product Management ReviewerDocument8 pagesProduct Management ReviewerADAY, KRISDYLYN A.No ratings yet
- New Product Development (NPD)Document29 pagesNew Product Development (NPD)Shubhranshu ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- LO3 Discuss The Process Required To CommercialiseDocument35 pagesLO3 Discuss The Process Required To CommercialiseLucio StefanoNo ratings yet
- New Product Development: To Meet Wikipedia's - PleaseDocument7 pagesNew Product Development: To Meet Wikipedia's - PleaseRishi GohilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document6 pagesChapter 4Sine EntertaimentNo ratings yet
- Managing New Products: The Power of InnovationDocument34 pagesManaging New Products: The Power of InnovationwaqaasrumaniNo ratings yet
- Ic Lo3Document36 pagesIc Lo3Zilen SalamNo ratings yet
- PBM Ch.5 - NPDDocument20 pagesPBM Ch.5 - NPDDeepali PatilNo ratings yet
- Module 3 IMDocument42 pagesModule 3 IMAtul KashyapNo ratings yet
- c1 IntroductiontoproductdevelopmentDocument50 pagesc1 IntroductiontoproductdevelopmentAhnaf Fadhlur Rahman Bin Awang HanibNo ratings yet
- POM Unit IIDocument13 pagesPOM Unit IIShiVâ SãiNo ratings yet
- Product Design & Development: The Generic Process For Developing New ProductsDocument7 pagesProduct Design & Development: The Generic Process For Developing New ProductsRandeep DevNo ratings yet
- NPD 1Document17 pagesNPD 1elmakayaNo ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument7 pagesNew Product DevelopmentDeepthi VadlaNo ratings yet
- New Production Development Process: Presented in The Class Of: - Submitted By: - Dr. Manoj KumarDocument25 pagesNew Production Development Process: Presented in The Class Of: - Submitted By: - Dr. Manoj KumarTina SainiNo ratings yet
- Discovering New Product Development StrategyDocument7 pagesDiscovering New Product Development StrategyLi An BautistaNo ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument5 pagesNew Product DevelopmentRohan AroraNo ratings yet
- Mk302E-Marketing Fundamentals Ii: 2017 Second SemesterDocument41 pagesMk302E-Marketing Fundamentals Ii: 2017 Second Semestergrou grouNo ratings yet
- New Product: Development ProcessDocument15 pagesNew Product: Development Processsadiya afzalNo ratings yet
- NPD Chapter Fourteen 2023Document35 pagesNPD Chapter Fourteen 2023Ola MikatiNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER - 4 Product and Service ConceptDocument26 pagesCHAPTER - 4 Product and Service ConceptTesfahun TegegnNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 7 Pemasaran Pertanian 2021Document27 pagesPertemuan 7 Pemasaran Pertanian 2021GIA AMALIA RIDHA RIDHANo ratings yet
- Product Planning Process - 1Document75 pagesProduct Planning Process - 1Raman KulkarniNo ratings yet
- The Process: Business Engineering ProductDocument12 pagesThe Process: Business Engineering Producthemu22No ratings yet
- Ifci Doc 7Document9 pagesIfci Doc 7satexNo ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument18 pagesNew Product Developmentirshad69No ratings yet
- Innovation Management Iii Bcom (Unit Iv)Document11 pagesInnovation Management Iii Bcom (Unit Iv)Commerce DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Learning Objective of The Chapter: Product AND Service Concept Product AND Service ConceptDocument24 pagesLearning Objective of The Chapter: Product AND Service Concept Product AND Service ConceptHibo AnwarNo ratings yet
- MKTG 361 - Instructor - Chapter 12Document52 pagesMKTG 361 - Instructor - Chapter 12colinmac8892No ratings yet
- Topic: New Product Development: Marketing ManagementDocument41 pagesTopic: New Product Development: Marketing ManagementATHIRA RNo ratings yet
- EntrepreneurshipDocument5 pagesEntrepreneurshipLeon NyNo ratings yet
- Pom Unit-2Document34 pagesPom Unit-2bhadrichandu961No ratings yet
- Chapter-III Product and Service DesignDocument14 pagesChapter-III Product and Service DesignGebrekiros ArayaNo ratings yet
- New Product Development: Identifying Need Creating ValueDocument20 pagesNew Product Development: Identifying Need Creating ValueSharvaree TawareNo ratings yet
- Succeed Through Customer Knowledge: A Guide to Practical Customer-Originated MarketingFrom EverandSucceed Through Customer Knowledge: A Guide to Practical Customer-Originated MarketingNo ratings yet
- Group3 The Development of Moral Character of Moral Agent EspantoHipolitoLepitinNamoc 1Document5 pagesGroup3 The Development of Moral Character of Moral Agent EspantoHipolitoLepitinNamoc 1Novelyn DuyoganNo ratings yet
- 1b.exadata X9M 2Document29 pages1b.exadata X9M 2Edu KiaiNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan - Yr 9 Vis ArtDocument5 pagesUnit Plan - Yr 9 Vis Artapi-333348168No ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1CJ CastroNo ratings yet
- IIRDocument2 pagesIIRJagan FaithNo ratings yet
- Marking Scheme According To AIDocument2 pagesMarking Scheme According To AIAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Fraud and ErrorsDocument3 pagesChapter 12 Fraud and ErrorsMajoy BantocNo ratings yet
- Polyethylene PolyamineDocument6 pagesPolyethylene PolyamineAV kayanNo ratings yet
- Anti LeproticDocument9 pagesAnti LeproticMeenakshi shARMANo ratings yet
- ParaklesisDocument23 pagesParaklesisDiana ObeidNo ratings yet
- Tikkun Kisay HaShemDocument47 pagesTikkun Kisay HaShemYochananMauritzHummasti100% (1)
- 500KVA Rigsafe Framed Generator (8900Kgs)Document1 page500KVA Rigsafe Framed Generator (8900Kgs)Elsad HuseynovNo ratings yet
- Predicates and ArgumentsDocument4 pagesPredicates and ArgumentsOanh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Positive and Negative Impact of Inclusive LeadershipDocument9 pagesThe Positive and Negative Impact of Inclusive LeadershipAmbreen ZainebNo ratings yet
- Case Study - of Chapel of San Pedro CalungsodDocument5 pagesCase Study - of Chapel of San Pedro CalungsodJosielynNo ratings yet
- Tea Board of India PDFDocument18 pagesTea Board of India PDFDebasish RazNo ratings yet
- Aeroacoustic Optimization of Wind Turbine Airfoils by Combining Thermographic and Acoustic Measurement DataDocument4 pagesAeroacoustic Optimization of Wind Turbine Airfoils by Combining Thermographic and Acoustic Measurement DatamoussaouiNo ratings yet
- Deutz D 2011 W, TD 2011 W, TCD 2011 W Workshop Manual - Competence Level 2Document266 pagesDeutz D 2011 W, TD 2011 W, TCD 2011 W Workshop Manual - Competence Level 2Marcin EldorNo ratings yet
- Understanding EarsDocument1 pageUnderstanding EarsmerkyworksNo ratings yet
- XeroxWC 5020DN Service Manual 03.02.2012 PDFDocument432 pagesXeroxWC 5020DN Service Manual 03.02.2012 PDFSergey100% (1)
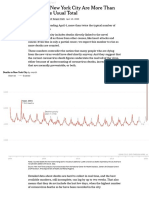
- Deaths in New York City Are More Than Double The Usual TotalDocument3 pagesDeaths in New York City Are More Than Double The Usual TotalRamón RuizNo ratings yet
- REACH ArticlesDocument12 pagesREACH ArticlesChristian SugasttiNo ratings yet
- Aurora National High School: Report On AttendanceDocument2 pagesAurora National High School: Report On AttendanceLimuel CaringalNo ratings yet
- Retail ImageDocument76 pagesRetail ImageayushiNo ratings yet
- Output D4Document34 pagesOutput D4Angel MingaNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project Edi IrawanDocument75 pagesFinal Year Project Edi IrawanEdi IrawanNo ratings yet
- Leave Management System: Software Requirements Specification DocumentDocument6 pagesLeave Management System: Software Requirements Specification Documentk767No ratings yet