0% found this document useful (0 votes)
652 views13 pagesBasic Electronics Module 1
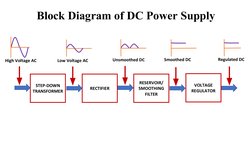
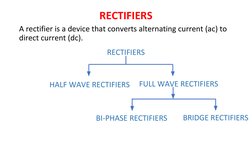
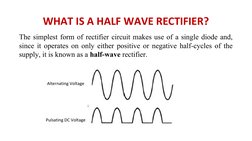
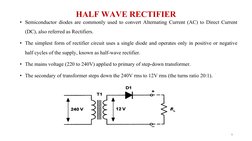
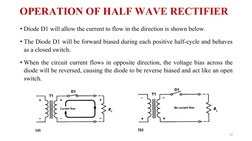
The document discusses power supplies and rectifiers. It describes the basic components and operation of a DC power supply including step-down transformers, rectifiers, reservoir/smoothing circuits and voltage regulators. It also explains half-wave rectifiers and their operation using a single diode to convert alternating current to pulsating direct current.
Uploaded by
varun186Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
652 views13 pagesBasic Electronics Module 1
The document discusses power supplies and rectifiers. It describes the basic components and operation of a DC power supply including step-down transformers, rectifiers, reservoir/smoothing circuits and voltage regulators. It also explains half-wave rectifiers and their operation using a single diode to convert alternating current to pulsating direct current.
Uploaded by
varun186Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd