Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TC
Uploaded by
Precious Jancine Darisan Moral0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views4 pagesTC
Uploaded by
Precious Jancine Darisan MoralCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
1. Which of the following is the function of the respiratory 4.
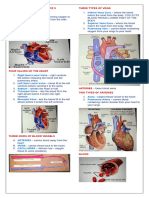
Heart - Pumps blood delivering it to the other parts of
system? the body
a. send signals to the spinal cord and instruct 5. Organs - Receives oxygenated blood
other organs what to do. 6. Arteries - Carry blood away from the heart
b. take waste products and bring them out of the 7. Veins - Carry blood towards the heart
body. 8. Capillaries - Smallest blood vessel where the exchange
c. to allow the exchange of gases to provide of oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs.
parts of the body with oxygen.
d. to take in glucose and transform it into energy. a. What is the pathway that the respiratory gases take during
2. What are the parts of the respiratory system? (a) inhalation and (b) exhalation?
a. lungs, air sac, ribs, liver (a) inhalation - nostrils → pharynx → larynx → trachea
b. lungs, trachea, larynx, pharynx, bronchi, → bronchi → bronchioles → lungs.
bronchioles, alveoli, nasal cavity (b) exhalation - lungs → bronchioles → bronchi →
c. lungs, trachea, larynx, pharynx, bronchi, trachea → larynx → pharynx → nostrils
bronchioles, alveoli, nasal cavity, heart b. What mechanism induces the respiratory gases to exchange
d. throat, bronchioles, bronchi, alveoli, stomach, in the alveoli of the lungs and the capillary beds in tissues?
ribs Diffusion is the mechanism that induces gas exchange.
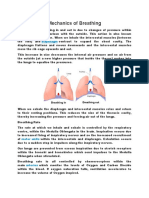
3. What is the flow of air during inhalation?
a. lungs, mouth a. How are the circulatory and respiratory system related?
b. mouth, lungs, respiratory tubes The respiratory system aids in taking in and out
c. mouth, respiratory tubes, lungs respiratory gases. The blood, a part of the circulatory
d. mouth, respiratory tubes, stomach, lungs system, is responsible for delivering these respiratory
4. Where is the site of gas exchange and what material gases throughout the body.
diffuses in and out of the blood? b. How can you identify the individual’s total lung capacity?
a. alveoli, O2 and CO2 Total lung capacity can be calculated by adding the
b. diaphragm, O2, and CO2 residual volume to the individual’s vital capacity.
c. lungs, Alveoli, O2, and glucose
d. lungs, Alveoli, O2 and N2 What is the flow of blood (a) from the body to the lungs and
5. What organ filters out air? (b) from the lungs to the other parts of the body?
a. Cilia
b. lungs (a) vena cava → right atrium →tricuspid valve → right
c. nostrils ventricle → pulmonary valve → pulmonary artery → lungs
d. trachea (b) pulmonary vein → left atrium → bicuspid valve → left
6. What do you call the flap that covers the passageway for ventricle → aortic valve → aorta → all parts of the body.
air when eating or drinking?
a. bronchi a. Identify the part of the circulatory system that is being
b. epiglottis described in each item.
c. larynx 1. The biggest artery. aorta
d. pharynx 2. The vein that carries oxygenated blood towards the
7. What do you call the voice box which enables a person to heart. Pulmonary vein
produce sounds and speak? 3. The artery that carries deoxygenated blood towards
a. alveoli the heart. Pulmonary artery.
b. bronchi 4. The smallest blood vessel. Capillaries
c. larynx 5. The heart's chamber that receives oxygenated blood.
d. pharynx left atrium
8. Where is the first entry of air during inhalation? 6. The chamber of the heart that receives
a. bronchioles deoxygenated blood. Right atrium
b. mouth 7. A blood vessel where deoxygenated blood from the
c. nostrils body flow. vein
d. trachea 8. The chamber with a thicker muscle. Left ventricle
9. What will happen if the respiratory and digestive tracts 9. The heart's chamber above the ventricle. atrium
are completely separate in humans? 10. The valve between the left atrium and left ventricle.
a. it is impossible to breathe Mitral valve
b. it will be harder to swallow the food
c. there would be no need for an epiglottis Parts of the circulatory System
d. trachea is not necessary anymore. 1. Vena cava-The largest vein which carries deoxygenated
10. Which of the following is anatomically incorrect? blood to the heart
a. The lungs contain many alveoli. 2. Aorta- It is the biggest artery that supplies oxygenated
b. The nasal and oral cavities are connected to the blood throughout the body.
larynx through the pharynx. 3. Pulmonary Artery- The blood vessel where
c. There are two nasal cavities in the nose. deoxygenated blood flows from the heart to the lungs.
d. The trachea enters the lungs. 4. Pulmonary Vein- The blood vessel where oxygenated
blood flows from the lungs to the heart.
1. Blood- The one that circulates, and delivers respiratory 5. Right Atrium- The chamber of the heart where the
gases to the heart and throughout the body deoxygenated blood enters first.
2. Oxygen -The one that is picked up by blood in the lungs 6. Right Ventricle- It pumps blood from the heart to the
and circulate it throughout the body. lungs.
3. Carbon dioxide - The one that is picked up by blood in 7. Left Atrium- The chamber of the heart where the
the organs and deliver it back to the heart. oxygenated blood enters first
8. Left Ventricle- The thickest chamber of the heart. 2. Which of the following is not a component of the
DNA?
a. Identify what is being described in each item. a. nitrogenous base b. nucleotide c. protein d. sugar
1. The liquid component of blood. plasma 3. Which of the following refers to the coding region of the
2. These are secreted by the hormonal organs into the blood genes?
which mixes directly to the plasma. hormones a. enhancer region b. exon c. intron d. promoting
3. These are round and flat cells with an indention in the region
center like doughnuts without a hole. Red blood cells 4. Which of the following refers to the non-coding region of
4. This atom is the one that binds to the gas molecules. the genes?
Iron atom a. enhancer region b. exon c. intron d. promoting
5. It refers to hemoglobin loaded with oxygen. region
oxyhemoglobin 5. Which of the following allows the activation of the genes
6. It is the form of hemoglobin without oxygen that is to encode for protein?
purple to bluish. deoxyhemoglobin a. enhancer region b. exon c. intron d. promoting
region
Instruction: Write true if the statement is correct and false if 6. Which of the following is made up of DNA strand and
incorrect. histone proteins?
1. Red blood cells contain a nucleus. false a. chromatic fiber b. chromosome c. genes d.
2. The red blood cells can carry respiratory gases through nucleosome
its hemoglobin. true 7. In eukaryotes, the DNA is located in what region?
3. Bone marrow is the site of red blood cell production. a. cell membrane b. cytoplasm c. mitochondria d.
true nucleus
4. Deoxyhemoglobin is the form of hemoglobin loaded with 8. In prokaryotes, the DNA is located in what region?
oxygen. false a. cell membrane b. cytoplasm c. mitochondria d.
5. The white blood cells are more numerous than red blood nucleus
cells. false 9. Which of the following refers to the observable traits of
6. Hemoglobin consists of four globin chains. true an individual?
7. The size of the red blood cells is bigger than white blood a. DNA b. genes c. genotype d. phenotype
cells. false 10. Which of the following refers to the specific genetic
8. Substances such as hormones are directly transported via element that regulates trait variation?
the fluid part of the blood called plasma. true a. DNA b. genes c. genotype d. phenotype
9. Oxyhemoglobin is characterized by a purple to a bluish
color. false Gregor Johann Mendel, the Father of Genetics, was an Austrian
10. Hemoglobin is the iron-containing protein present in the monk.
red blood cells. True Influenced by his great love for science and works of previous
scientists like Charles Darwin (Origin of Species), he started with
a. Write true if the statement is correct. Otherwise, write false. his pea plant experiment.
1. Consult a doctor only when there is a pain in the body. 1. Parental generation (P generation) – the initial
False generation.
2. Second-hand smoking is safer than first-hand smoking. 2. First filial generation (F1 generation) – the first set of
false offsprings from parent generation. The F1 generation can
3. Smoking does not affect the heart and lungs. false reproduce to make the F2 generation and so on.
4. Cholesterol in the body is useful when it is controlled. 3. Pure-bred plants - these refer to plants that “always”
true produce an offspring with identical trait as the parent for
5. Obesity can cause problems in the circulatory system. many generations. For example, a parent plant with a tall
true trait crossed by a plant with the same trait will produce a
6. Eating a well-balanced meal can both be beneficial for 100% offspring with the tall trait.
both the circulatory and respiratory systems. true 4. Self-fertilization – some plants can fertilize by
7. The digestive system is connected to both circulatory and themselves. It is possible because some plants such as
respiratory systems. true pea
8. Avoiding voluminous alcohol intake will have little
effect on our health. false Law of dominance- Mendel’s law of dominance relies on the
9. Individuals who have the right body index can splurge on concept of dominant and recessive traits.
any food. false Law of segregation- The law of segregation states that all the
10. Giving up vices and lifestyle change can help us maintain genes for all the traits of an offspring are equally distributed or
a healthy body. true segregated in all the resulting gametes after meiosis.
Law of independent Assortment- The law of independent
a. Identify the term being described in each item. assortment explains that genes responsible for the expression of
1. It is also known as the non-coding region of the gene. different traits are sorted independently from each other.
Intron
2. It is the physical feature of an individual. Phenotype 1. Which law explains the presence of dominant and
3. It regulates the physical manifestations of a trait. recessive traits among organisms?
Genotype a. dominance b. genetic inheritance
4. It is known as the genetic material. DNA c. independent assortment d. segregation
5. It is a part of a gene that codes for important proteins. 2. Which law explains the segregation of the allele from
Exon parents to offspring?
1. Which of the following is made up of coiled chromatin a. dominance b. genetic inheritance
fibers? c. independent assortment d. segregation
a. Chromosome b. DNA c. genes d. nucleosome
3. Which law explains the random recombination of alleles a. allele b. chromatin c. DNA d. nucleosome
from the parents? 5. Which of the following refers to the transmission of traits
a. dominance b. genetic inheritance from parents to offsprings?
c. independent assortment d. segregation a. DNA b. genes c. genetics d. inheritance
4. Which of the following organism was used by 6. Which of the following is an example of incomplete
Mendel in his experiments? dominance inheritance?
a. Arabidopsis b. Mango c. Pea plant d. Zebrafish a. ABO blood type b. color blindness
5. Which term refers to the transmission of traits from c. feather color d. petal color
parents to offsprings? 7. Which of the following is an example of codominance
a. DNA b. genes c. genetics d. inheritance inheritance?
6. Which process allows the horizontal transfer of a. ABO blood type b. color blindness
DNA from one cell to another? c. feather color d. petal color
a. cell respiration b. mitosis 8. Which of the following is an example of sex-linked
c. photosynthesis d. transpiration inheritance?
7. Which process allows the transfer of materials from the a. ABO blood type b. color blindness
parents to the offspring? c. feather color d. petal color
a. cell respiration b. meiosis c. mitosis d. 9. Which of the following is an example of multiple allele
transpiration inheritance?
8. Which of the following refers to the copy of genes for a a. ABO blood type b. color blindness
specific trait? c. feather color d. petal color
a. alleles b. chromatin c. chromosome d. DNA 10. Which of the following is not considered as non-
9. Which of the following refers to the tangible trait in an Mendelian genetics?
organism? a. codominance b. incomplete dominance
a. DNA b. genes c. genotype d. phenotype c. law of dominance d. sex-linked trait
10. Which of the following refers to the specific genetic
element that regulates trait variation? Species Richness- Species richness refers to the number of species
a. DNA b. genes c. genotype d. phenotype found in an area.
Abundance- Species abundance is the number of members that a
A. Incomplete dominance - Incomplete dominance is a species has in an area.
pattern of inheritance characterized by the formation of a Endangered Species- Endangered species are organisms that are
trait that is in between the phenotypes of the parents. being threatened with destruction.
B. Codominance- Codominance is a non-Mendelian type of Biodiversity Hotspot- A biodiversity hotspot is an area with high
dominance where the alleles of a gene pair in a biodiversity that is at risk of being destroyed and the organisms
heterozygote are fully expressed. being affected.
C. Sex-linked traits- The X and Y not only carry the genes Endemic Species- Endemic species are organisms that are
that determine sex but also some other characteristics. exclusively found in one area.
Genes that go along with either sex chromosome are said
to be sex-linked. a. Identify the following terms based on the given information.
D. Multiple alleles- In some traits, a certain gene can have 1. Species which can only be found in a certain place is
more than a pair of alleles that controls the expression of called an_______________. endemic species
traits. 2. _______________ are those organisms whose number of
individuals in the natural environment is lower than
AB blood type Codominance usual, close to extinction. endangered species
Baldness Sex-linked trait 3. _______________ is the vanishing of a specific species
Chicken feather color Codominance on Earth. extinction
Flower petal color Incomplete dominance 4. _______________ pertains to the total number of
Hemophilia Sex-linked trait individuals of a species. abundance
Color blindness Sex-linked trait 5. _______________ is the number of individuals per
Hypertrichosis Sex-linked trait species relative to the area of a particular place. species
ABO blood type Multiple allele density
Horse height Codominance
Sickle cell Codominance Write true if the given statement is correct and write the correct
word in place of the underlined ones if the statement is false.
1. Which of the following explains the pattern of 1. There are about 14 000 – 15 310 plant species in the
inheritance characterized by the formation of a trait that Philippines. - true
is in between the phenotypes of the parents? 2. One of the most famous endemic species in the
a. codominance b. incomplete dominance Philippines, the Philippine tamaraw is found in
c. multiple alleles d. sex-linked trait Mindanao. – Mindoro
2. Which of the following non-Mendelian concept explains 3. Pithecophaga jefferyi, the Philippine eagle, can be found
a type of dominance where the alleles of a gene pair in a in Mindanao.
heterozygote are fully expressed? - true
a. codominance b. incomplete dominance 2. Three measures of diversity are richness, abundance, and
c. multiple alleles d. sex-linked trait species density. - true
3. Which of the following refers to genes that go along with 3. Species density is equal to the total number of
either sex chromosome? individuals per species.
a. codominance b. incomplete dominance - abundance
c. multiple alleles d. sex-linked trait 4. Abundance is computed by counting the total number of
4. Which of the following refers to a variant copy of a individuals per species and dividing it by the total unit
specific gene? area. - species density
5. The endemic species Sundasciurus samarensis is found in 4. This is the snake that was introduced into the island of
Mindoro. Samar Guam, which led to the extinction of species. Brown
6. Abundance and species density are used to express the tree snake
richness of different life forms in an area. - true 5. These are the organisms that went extinct in #4. Birds
9. Diversity can be characterized by total abundance and 6. This disease is causing extinction in frog species
species density. - true worldwide. Chytridiomycosis
10. Endemic species are species found in several countries. - 7. These are examples of causes of habitat destruction.
only one Country Overpopulation, deforestation, pollution, etc.
8. This refers to unpredictable and rapid changes in
Identify what is asked in each item. environmental conditions and climate. Climate change
1. A species only found in a certain place. Endemic species 9. These are species that are not normally found in an area,
2. The Philippines is named like this in 2000 because of its but have thrived there because they were introduced by
biodiversity. Biodiversity hotspot humans. Invasive species
3. Philippine waters are a center of this type of biodiversity. 10. This is what Republic Act 9147 is known as.
Marine Conservation and Protection of Wildlife
4. These are organisms with numbers in the environment Resources and Their Habitats Act
that are lower than usual. Endangered species
5. This refers to the disappearance of a species on Earth. Instructions: Identify what can possibly cause extinction in these
Extinction situations:
6. This refers to the number of a species in a given place. 1. A snake being introduced into an area. Invasive species
Richness 2. Humans are cutting down trees at a very fast rate.
7. This is the number of members of a species in a given Habitat destruction
place. Abundance 3. Deforestation. Habitat destruction
8. This is the number of individuals per species relative to 4. A factory is built beside a river. Pollution
the area of a certain place. Density 5. More lions migrate into an area. Predation or
9. This refers to a pattern of distribution that is clumped. competition
Aggregation 6. Two organisms are competing for water. Competition
10. Give an example of an endemic Philippine species. 7. A species of insect is brought by humans into a forest.
Philippine eagle, tamaraw, many species of orchids, Invasive species
etc 8. A species of fish escaped an aquarium and reproduced in
a river. Invasive species
Identify the cause of possible extinction in the following scenarios. 9. A new parasite became prevalent. Disease
1. Deforestation due to logging and mining activities 10. A virus spread into an area. Disease
greatly affects the biodiversity of flora and fauna. -
habitat degradation Instruction: Answer the following questions.
1. Fire ants have affected native communities with burning 1. How does extinction impact the environment?
stings and live in the soil. - introduction of invasive The removal of a species, especially an important one,
species can lead to ecological imbalance.
2. Melted ice in the poles results in changes in sea levels 1. How can you help prevent the extinction of Philippine
and consequently affects incompatible habitats of species?
organisms resulting in extinction. - Reducing the amount of wastes we produce,
climate change or environmental phenomena informing people on the impact of humans,
4. Large numbers of mice feeding on albatrosses, petrels, conserving resources, and more.
and shearwaters. – predation 2. What are helpful ways of conservation to prevent
5. Chytrid, a toxic fungus decreased amphibian species for extinction?
many years and left some already close to extinction. - Information and education, the use of
diseases environmentally-friendly products, reducing wastes,
6. Several American crows died because of encephalitis. - and more.
diseases 3. Why should the environment be cared for to prevent
7. About 6 million North American bats died due to the extinction?
white-nose syndrome caused by a fungus. - diseases Maintaining good environmental conditions can also
8. Pollution poses several critical threats to birds, help organisms to survive, which can lower chances of
amphibians, and mammals. - habitat degradation extinction caused by humans.
9. Environmental pollutants due to human activities leading
to the extinction of some plant species in Mindoro. -
habitat degradation
10. Adverse geographical conditions resulted in the
extinction of the stegodon in the Philippines.
environmental phenomena
Instruction: Identify what is being described by each statement.
1. These are examples of environmental phenomena that
can cause extinction. Disasters
2. This refers to an animal eating another animal.
Predation
3. This refers to an organism trying to obtain resources at
the expense of another organism. Competition
You might also like
- 1st Summative Test Grade 9Document4 pages1st Summative Test Grade 9Jane Limsan Paglinawan87% (61)
- L95 NecropsyDocument7 pagesL95 NecropsyKING 5 News100% (1)
- 1st Periodical Test Grade 9Document5 pages1st Periodical Test Grade 9Nhoj Kram Alitnacnosalliv80% (51)
- Your Breath On Yoga: The Anatomy & Physiology of Breathing for Teachers and Students of YogaFrom EverandYour Breath On Yoga: The Anatomy & Physiology of Breathing for Teachers and Students of YogaNo ratings yet
- Lung Dissection Lab ReportDocument10 pagesLung Dissection Lab ReportSantiago MacíasNo ratings yet
- New MCQDocument129 pagesNew MCQAlhajiNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology CCEA Revision GuideDocument60 pagesGCSE Biology CCEA Revision GuideCaolán O'KaneNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Human Body Systems Lesson 3: The Circulatory and Respiratory SystemsDocument10 pagesUnit 1: Human Body Systems Lesson 3: The Circulatory and Respiratory SystemseisachannelestNo ratings yet
- Worksheets-Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument8 pagesWorksheets-Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsCarlos GuardadoNo ratings yet
- G9 NAT REVIEW March 5, 2024Document11 pagesG9 NAT REVIEW March 5, 2024Arrah Khay Casidsid SolimanNo ratings yet
- 5 Select Type Test ItemsDocument11 pages5 Select Type Test ItemsEdmike BucogNo ratings yet
- Circulatory and Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory and Respiratory SystemGaby GarciaNo ratings yet
- Science-Module 1 and 2 - AlcalaDocument7 pagesScience-Module 1 and 2 - AlcalaClaire AlcalaNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 9Document4 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 9JulieNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemsDocument85 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemsxoxkakidoxoxNo ratings yet
- 1st SUMMATIVE TEST - Science 9Document3 pages1st SUMMATIVE TEST - Science 9ericka mae tizonNo ratings yet
- 1st MT Test - Science 9Document3 pages1st MT Test - Science 9April AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- What I Know: Pre - TestDocument8 pagesWhat I Know: Pre - TestPamela Jane GarciaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 ExamDocument5 pagesScience 9 ExamGusthe Jebb AzarconNo ratings yet
- INSTRUCTIONS: Read The Following Questions Comprehensively. Be Wary of The Options, Choose Only The Best. ONLY THEDocument2 pagesINSTRUCTIONS: Read The Following Questions Comprehensively. Be Wary of The Options, Choose Only The Best. ONLY THEKristine Ibarreta-JazulNo ratings yet
- 1 PERIODICAL TEST (SY 2019-2020) Long Test Grade 9 Science Direction: Read Each Statement Carefully. Write The Letter of Your Answer On Your PaperDocument2 pages1 PERIODICAL TEST (SY 2019-2020) Long Test Grade 9 Science Direction: Read Each Statement Carefully. Write The Letter of Your Answer On Your PaperLA Gonzales86% (7)
- PT - Science 9 - Q1Document4 pagesPT - Science 9 - Q1gonedem793No ratings yet
- Summative Test Science 9Document2 pagesSummative Test Science 9JennilynAgoot90% (10)
- Exam CirculatoryDocument1 pageExam CirculatoryLuisa RamosNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 9Document4 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 9Jocelyn MarmolNo ratings yet
- Third Summative Test in Science - 2ND QuarterDocument3 pagesThird Summative Test in Science - 2ND QuarterSuiluj TorculasNo ratings yet
- PT - Science 9 - Q1Document4 pagesPT - Science 9 - Q1Reynaldo IskumburuNo ratings yet
- Biology Final G8 S2 2021 FT 2022 FixDocument9 pagesBiology Final G8 S2 2021 FT 2022 FixnoorlailyNo ratings yet
- Instruction: Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer.: Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesInstruction: Encircle The Letter of The Correct Answer.: Respiratory SystemEmman Revilla0% (1)
- Long Quiz 1Document1 pageLong Quiz 1Kristine Joy PanaguitonNo ratings yet
- PT - Science 9 - Q1Document4 pagesPT - Science 9 - Q1Gierome Ian BisanaNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 9Document4 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 9Argie Corbo BrigolaNo ratings yet
- First Quarter ST Item BankDocument4 pagesFirst Quarter ST Item BankBERITH GRACE MAGCALASNo ratings yet
- Transportaion in Plants and AnimalsDocument4 pagesTransportaion in Plants and AnimalsroopamsNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Test Grade 9Document4 pages1st Periodical Test Grade 9Adrian FromPHNo ratings yet
- First Quarterly Exam in Science 9Document4 pagesFirst Quarterly Exam in Science 9Alyssa F. DapadapNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Final ExamDocument4 pagesScience 9 Final ExamGusthe Jebb AzarconNo ratings yet
- Science 9 (W1)Document17 pagesScience 9 (W1)Gregorio RizaldyNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 9Document4 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 9Naylle Alivio100% (1)
- ST IN Grade 9 ScienceDocument4 pagesST IN Grade 9 ScienceFatima Ybanez Mahilum-Limbaga0% (1)
- G9, ST1, RemedialDocument1 pageG9, ST1, RemedialACENo ratings yet
- Science 9 Quiz - Q1Document2 pagesScience 9 Quiz - Q1Paul Patrick GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Science Grade 9 First Quarter ReviewersDocument4 pagesScience Grade 9 First Quarter ReviewersHyacinth LadianaNo ratings yet
- Science 9Document3 pagesScience 9Hezl Valerie ArzadonNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 9Document7 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 9Princess Arjona BaluranNo ratings yet
- Notes (Transport System in Humans)Document10 pagesNotes (Transport System in Humans)Hazrin ShahNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Module 1 Quarter 1 The Human Circulatory and Respiratory SystemDocument23 pagesScience 9 Module 1 Quarter 1 The Human Circulatory and Respiratory SystemMaricel PenaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Science 9..Document4 pagesReviewer in Science 9..nanami's ChildNo ratings yet
- Post Test M1 G9Document2 pagesPost Test M1 G9Jannah EsmeroNo ratings yet
- M1 Science 9Document3 pagesM1 Science 9guadalupeNo ratings yet
- Respiratory ReviewerDocument8 pagesRespiratory ReviewerBLAIRY ZYNo ratings yet
- PT - Science 9 - Q1Document4 pagesPT - Science 9 - Q1Niña Rica TecsonNo ratings yet
- Respi Quiz 1Document2 pagesRespi Quiz 1Lyka Rose SaycoNo ratings yet
- First Quarter Test in Grade 9 Science: Caraga Administrative RegionDocument3 pagesFirst Quarter Test in Grade 9 Science: Caraga Administrative RegionCary Clark OriasNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodic Test - Science 9Document3 pages1st Periodic Test - Science 9Irish Jhaizel Kaye FuentesNo ratings yet
- QUIZDocument2 pagesQUIZChristine BelaleNo ratings yet
- Human Body and Organ SystemDocument7 pagesHuman Body and Organ SystemAaryan KakadNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and PlantsDocument12 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 7 Science Solutions Chapter 11 Transportation in Animals and PlantsPriyanka NegiNo ratings yet
- Respiratory and Excretory System ReviewDocument27 pagesRespiratory and Excretory System ReviewJoyce Catherine Buquing UysecoNo ratings yet
- Direction: Read Each Statement Carefully. Write The Letter of Your Answer On Your PaperDocument3 pagesDirection: Read Each Statement Carefully. Write The Letter of Your Answer On Your PaperFerna Joy LapinigNo ratings yet
- Q1 Module 1Document120 pagesQ1 Module 1Jan IceNo ratings yet
- Science Test: Chapter I Respiratory and Circulatory System Term I, Semester IDocument4 pagesScience Test: Chapter I Respiratory and Circulatory System Term I, Semester IimandaNo ratings yet
- Cardio Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesCardio Lesson PlanAmiel Francisco Reyes100% (1)
- (Lung Biology in Health and Disease, V. 137) Richard D Bland - Jacqueline J Coalson-Chronic Lung Disease in Early Infancy-Marcel Dekker (2000)Document1,080 pages(Lung Biology in Health and Disease, V. 137) Richard D Bland - Jacqueline J Coalson-Chronic Lung Disease in Early Infancy-Marcel Dekker (2000)Uri MoraNo ratings yet
- Be HealthyDocument262 pagesBe HealthyKaushal PandeyNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFsam KSSM 2019 DP DLP BIOLOGY FORM 4 PART 2-8Document1 page1 PDFsam KSSM 2019 DP DLP BIOLOGY FORM 4 PART 2-8deathangel88 GtNo ratings yet
- 病理國考複習 PDFDocument61 pages病理國考複習 PDFAnonymous ZUQcbcNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of BreathingDocument5 pagesMechanics of BreathingMark Lyndon M OrogoNo ratings yet
- Laporan KatakDocument17 pagesLaporan Katakbertha tandiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Nursing Part 1Document8 pagesFundamentals of Nursing Part 1Evergreen Verds100% (1)
- Materi Kelainan ParuDocument72 pagesMateri Kelainan ParuDebiNingtyasDwiKusumaWardaniNo ratings yet
- DR - Wahid Helmi Ped Rev PDFDocument2,088 pagesDR - Wahid Helmi Ped Rev PDFNatalia NatNo ratings yet
- Nursing Pediatric Case StudyDocument9 pagesNursing Pediatric Case StudyKJay Solijon100% (1)
- Interstitial Lung Diseases (ILD)Document17 pagesInterstitial Lung Diseases (ILD)Rashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Science - 2010 02 12Document163 pagesScience - 2010 02 12Mi LaNo ratings yet
- FundamentalsDocument8 pagesFundamentalsFrancis Neil BacasnotNo ratings yet
- 9B Fit and HealthyDocument8 pages9B Fit and HealthyMaoga2013No ratings yet
- CopdDocument51 pagesCopdFretzie Anne Gonzales Gomez100% (2)
- Management of Patients With Burn Injury: Faculty: Rubina Shehzadi Nursing LecturerDocument42 pagesManagement of Patients With Burn Injury: Faculty: Rubina Shehzadi Nursing LecturerYou TuberNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Thorax: Sophie TatishviliDocument31 pagesLungs and Thorax: Sophie TatishviliAstha Tusharbhai PatelNo ratings yet
- Common Misconceptions in Primary School ScienceDocument16 pagesCommon Misconceptions in Primary School ScienceMos Rengie0% (1)
- 4 Respiratory ExaminationsDocument53 pages4 Respiratory Examinationscawsey mohamedNo ratings yet
- Artaud, Antonin - The Theater and Its DoubleDocument41 pagesArtaud, Antonin - The Theater and Its DoubleSeeWindNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation in Interstitial Lung Diseases: ReviewDocument7 pagesPulmonary Rehabilitation in Interstitial Lung Diseases: ReviewPrasasti 19No ratings yet
- Makalah Bhs Inggris Sistem RespirasiDocument13 pagesMakalah Bhs Inggris Sistem RespirasiDewa Ayu Made FebriariNo ratings yet
- Copd Copd: What Is COPD? Risk FactorsDocument1 pageCopd Copd: What Is COPD? Risk FactorsSirikit MaddelaNo ratings yet
- DLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W3Document4 pagesDLL - Science 4 - Q2 - W3KRISTINE JOAN BARREDONo ratings yet
- Death and Its CauseDocument22 pagesDeath and Its Causeअनूप ठाकुर100% (1)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet