Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cea 223 Mod 7
Cea 223 Mod 7
Uploaded by
Phoemela0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesOriginal Title
CEA 223 MOD 7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesCea 223 Mod 7
Cea 223 Mod 7
Uploaded by
PhoemelaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
CEA 223
ENGINEERING UTILITIES 1
MODULE 7:
BUILDING TELECOMMUNICATION
SYSTEMS
FUNDAMENTALS OF
TELECOMMUNICATION
Telecommunication
- it is the transmission, emission,
or reception of signs, signals,
writing, images, sounds, or
information of any nature by TRANSMISSION MEDIA
wire, radio, optical, or other
Electromagnetic systems. Cable
Telecommunication system - it is the most common medium
through which voice and data
- uses electricity, light (visible and usually move from one network
infrared), or radio waves to device to another.
transmit signals that carry voice
and data transmissions. Coaxial cable or coax
Telecommunications systems
- is a type of electrical cable
maybe analog or digital.
consisting of an inner conductor
TELECOMMUNICATION NETWORKS surrounded by a concentric
conducting shield, with the two
Telecommunications network separated by a dielectric
- it is a collection of (insulating material); many
communication equipment and coaxial cables also have a
devices that are interconnected protective outer sheath or jacket.
so they can communicate in Optical fibers
order to share data, hardware,
and software or perform an - are long, thin strands of very
electronic function. The network pure silicon glass or plastic
includes a series of connecting about the diameter of a human
points called nodes (e.g., a hair.
telecommunication terminal
Wireless
such as a telephone receiver or
computer) that are - ais a term used to describe
interconnected with cables telecommunications in which
(wiring). Networks can also electromagnetic waves (instead of
interconnect with other networks some form of wire) carry the
and contain Subnetworks. signal.
Network Topology
- it describes the configuration of
a network, including its nodes,
connecting cables and
equipment. It describes the
manner in which the cable is run
to individual workstations on the
network.
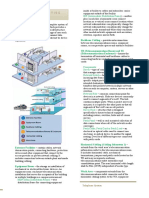
STRUCTURED BUILDING SUBSYSTEMS OF STRUCTURED
TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS CABLING SYSTEMS
Telecommunication cabling Interbuilding backbone
- it is the medium through which - it is the cabling and pathways
voice and data move from one outside of the building.
telecommunication device to Interbuilding backbone caries
another. telecommunication services to
the building.
Pathway
Building entrance facility
- it is a passageway, and thus a
path, for cable to travel when - it is an entrance to the building
interconnecting devices, for both public and private
components, and equipment in a network service cables. It
telecommunication system. includes the cables, connecting
hardware, protection devices,
Backbone
and other equipment needed to
- it is a generic term used to connect the interbuilding
describe a main pathway or backbone cabling to the
cabling media that interconnects backbone cabling in the building.
a number of telecommunication
Telecommunications equipment
devices.
room
Structured Cabling Systems
- it is a centralized space for
Structured cabling system housing main
telecommunications equipment.
- it is the cabling, devices, and
equipment that integrate the Telecommunications closet
voice, data, video, and electronic
- it is a dedicated room on each
management systems of a (e.g.,
floor in a building that houses
security safety access, building
intermediate voice and data
alarms, energy control on).
telecommunications equipment
systems, and Design
and related cable connections.
management and so and
installation of structured cabling Backbone pathway
to systems national adheres and
- it connects the entrance
international standards.
facilities/equipment room to the
telecommunications closets for
cabling that interconnects
equipment and devices in these
spaces.
Horizontal pathways
- it connect the backbone cabling
entering the telecommunications
closet with the terminal
equipment in the work area (e.g.,
computers, data terminals,
telephones, and so on).
Work area
- it is the space containing
workstation (terminal) equipment
and components.
-
ADVANCED HOME WIRING SYSTEMS
Advanced home wiring system allows
a homeowner to integrate the control
and management of the following
subsystems:
Communication subsystem (e.g.,
intercom, phone, message
recording, fax and e-mail)
Entertainment subsystem (e.g.,
whole-house stereo, VCR, cable,
digital and satellite television, and
home theater system)
Home office subsystem (e.g.,
computers, printers and scanners)
Environmental control/energy
management subsystem (e.g.,
control of HVAC equipment, water
heater, lighting and other
appliances)
Security/property protection
subsystem (e.g., video surveillance
with closed circuit TV, control
entry gates and garage doors,
control lawn irrigation
You might also like
- Networking DocumentationDocument26 pagesNetworking DocumentationAdwitiya Saigar100% (4)
- Telecommunication SystemDocument11 pagesTelecommunication SystemA I Y R ANo ratings yet
- Activity 11 PDFDocument5 pagesActivity 11 PDFgabrielaNo ratings yet
- Arinc 429: Table 1. Partial List of IdsDocument11 pagesArinc 429: Table 1. Partial List of IdsvinayNo ratings yet
- 7 Telecommunications SystemsDocument11 pages7 Telecommunications SystemsCamille SalmasanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities Module 5Document11 pagesEngineering Utilities Module 5Sofia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities Module 5Document11 pagesEngineering Utilities Module 5hgfhfghfghgNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities Module 5Document11 pagesEngineering Utilities Module 5Neerom BaldemoroNo ratings yet
- Engineering Utilities Module 5Document11 pagesEngineering Utilities Module 5Sofia GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2.5.0Document11 pagesLecture Notes 2.5.0krsdz1500No ratings yet
- Bu 4 - AuxillaryDocument5 pagesBu 4 - AuxillarySharmaine Danica MarceloNo ratings yet
- Eng Uti G7Document10 pagesEng Uti G7Narte, Angelo C.No ratings yet
- 06-Communications and Computer NetworkingDocument28 pages06-Communications and Computer NetworkingM. RazaNo ratings yet
- Term Paper of Computer Networking: (Design Wireless Network)Document8 pagesTerm Paper of Computer Networking: (Design Wireless Network)shahrukh_readNo ratings yet
- Common Telecommunications DevicesDocument5 pagesCommon Telecommunications DevicesHeidi Joy JameroNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication and NetworkDocument59 pagesTelecommunication and NetworkPriya deyNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Support Service: Learning Guide #3Document15 pagesInformation Technology Support Service: Learning Guide #3mohammed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computing ReviewerDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Computing ReviewerKyle AbiogNo ratings yet
- Building Telecommunication SystemsDocument22 pagesBuilding Telecommunication SystemsA.M BravoNo ratings yet
- Network and TelecommunicationsDocument16 pagesNetwork and TelecommunicationsShunmugapriyan MuruganNo ratings yet
- NetworkingDocument8 pagesNetworkingGinalyn Melig BandaoNo ratings yet
- Telephone and CommunicationDocument54 pagesTelephone and CommunicationSagar GoyalNo ratings yet
- Information Technology: Project Report On NetworkingDocument11 pagesInformation Technology: Project Report On NetworkingArjun VashishtaNo ratings yet
- InternetNotes PDFDocument11 pagesInternetNotes PDFSungram SinghNo ratings yet
- Intro To Netwoks - TCP - IP - OSI - ModelDocument43 pagesIntro To Netwoks - TCP - IP - OSI - ModelSaad AliNo ratings yet
- Communicaton N Networks NotesDocument10 pagesCommunicaton N Networks NotesPrincess SyakayuwaNo ratings yet
- Networking Fundamentals: Selected ConceptsDocument32 pagesNetworking Fundamentals: Selected ConceptsAlbert Azai BautistaNo ratings yet
- GENSODocument3 pagesGENSOhananbuday4No ratings yet
- Management Development Program On Network Administration SkillsDocument43 pagesManagement Development Program On Network Administration SkillsJelamDavdaNo ratings yet
- After MidtermDocument58 pagesAfter MidtermsucessfulwayNo ratings yet
- Networking FundamentalsDocument28 pagesNetworking FundamentalsRonaldo MaberitNo ratings yet
- Ee ReportDocument34 pagesEe ReportSensei EimeyZINGNo ratings yet
- Structured Cabling SystemDocument12 pagesStructured Cabling SystemA.M BravoNo ratings yet
- Section 2 - The Functions of The Basic Components of A NetworkDocument4 pagesSection 2 - The Functions of The Basic Components of A NetworkJade SpencerNo ratings yet
- PROYECTODocument11 pagesPROYECTOAzteca PicksNo ratings yet
- Types of Networks: Communication Media Scale Topology Organisational Scope Communication ProtocolDocument16 pagesTypes of Networks: Communication Media Scale Topology Organisational Scope Communication Protocolchinki176No ratings yet
- Pengantar Jaringan Komputer Dan Komunikasi DataDocument46 pagesPengantar Jaringan Komputer Dan Komunikasi DataRiåñŜahpŭträNo ratings yet
- Network - Introduction: (N.) A Network Is A Group of Two or More Computer Systems Linked TogetherDocument5 pagesNetwork - Introduction: (N.) A Network Is A Group of Two or More Computer Systems Linked TogetherlolyswarNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Reading1 - NetworksandTelecommunicationsDocument8 pagesModule 6 - Reading1 - NetworksandTelecommunicationsChristopher AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Ee Act 2Document12 pagesEe Act 2Isip, Dirk Lou V.No ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument16 pagesComputer NetworkMeenatchi VaradarasuNo ratings yet
- IT Reviewer 2Document5 pagesIT Reviewer 2Anne Thea AtienzaNo ratings yet
- NetworkDocument43 pagesNetworkpandi1985No ratings yet
- Scope of Networks: Local Area NetworkDocument19 pagesScope of Networks: Local Area NetworkAnuradha UdeshNo ratings yet
- Purpose: Arpa ArpanetDocument10 pagesPurpose: Arpa ArpanetSanchit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Network and Network TypesDocument61 pagesNetwork and Network TypesD.V. ClassesNo ratings yet
- Networks and TelecommunicationsDocument14 pagesNetworks and Telecommunicationsapi-3710170No ratings yet
- Engleski Jezik 1-PrezentacijaDocument20 pagesEngleski Jezik 1-PrezentacijaJosip KapularNo ratings yet
- Dr. John Sum: Institute of Electronic Commerce National Chung Hsing UniversityDocument66 pagesDr. John Sum: Institute of Electronic Commerce National Chung Hsing UniversityJeeNo ratings yet
- Connection Method: Arpa ArpanetDocument9 pagesConnection Method: Arpa ArpanetpraveenembassyNo ratings yet
- Dr. John Sum: Institute of Electronic Commerce National Chung Hsing UniversityDocument66 pagesDr. John Sum: Institute of Electronic Commerce National Chung Hsing UniversityVenugopal Athiur RamachandranNo ratings yet
- CSC 465 Lecture-1 Notes DASDocument18 pagesCSC 465 Lecture-1 Notes DAS21303166No ratings yet
- Section B: Nathaniel Jimena Ait - Networking - Year 12Document8 pagesSection B: Nathaniel Jimena Ait - Networking - Year 12api-517796348No ratings yet
- Networking Fundamentals: by Praphul KolteDocument31 pagesNetworking Fundamentals: by Praphul KolteayurvedicmNo ratings yet
- MIS UNIT 4 Telecommunications Network AlternativesDocument9 pagesMIS UNIT 4 Telecommunications Network AlternativesAhlette ReyesNo ratings yet
- Communication and Computer Network Data CommunicationDocument15 pagesCommunication and Computer Network Data CommunicationAhmed SalihNo ratings yet
- CN Chapter1Document22 pagesCN Chapter1nishitha.eeeNo ratings yet
- Communication SystemsDocument47 pagesCommunication Systemsismahan mukhtarNo ratings yet
- "Computer Networks" Redirects Here. For The Periodical, "Datacom" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See Datacom (Disambiguation)Document13 pages"Computer Networks" Redirects Here. For The Periodical, "Datacom" Redirects Here. For Other Uses, See Datacom (Disambiguation)sheikhkhalidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information and Communication TechnologyDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Information and Communication TechnologyAlthea Franchine BautistaNo ratings yet
- Networking: Submitted By:-Ankit Raj Srivastava Abhishek Sharma Ravi KiranDocument16 pagesNetworking: Submitted By:-Ankit Raj Srivastava Abhishek Sharma Ravi KiranAnkit Raj SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- HTML StylesDocument19 pagesHTML StylesKawaii GlamourNo ratings yet
- Object Detection and Identification A Project Report: November 2019Document45 pagesObject Detection and Identification A Project Report: November 2019Natasha SinaNo ratings yet
- Encschsyll PDFDocument129 pagesEncschsyll PDFDinesh AjayNo ratings yet
- Nptel Week1Document134 pagesNptel Week1Abrar AhamadNo ratings yet
- Computer Communication Lab - ManualDocument26 pagesComputer Communication Lab - ManualyashitaNo ratings yet
- Selection of Variables For Credit Risk Data Mining Models: Preliminary ResearchDocument28 pagesSelection of Variables For Credit Risk Data Mining Models: Preliminary ResearchMirjana Pejic BachNo ratings yet
- Esas Objectives 2022-23Document13 pagesEsas Objectives 2022-23Jevan SoberanoNo ratings yet
- Ai Scripts Release Notes 7.0R3.1Document22 pagesAi Scripts Release Notes 7.0R3.1WaqasMirzaNo ratings yet
- 05258870Document12 pages05258870shirtquittersNo ratings yet
- LtsDocument3 pagesLtslolaNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning LabDocument23 pagesMachine Learning Labops sksNo ratings yet
- Guide Book - Group 3Document11 pagesGuide Book - Group 3api-542021754No ratings yet
- Arduino and RFID From SeeedstudioDocument12 pagesArduino and RFID From SeeedstudioMarius DanilaNo ratings yet
- Math BlockDocument3 pagesMath BlocklynnasyNo ratings yet
- Verilog Receiver (Uart - RX.V)Document3 pagesVerilog Receiver (Uart - RX.V)Lucian ELNo ratings yet
- LogRhythm7 OverviewDocument23 pagesLogRhythm7 OverviewNguyen Tuan NgocNo ratings yet
- Ppl-Unit-3 R16Document24 pagesPpl-Unit-3 R16Viswanadh JvsNo ratings yet
- RobotDocument5 pagesRobotAbdessamad GabbadiNo ratings yet
- Information Technology and Business Process ManagementDocument3 pagesInformation Technology and Business Process ManagementNirupama RoyNo ratings yet
- SloanDocument30 pagesSloanKritika AhujaNo ratings yet
- Interview QuestionsDocument12 pagesInterview Questionsswapnadip kumbharNo ratings yet
- Practical Genetic AlgorithmsDocument13 pagesPractical Genetic AlgorithmsMourad KattassNo ratings yet
- ISO 6743-1 - 2002 - Part. 1 - Family A - Total Loss SystemsDocument9 pagesISO 6743-1 - 2002 - Part. 1 - Family A - Total Loss SystemsMassimiliano VolaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Tyre Inflation SystemDocument53 pagesAutomatic Tyre Inflation SystemMayur Salunke100% (1)
- Final Apgo Uwise Student HDocument9 pagesFinal Apgo Uwise Student HAishwarya JeeNo ratings yet
- Rience 1-3Document22 pagesRience 1-3ishaqhannan.2020No ratings yet
- NAV2013 01 Reporting PDFDocument82 pagesNAV2013 01 Reporting PDFMiguel De Dios SinovasNo ratings yet