Professional Documents
Culture Documents
GASES PPT Notes
Uploaded by
Ryv0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageOriginal Title
GASES Ppt Notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageGASES PPT Notes
Uploaded by
RyvCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
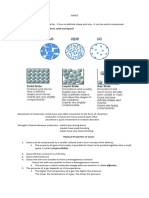
GASES
- A substance (such as oxygen or hydrogen) that is like air and it has no fixed shape.
- Gases have mass, volume, temperature and pressure because gas is a matter its just that the particles of gases are
far from each other compared to those particles in solids and liquids.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN MASS & VOLUME
Mass - is the amount of matter an object contains.
Volume - is how much space it takes.
What happens to the volume reading of the water-oil mixture when an air is introduced to it?
- The particles in a gas move quickly in all directions, but they don't get far before they bump into each other or the
walls of their container. When gas particles hit the walls of their container they cause pressure.
COMMONLY USED UNITS FOR VOLUME AND PRESSURE
Variable SI Unit Metric Unit English Unit
Volume Cubic meter Liter (L) Quart (qt)
(m3) Milliter (mL) Gallon (gal)
Cubic decimeter
(dm3)
Cubic centimeter
(cm3)
Pressure Pascal (Pa) Atmosphere Torr
(atm) Lb/in2 (psi)
Milliters of
mercury
(mm Hg)
Centimeters of
mercury (cm Hg)
PRESSURE UNITS AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS:
1atm = 760mmHg =76cmHg = 760
torr = 101,325 Pa =14.6956 psi
TEMPERATURE UNITS AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS:
0°C = 273.15 K
0°C = 32 °F
VOLUME UNITS AND THEIR EQUIVALENTS:
1 ml = 1cm³
1 L = 1dm³
1m³ = 1000 L
You might also like
- G12 - Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument21 pagesG12 - Kinetic Molecular TheoryThea NavarezNo ratings yet
- Science Properties of Gas Notes Grade 10Document2 pagesScience Properties of Gas Notes Grade 10stephanie adorioNo ratings yet
- GASES#2Document3 pagesGASES#2jacobambuan0805No ratings yet
- ch1.1 FMDocument11 pagesch1.1 FMمؤيد العتيبيNo ratings yet
- 6.6 The Gas Laws: Chapter 6 The States of MatterDocument11 pages6.6 The Gas Laws: Chapter 6 The States of MatterBenson Anselmo0% (1)
- GASESDocument9 pagesGASEStxm4kb4h46No ratings yet
- GASESDocument9 pagesGASEStxm4kb4h46No ratings yet
- Ass #1 ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesAss #1 ThermodynamicsJosh BarriosNo ratings yet
- HW #1 Thermodynamics 1Document7 pagesHW #1 Thermodynamics 1Josh BarriosNo ratings yet
- Ass #1.0 ThermodynamicsDocument7 pagesAss #1.0 ThermodynamicsJosh BarriosNo ratings yet
- Fluid Statics Lecture NotesDocument8 pagesFluid Statics Lecture NotesChailynn CanilaoNo ratings yet
- Measurements and UnitsDocument18 pagesMeasurements and UnitsSrynnENo ratings yet
- Pressure: This Article Is About Pressure in The Physical Sciences. For Other Uses, SeeDocument7 pagesPressure: This Article Is About Pressure in The Physical Sciences. For Other Uses, SeekopokopoNo ratings yet
- Converting Occupational Exposure Limits From MGDocument6 pagesConverting Occupational Exposure Limits From MGmajedzNo ratings yet
- Gaseous State (Package)Document55 pagesGaseous State (Package)Draw with Hassan JamalNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Gases: Gas Is One of The Three Forms of Matter. Every Known Substance Is Either A Solid, Liquid or ADocument4 pagesBehavior of Gases: Gas Is One of The Three Forms of Matter. Every Known Substance Is Either A Solid, Liquid or AEmily Magdua-ManoguidNo ratings yet
- BorderDocument9 pagesBorderの雪No ratings yet
- Act#1 AvsDocument3 pagesAct#1 AvsAndy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals OF Fluid MechanicsDocument7 pagesFundamentals OF Fluid MechanicsMike Adrian CerbitoNo ratings yet
- Conversion FactorsDocument4 pagesConversion FactorssekharbhattaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Fluid12Document6 pagesFundamentals of Fluid12Mike Adrian CerbitoNo ratings yet
- Weather & Meteorology Lecture 2 BulletsDocument6 pagesWeather & Meteorology Lecture 2 BulletsHibbaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics: Chapter-1Document6 pagesFluid Mechanics: Chapter-1Ahmed SuhailNo ratings yet
- 3.module 2. Measuremsnts in Analytical ChemistryDocument19 pages3.module 2. Measuremsnts in Analytical ChemistryKim MalangNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know GasesDocument11 pagesGetting To Know GasesShiela Mae LailaNo ratings yet
- LessonsDocument58 pagesLessonsMarvin CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of FluidDocument5 pagesFundamentals of FluidMike Adrian CerbitoNo ratings yet
- Pressure: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesPressure: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadarla999No ratings yet
- Module 1Document3 pagesModule 1ernan nonoNo ratings yet
- Modelling FundamentalsDocument33 pagesModelling FundamentalsAndreaNo ratings yet
- 02 Unit System and Characteristic of FluidDocument13 pages02 Unit System and Characteristic of FluidMuhammad Fakhri KusnanNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document12 pagesLecture 2Samaseen PrabhatNo ratings yet
- KhalidDocument3 pagesKhalidSyed Adnan AqibNo ratings yet
- FL101Document64 pagesFL101nhalieza10670% (1)
- Conversion Tables of Measuring UnitsDocument14 pagesConversion Tables of Measuring UnitsVic ValdezNo ratings yet
- UnitsMSE170 RaoDocument1 pageUnitsMSE170 RaoJhon Harold Mercado JuanNo ratings yet
- Conversion FactorsDocument2 pagesConversion FactorsKathleen May BarrilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Eng CalDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Eng CalShalfiq Mat ZariNo ratings yet
- 1 Fundamentals, StaticsDocument14 pages1 Fundamentals, StaticsTom ManNo ratings yet
- Air Test ReviewDocument3 pagesAir Test Reviewgarrettsgirlx28No ratings yet
- BSC 1st Year Notes ChemistryDocument33 pagesBSC 1st Year Notes ChemistrySandipan SahaNo ratings yet
- G10 LAP 4.1 Properties of GasesDocument5 pagesG10 LAP 4.1 Properties of GasesAzria SolanaNo ratings yet
- ECU Calibration Diesel Engine Units Conversion TableDocument4 pagesECU Calibration Diesel Engine Units Conversion TableM AliNo ratings yet
- Pressure Units ConversionsDocument3 pagesPressure Units ConversionsK S RaoNo ratings yet
- Boyle's Law Practice WorksheetDocument1 pageBoyle's Law Practice WorksheetUnexpected TheoryNo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas PDFDocument25 pagesHvac Formulas PDFManish SinghNo ratings yet
- Hvac Formulas - Ii - PDFDocument25 pagesHvac Formulas - Ii - PDFmrcNo ratings yet
- Hvac FormulasDocument25 pagesHvac FormulasMuhammadYounusNo ratings yet
- Unit ConversionsDocument2 pagesUnit Conversionsangry_granNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 IntroDocument59 pagesChapter 7 IntroاشرفاللساميNo ratings yet
- SH 5107 Principles of Airflow 2021 Version 1Document126 pagesSH 5107 Principles of Airflow 2021 Version 1Shuyuan LuNo ratings yet
- M H2 ODocument5 pagesM H2 OMOHD JIDINo ratings yet
- Temperature - Humidity ChartDocument8 pagesTemperature - Humidity ChartAmandaEdwinNo ratings yet
- Unit Conversion FactorsDocument3 pagesUnit Conversion FactorsCHANADASNo ratings yet
- JJ309 Chapter 1Document49 pagesJJ309 Chapter 1Amar ZalleeNo ratings yet
- Units and Materials and Energy BalancesDocument8 pagesUnits and Materials and Energy BalancesECRDNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lecture 5Document19 pagesFluid Mechanics Lecture 5Muhammad ShahayarNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q4 Module 1Document4 pagesScience10 Q4 Module 1bongatomarieveroniqueNo ratings yet
- Sizing: Definitions and Units of Measurement 2.1Document10 pagesSizing: Definitions and Units of Measurement 2.1Anonymous YWS7ndsiNo ratings yet