Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quadratic Equation
Uploaded by
rijaho3110Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quadratic Equation
Uploaded by
rijaho3110Copyright:
Available Formats
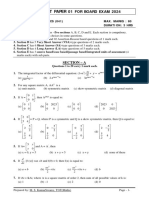
DPT Quadratic Equations - 1
1. Discriminant of equation x 2 1 x 0 14. If equation 2Px 2 8 x P 0 has equal roots then value
(a) – 3 (b) 3 (c) 3 (d) 0 of P is :
(a) P 2 2 (b) P = 4
2. Solution of equation x 2 9 0
(c) P 2 2 (d) P 2 2
(a) 3 (b) 9 (c) 3 (d) none
3. If Px2 4x 1 0 has real roots then value of P is : 15. If 1 2 and 1 2 are the roots then equation is :
(a) 16 4P (b) P 4 (a) x 2 2 x 1 0 (b) x 2 2 x 1 0
(c) P > 4 (d) P 4 (c) x 2 x 1 0 (d) x 2 x 2 0
4. If x 2 Px 0 has equal roots then value of P is :
16. If one root of the equation ax 2 10 x 5 0 is three
(a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 0 times the other than, value of a is :
5. The sum of number and its reciprocal is 5/2 then the (a) 15/4 (b) 4/15 (c) 2/5 (d) none
number is :
(a) 1/2 (b) 1 (c) 1 and 1/2 (d) 2 and 1/2 17. If and are the roots of equation x 2 3ax 2a 2 0
and 2 2 5 then value of a is :
6. If p and q are the roots of the equation 3 x 2 7 x 3 0
then p.q is : (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 1 (d) 1 / 2
(a) 9 (b) – 7/3 (c) – 1 (d) none
18. Equation x 2 px q 0 has equal roots and value of p
7. Equation whose roots are 1 and 2 is :
is one then value of q is :
(a) x 2 2 x 3 0 (b) x 2 3 x 2 0 (a) 1 (b) 1/2 (c) 1/3 (d) 1/4
(c) x 2 3 x 2 0 (d) x 2 3 x 2 0 19. Solution of equation 3 x 1 31 x 2 is :
(a) 3/2 (b) – 1 (c) 0 (d) 1
8. If one root of the equation x 2 2 x 1 0 is 1, then other
root is : 20. (a 1) x 2 2 x 3 0 has equal roots then value of a is:
(a) – 1 (b) 2 (c) 1 (d) 1/2
(a) 1/2 (b) 2/3 (c) 3/4 (d) 1
9. Equation x 5Kx 16 0 has no real roots then value
2
21. If x is real then minimum value of x 2 6 x 10 is :
of K is :
(a) 3/2 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 1
64 8 8
(a) K (b) K 22. If the roots of a equation are 1/2 and 2/5 then equation
2
25 5 5 is :
64 (a) 10 x 2 9 x 2 0 (b) 10 x 2 9 x 2 0
(c) K
2
(d) Both (a) and (b)
25
(c) 5 x 2 7 x 1 0 (d) 5 x 2 7 x 1 0
10. Roots of equation x 2 2 3 x 1 0 are :
(a) real and equal (b) real and unequal 23. If x y 12 , y z 16 and z x 14 then value of x,
(c) no real roots (d) none y and z is :
(a) x = 5, y = 9, z = 7 (b) x = 9, y = 7, z = 5
Solution of quadratic equation a( x 1) x(a 1) is :
2 2
11. (c) x = 5, y = 7, z = 9 (d) none
(a) – a (b) a (c) – 1/a (d) a2 24. If 10 and 6 then the equation whose
roots are and is :
12. If and are the roots of the equation x 2 2 x 1 0
(a) x 2 8 x 2 0 (b) x 2 10 x 16 0
then
2 2
(a) 3 (b) – 3 (c) 2 (d) – 1 (c) x 2 8 x 2 0 (d) x 2 10 x 16 0
13. If 3 3 and 3 3 are the roots then equation is : 25. The roots of equation x 2 4 x 6 0 is :
(a) x 2 6 x 9 0 (b) x 2 9 x 6 0 (a) 4 40 (b) 2 10
(c) x 2 3 x 9 0 (d) none (c) 2 20 (d) 2 20
H.O. : 276, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319 Quadratic Equations | 1
DTP quadratic equation - 01
1. (a) 2. (c) 3. (b) 4. (d) 5. (d) 6. (d) 7. (b) 8. (c) 9. (b) 10. (b)
11. (b) 12. (c) 13. (d) 14. (a) 15. (a) 16. (a) 17. (c) 18. (d) 19. (d) 20. (b)
21. (d) 22. (a) 23. (c) 24. (b) 25. (b)
2| Quadratic Equations H.O. : 276, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319
H.O. : 276, Zone-II, M.P. Nagar, Bhopal : 0755-4295319 Quadratic Equations | 3
You might also like
- PACE Final Lap (Algebra) Q & SDocument122 pagesPACE Final Lap (Algebra) Q & SAnwesh SahaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Eq. Assignment-3Document2 pagesQuadratic Eq. Assignment-3On ColdNo ratings yet
- DPP 2Document3 pagesDPP 2DHRUV WORLDNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024ravindramaithul124421No ratings yet
- Quadratic Eq. Assignment-2Document3 pagesQuadratic Eq. Assignment-2On ColdNo ratings yet
- Sartaj CL Asses: Test SeriesDocument8 pagesSartaj CL Asses: Test SeriesM. Shoeb SultanNo ratings yet
- Maths Class XII Mock Test Paper 01 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class XII Mock Test Paper 01 For Board Exam 2024adityakvgb2010No ratings yet
- Algebra - Most Important Question Bank For JEE MainDocument32 pagesAlgebra - Most Important Question Bank For JEE MainyyNo ratings yet
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument15 pagesIlovepdf MergedPrince DhananiNo ratings yet
- 8th AlgebraDocument3 pages8th AlgebrasushskyNo ratings yet
- TWPT Quadratic Equation-01 24.05.20220Document4 pagesTWPT Quadratic Equation-01 24.05.20220Manish Choudhary HarnawaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations & Inequations - MEQBDocument10 pagesQuadratic Equations & Inequations - MEQBSaksham Kumar GargNo ratings yet
- Memory Based Qusetions - MathsDocument2 pagesMemory Based Qusetions - Mathsboorsudithi0No ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 01 For Board Exam 2023K Pradeep kumarNo ratings yet
- 12th Maths Preboard-1 2021Document7 pages12th Maths Preboard-1 2021Little GardenNo ratings yet
- In PS: Nimcet - 2022Document17 pagesIn PS: Nimcet - 2022Avishek JhaNo ratings yet
- JEE IITmatrices and DeterminantsDocument5 pagesJEE IITmatrices and DeterminantsDipayan Das100% (1)
- 01 - Quadratic EquationsDocument11 pages01 - Quadratic Equationsjellohuman127No ratings yet
- Class 10 Mock Test 01Document5 pagesClass 10 Mock Test 01Heavy Metal GodNo ratings yet
- Math Practise Paper X For XBDocument7 pagesMath Practise Paper X For XBRAJ SHEKHARNo ratings yet
- Math Practise Paper X For XBDocument7 pagesMath Practise Paper X For XBRAJ SHEKHARNo ratings yet
- 2024 Maths Preparation Test-2 For QUADRATIC JEE Main-1 LIVE QUIZDocument7 pages2024 Maths Preparation Test-2 For QUADRATIC JEE Main-1 LIVE QUIZSamarth GulatiNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 10 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 10 For Board Exam 2024Roses Are RosieNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument5 pagesQuadratic EquationsGIRIDHARAN MURUGANNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024 AnswersDocument15 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024 Answersprayanshjoshi830No ratings yet
- Xii - Mock Test - 1Document6 pagesXii - Mock Test - 1Kartik ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 08 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 08 For Board Exam 2024Priyanshu YadavNo ratings yet
- N (N + 1) (N + 5) Is Not A Multiple of 3 Where N Is A Positive IntegerDocument2 pagesN (N + 1) (N + 5) Is Not A Multiple of 3 Where N Is A Positive IntegerMadhavan SowrirajanNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Assingment 1Document15 pagesQuadratic Assingment 1Anand Kumar JatavNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 04 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 04 For Board Exam 2024ravindramaithul1244210% (1)
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 06 For Board Exam 2023Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 06 For Board Exam 2023vivekdaiv55No ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations: Er. Vineet Loomba, B.Tech. IIT RoorkeeDocument2 pagesQuadratic Equations: Er. Vineet Loomba, B.Tech. IIT RoorkeeAnubhuti SinghNo ratings yet
- (B) LCM 18. (A) 180 Min 19. (D) 10: Case StudyDocument8 pages(B) LCM 18. (A) 180 Min 19. (D) 10: Case StudyTHANUSH JNo ratings yet
- SQP 3 2023-24Document6 pagesSQP 3 2023-24zainab.hana70511No ratings yet
- CET Mock Test 30th April 2009Document19 pagesCET Mock Test 30th April 2009api-3849133No ratings yet
- Answer All The Following Questions Which Are Single Option CorrectDocument7 pagesAnswer All The Following Questions Which Are Single Option CorrectiamrockyNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 3 (Class XII)Document7 pagesSample Paper 3 (Class XII)Archit JainNo ratings yet
- SQP 2 2023-24Document6 pagesSQP 2 2023-24zainab.hana70511No ratings yet
- Quadratic Home AssignmentDocument4 pagesQuadratic Home AssignmentSunilSutharNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation Clip-MainsDocument4 pagesQuadratic Equation Clip-MainsSipra PaulNo ratings yet
- XII-PTS-21 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTADocument8 pagesXII-PTS-21 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTAmaanya.ailawadi3No ratings yet
- Class 12 Maths Pre board-II 2023Document4 pagesClass 12 Maths Pre board-II 2023vvs.gandhi. SREENIVASAPERUMALNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationDocument4 pagesQuadratic EquationAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- Xii Sample Paper Test 07Document6 pagesXii Sample Paper Test 07Prasanna SaravananNo ratings yet
- MCQ Worksheet-I: Class X: Chapter - 2 PolynomialsDocument1 pageMCQ Worksheet-I: Class X: Chapter - 2 PolynomialsMehul MayankNo ratings yet
- Amj Mathematics 1Document16 pagesAmj Mathematics 1sonalimandal.1985No ratings yet
- 1 Quadratic Equations Objective Mathematics For Iit Jee Mains Advance - 4Document9 pages1 Quadratic Equations Objective Mathematics For Iit Jee Mains Advance - 4brcraoNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2023Document7 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2023Aditya JhaNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument72 pagesUntitledParth NikamNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 2Document9 pagesPractice Paper 2padmaNo ratings yet
- 024e500ce0750-NIT New Test Series NT - 02Document7 pages024e500ce0750-NIT New Test Series NT - 02Aman GoelNo ratings yet
- Polinomlar 6Document6 pagesPolinomlar 6emrecan yıldırımNo ratings yet
- M. C. A. Entrance Total Questions: 100 Part-I Mathematics 1.if Two Roots of The Equation 7Document10 pagesM. C. A. Entrance Total Questions: 100 Part-I Mathematics 1.if Two Roots of The Equation 7Zendash BannerNo ratings yet
- MCQ Test (Fundamentals)Document1 pageMCQ Test (Fundamentals)Sounak RahaNo ratings yet
- CBT - 2 Basic 09.08.2020 SundayDocument3 pagesCBT - 2 Basic 09.08.2020 SundayIbitda HuoNo ratings yet
- 12th Maths Preboard-1 2021Document7 pages12th Maths Preboard-1 2021dev sharmaNo ratings yet
- One Mark Questions (Updated)Document3 pagesOne Mark Questions (Updated)Dhaya VNo ratings yet
- Maths SQP 1Document7 pagesMaths SQP 1qutubkhan.nalwalaNo ratings yet
- Maths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class Xii Sample Paper Test 02 For Board Exam 2024Navya KhemkaNo ratings yet
- Class10 Math Pairoflinearequationsintwovariables Questionbank 59280Document39 pagesClass10 Math Pairoflinearequationsintwovariables Questionbank 59280Dhanjith VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Numbers. Divisibility Tests, HCF and LCMDocument74 pagesNumbers. Divisibility Tests, HCF and LCMAjay BhatNo ratings yet
- Teaching Program Year 7Document41 pagesTeaching Program Year 7Evan TranNo ratings yet
- 2019 Fourier SeriesDocument24 pages2019 Fourier SeriesAhmed RahatNo ratings yet
- Training Module v2Document59 pagesTraining Module v2Matheo MathewNo ratings yet
- Order Prime GraphDocument8 pagesOrder Prime GraphsattanathanNo ratings yet
- Lecture (4) Mathematical Modeling in Mechanical and Electrical SystemDocument6 pagesLecture (4) Mathematical Modeling in Mechanical and Electrical SystemAbdullah Mohammed AlsaadouniNo ratings yet
- 5.4 Exercise Set: Practice ExercisesDocument11 pages5.4 Exercise Set: Practice ExercisesBunga NoionlaNo ratings yet
- 4.5 Autoregressive Processes AR (P) : Definition 4.7. AnDocument2 pages4.5 Autoregressive Processes AR (P) : Definition 4.7. AnharryNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Aman MathurNo ratings yet
- The KEY - Numerical Solutions of The Modified Burger'sDocument9 pagesThe KEY - Numerical Solutions of The Modified Burger'spinguino309No ratings yet
- Notes Similar FiguresDocument5 pagesNotes Similar Figuresapi-267334776No ratings yet
- KorelDocument72 pagesKorelNoer HajatiNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series Solved Problems - PDFDocument32 pagesFourier Series Solved Problems - PDFparthfernandezNo ratings yet
- HSC Higher Mathematics 2nd Paper Note 7th Chapter Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Trigonometric EquationsDocument25 pagesHSC Higher Mathematics 2nd Paper Note 7th Chapter Inverse Trigonometric Functions and Trigonometric Equationsbappyskhossain2No ratings yet
- Differential Equation MathsDocument45 pagesDifferential Equation MathsPavan Boro100% (2)
- Quadratic ExpressionsDocument24 pagesQuadratic ExpressionsSuresh NNo ratings yet
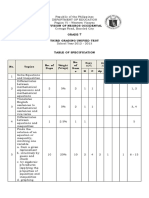
- Division of Negros Occidental: Weight (%tage) Easy Ave. DifficultDocument3 pagesDivision of Negros Occidental: Weight (%tage) Easy Ave. DifficultPeterNo ratings yet
- Differential CalculusDocument22 pagesDifferential CalculusjinkoloyNo ratings yet
- Integral Methods in Science and EngineeringDocument429 pagesIntegral Methods in Science and EngineeringRichard BaliliNo ratings yet
- Differential and Difference EquationsDocument31 pagesDifferential and Difference EquationscavanzasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Abstract Algebra (Math 113) : Alexander PaulinDocument83 pagesIntroduction To Abstract Algebra (Math 113) : Alexander Paulinsk9125770027No ratings yet
- FACTORISATIONDocument10 pagesFACTORISATIONPaula FanaNo ratings yet
- Cauchy EulerDocument2 pagesCauchy EulerKing OfheartsNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Computational Method For Mechanical Engineering M.E. 1 SemesterDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological University: Computational Method For Mechanical Engineering M.E. 1 SemesterMulu GirmayNo ratings yet
- PracticeDocument4 pagesPracticeEddy R. VélezNo ratings yet
- Algebraic Topology: M. S. Narasimhan S. Ramanan R. Sridharan K. VaradarajanDocument49 pagesAlgebraic Topology: M. S. Narasimhan S. Ramanan R. Sridharan K. VaradarajanSnehamoy DasNo ratings yet
- PMO Area Stage Answers OnlyDocument7 pagesPMO Area Stage Answers OnlyCedrixe MadridNo ratings yet
- Laplace Table PDFDocument2 pagesLaplace Table PDFPurukapoorNo ratings yet
- C1498117505umathematics 10th SolutionDocument148 pagesC1498117505umathematics 10th SolutionVimal sabariNo ratings yet