Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A7 Equilibrium
Uploaded by
jai.vasudev92Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A7 Equilibrium
Uploaded by
jai.vasudev92Copyright:
Available Formats
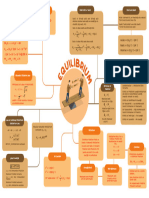
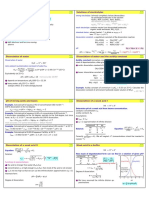
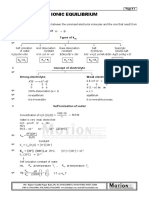
Solubility Product Hydrolysis of salts Acids and Base
+ (KSP)
Salts of strong base and strong acid Acids: Liberates H2 on reacting with metals
cC + dD
aA neutral solution and does not undergo hy- Turns blue litumus into red
drolysis. eg. naCl, KCl Base: Taste bitter and feel soapy
K sp = [C] c [D] d Salt of weak base and Strong Acid
Turns red litmus into blue
Ionic product Kw H 1
of water Kh = ; p = [pK 2 − pK b − log c]
Kb 2
Salt of weak Acid and weak base Acidic ⇒ [H 3 O + ] > [OH− ]
+ −
H 3 O + OH
2H 2 O
Kw 1 Basic ⇒ [H 3 O + ] < [OH− ]
Kh = ; p H = [pK w − pK a − pK b ]
K w = [H 3 O + ][OH− ] = 1 × 10−14 M 2 Ka × Kb 2 Neutral ⇒ [H 3 O + ] = [OH− ]
∴ [OH− ] = [H+ ] = 10−7 M @ 298 K
B
pK w = pK a + pK b = 14
UILI RI
Q
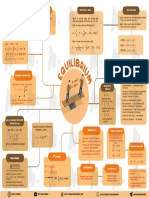
Factor's of reaction
UM
Ostwald's Dilution Law
Le Chatlier's Principle
E
Effect of concentration change
Applicable for weak K electrlytes concentration →, equilibrium shift
Direction of
K forward.
∴ K c = Cα 2 or α = c reaction
C Effect of pressure change equilibrium
So, α =
1
orα ∝ v Qc < Kc will shift in the direction having
smaller number of moles.
c Reaction goes
Where V is the volume of solution Effect of temperature change
from left to right
at infinite dilution For exothermic → low temperature
Qc < Kc favors formation of reactants.
Reaction goes from For Endothermic → High temperature
right to left favors formation of products.
Qc = Kc Effect of inert gas → No change
Law of chemical Equilibrium No net reaction Effect of catalyst → No change
occurs
Equilibrium Law
Relation between equilibrium
aA + bB
cC + dD constant ckp + kc Definition
[C] C [D] d
Kc = a 6
K p = K c (RT)∆ng Equilibrium set up in a
physical process like
[A] [B] Chemical reaction reach a
evaporation of water
state of dynamic equilibrium etc.
Here Kc is equilibrium constant
in which the rate of forward
(s)
(l) Chemical
reaction and reaction are
(l)
(g)
same and there is no net
(g)
(s) Equilibrium attained in
PH Concept charge in composition
a chemical reaction
Gibb's energy
3H 2 + N 2
2NH 3
∆G = RT ln K p H = − log[H+ ] Homogeneous Hetrogeneous
∆G = -ve, spontaneous reaction H + Possible only in a closed
p = − log[H 3 O ]
Reaction proceeds forward. system.
∆G = +ve, Non spontaneous 1 Reactant and product Reactant and
for weak acid → p H = (C K − log c) are in same phase product are in Both reaction occur at
reation 2 p a different phase same rate
Reaction proceeds backward
All measurable property
∆G = zero, equilibrium achieved remains constant
anand_mani16 DR. Anand Mani https://www.anandmani.com/ https://discord.io/anandmani t.me/neetplus
You might also like
- XXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973From EverandXXIVth International Congress of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Plenary and Main Section Lectures Presented at Hamburg, Federal Republic of Germany, 2–8 September 1973No ratings yet
- EquilibriumDocument1 pageEquilibriumsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- 7 EquilibriumDocument1 page7 EquilibriumMalola EducationNo ratings yet
- 7 EquilibriumDocument1 page7 EquilibriumPARAMBATH ANUP KUMARNo ratings yet
- HO / "' OH OH: Li SoDocument4 pagesHO / "' OH OH: Li So葉建豪No ratings yet
- 4-Acid-Base 1Document32 pages4-Acid-Base 1José de Jesús Treviño ReséndezNo ratings yet
- 6.ionic Equilibrium TheoryDocument4 pages6.ionic Equilibrium TheoryUMAIR ASHFAQNo ratings yet
- Hóa Phân Tích - Chap 2. Acid-Base EquilibriumtitrationDocument88 pagesHóa Phân Tích - Chap 2. Acid-Base Equilibriumtitrationnguyenthibaongoc20051No ratings yet
- Chap 2. Acid-Base Equilibrium&titrationDocument86 pagesChap 2. Acid-Base Equilibrium&titrationNgọc Việt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Apuntes Final Ácido Base Isomería ConformacionalDocument57 pagesApuntes Final Ácido Base Isomería ConformacionalNOVERON FLORES CARLOS ERASMONo ratings yet
- HW14 ElectrolysisDocument2 pagesHW14 Electrolysiss321012No ratings yet
- Conductometry Method: By: Rohayati, S.PD Translated By: Nurul Kusumawati., S.PD SMK Negeri 13 BandungDocument8 pagesConductometry Method: By: Rohayati, S.PD Translated By: Nurul Kusumawati., S.PD SMK Negeri 13 BandungAgung GunandarNo ratings yet
- Hint & Solution Chemistry: NH NH CLDocument10 pagesHint & Solution Chemistry: NH NH CLMadhu KumariNo ratings yet
- Notes 3 (Kinetic Examples) 12Document12 pagesNotes 3 (Kinetic Examples) 12Sharon FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: ELECTROLYTE: 10.1. Equilibrium Properties of ElectrolyteDocument64 pagesChapter 10: ELECTROLYTE: 10.1. Equilibrium Properties of ElectrolyteNguyễn Hoàng DũngNo ratings yet
- SynthesisDocument35 pagesSynthesisThy AnhNo ratings yet
- Arab International University Faculty of DentistryDocument18 pagesArab International University Faculty of DentistryMahmoud SulimanNo ratings yet
- 11 Equilibrium Study NotesDocument19 pages11 Equilibrium Study NotesVivek KumarNo ratings yet
- Fkche04 8Document4 pagesFkche04 8design designerista123No ratings yet
- Enol Dan EnolatDocument40 pagesEnol Dan EnolatRiyan KateeNo ratings yet
- CHEM-UA 652: Thermodynamics and Kinetics: Notes For Lecture 23Document5 pagesCHEM-UA 652: Thermodynamics and Kinetics: Notes For Lecture 23Nur Faiizah AfNo ratings yet
- Chem 30 Course Summary 4Document10 pagesChem 30 Course Summary 4dutritinh0806No ratings yet
- Chapter 21 NotesDocument43 pagesChapter 21 NotesTiffany YehNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equilibrium PDFDocument54 pagesIonic Equilibrium PDFBhushan50% (2)
- Ionic Equilibrium: Types of KDocument12 pagesIonic Equilibrium: Types of KBhushanNo ratings yet
- 6-Acid-Base 3Document22 pages6-Acid-Base 3José de Jesús Treviño ReséndezNo ratings yet
- Acid Base EwDocument130 pagesAcid Base EwJustine FalcasantosNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and Balancing Chemical EquationDocument36 pagesChemical Reaction and Balancing Chemical EquationChelsia Venice MorilloNo ratings yet
- Chap 5. Redox TitrationDocument46 pagesChap 5. Redox TitrationKoasa NishikiNo ratings yet
- Department of Chemistry: Smt. Chandibai Himathmal Mansukhani College UlhasnagarDocument28 pagesDepartment of Chemistry: Smt. Chandibai Himathmal Mansukhani College UlhasnagarPrashant ThoratNo ratings yet
- Formula Sheet - Ony PDFDocument5 pagesFormula Sheet - Ony PDFSana ImamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 SlidesDocument63 pagesChapter 8 SlidespoojaNo ratings yet
- Reaction and Syntesis of Alkynes: Pertemuan 13Document37 pagesReaction and Syntesis of Alkynes: Pertemuan 13Amelia ulfaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Acids Base EquilibriaDocument105 pagesChapter 5 Acids Base Equilibriantranh58No ratings yet
- Topic 8 - Acids and Bases 5Document1 pageTopic 8 - Acids and Bases 5Vashti ChowlaNo ratings yet
- Reactions Study List Through Chem 315 For Use As A Study Guide BeauchampDocument46 pagesReactions Study List Through Chem 315 For Use As A Study Guide BeauchampĐức LêNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols Carboxylic AcidsDocument5 pagesAlcohols Phenols Carboxylic AcidsAnanya AryaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Kimia Dasar Pertemuan 7 (Kesetimbangan Asam-Basa)Document95 pages2021 Kimia Dasar Pertemuan 7 (Kesetimbangan Asam-Basa)Muhammad AminNo ratings yet
- Ácidos Polipróticos (Espécies Intermediárias)Document7 pagesÁcidos Polipróticos (Espécies Intermediárias)Monique Lopes da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document6 pagesLecture 1Shailendra SinghNo ratings yet
- 05 Worksheet 3 (Gen Chem) RelevoDocument2 pages05 Worksheet 3 (Gen Chem) Relevocessarine relevoNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon: Reagent - Function: NotesDocument46 pagesHydrocarbon: Reagent - Function: NotesSowmya AnandNo ratings yet
- H2 Revision Notes For Promo 2022 (Lecture Notes Answers)Document28 pagesH2 Revision Notes For Promo 2022 (Lecture Notes Answers)22S35 TIOH JING KAINo ratings yet
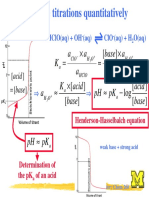
- Acid-Base Titrations Quantitatively: Acid A Base A A A K Acid K A Base Acid PK PHDocument5 pagesAcid-Base Titrations Quantitatively: Acid A Base A A A K Acid K A Base Acid PK PHRa saNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Titrations Quantitatively: Acid A Base A A A K Acid K A Base Acid PK PHDocument5 pagesAcid-Base Titrations Quantitatively: Acid A Base A A A K Acid K A Base Acid PK PHJohnS.GallianoNo ratings yet
- Geochemistry in Geothermal 1Document64 pagesGeochemistry in Geothermal 1Nurlia AduNo ratings yet
- Chemical EquilibriumDocument31 pagesChemical EquilibriumAshok MohantaNo ratings yet
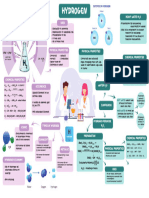
- Hydrogen - Mind MapDocument1 pageHydrogen - Mind Mapsarthakyedlawar04No ratings yet
- (Benjamin, Chapt. 3 pg.131-150) : Acids & BasesDocument12 pages(Benjamin, Chapt. 3 pg.131-150) : Acids & BaseswastequestNo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance Effect of Fluid and Nutrition: "A Stewart Approach"Document81 pagesAcid-Base Balance Effect of Fluid and Nutrition: "A Stewart Approach"albert hutagalungNo ratings yet
- Summary: Ionic EquilibriaDocument33 pagesSummary: Ionic Equilibriawewwchemistry100% (1)
- MTG Organic Reactions IMP PDF PDF Ether AlcDocument1 pageMTG Organic Reactions IMP PDF PDF Ether AlcGagan MadhokNo ratings yet
- Ka, Pka, and Buffers: Unit 14C: SkillsDocument8 pagesKa, Pka, and Buffers: Unit 14C: SkillsArisa PatthawaroNo ratings yet
- .J - S Ir: Iit-Jee Chemistry by N.J. SirDocument26 pages.J - S Ir: Iit-Jee Chemistry by N.J. SirGarvit VirmaniNo ratings yet
- 10 - Reaction With HalogenDocument8 pages10 - Reaction With HalogenMaitreya DasNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument11 pagesAcid BaseEdry SipNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument4 pagesIonic EquilibriumkodigudlaharshavardhanNo ratings yet
- 10 - Reaction With HalogenDocument4 pages10 - Reaction With HalogenMaitreya DasNo ratings yet
- Stability of Transition Metal ComplexesDocument6 pagesStability of Transition Metal ComplexesAdistaNo ratings yet
- DirectionalDocument4 pagesDirectionalHimdad Tahir100% (2)
- Industrial Pharmacy-1-QBDocument5 pagesIndustrial Pharmacy-1-QBprateeksha0% (1)
- Transport Policies and Strategies For DenmarkDocument22 pagesTransport Policies and Strategies For DenmarkKarthik Girish100% (2)
- Piña Chan y Navarrete-Archaeological Research in The Lower Grijalva River RegionDocument65 pagesPiña Chan y Navarrete-Archaeological Research in The Lower Grijalva River RegionggarfuNo ratings yet
- Thermosonication and Optimization of Stingless Bee Honey ProcessingDocument15 pagesThermosonication and Optimization of Stingless Bee Honey ProcessingsyazaqilahNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table WorksheetDocument23 pagesPeriodic Table Worksheetlakshmi ghayathri N.M.No ratings yet
- Glasswool Product Brochure: ISO 27001 ISO 14001 ISO 50001 OHSAS 18001Document9 pagesGlasswool Product Brochure: ISO 27001 ISO 14001 ISO 50001 OHSAS 18001Liviu ToaderNo ratings yet
- UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India - For SSC ExamsDocument4 pagesUNESCO World Heritage Sites in India - For SSC ExamsVishal GabaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Globalization Population and MobilityDocument56 pagesLesson 4: Globalization Population and MobilityAhrlynne Cuadrante Mendez RodaNo ratings yet
- Newton-Raphson Method: Numerical AnalysisDocument14 pagesNewton-Raphson Method: Numerical Analysisنورالهدى سعيد عبدNo ratings yet
- Fun Date IdeasDocument5 pagesFun Date IdeasClayton Jensen100% (1)
- DC TrainingDocument5 pagesDC TrainingVishal PanchaalNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Psychology G11Document4 pagesFinal Exam Psychology G11Meetali ArchitNo ratings yet
- Q1 - Modules 7 and 8 Coping Mechanism in Middle and Late Adolescence StudentsDocument24 pagesQ1 - Modules 7 and 8 Coping Mechanism in Middle and Late Adolescence StudentskeziahNo ratings yet
- Bio Intensive GardeningDocument13 pagesBio Intensive GardeningJAYSON GAYUMANo ratings yet
- The History of AstrologyDocument36 pagesThe History of AstrologyDharani Dharendra DasNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics: Rheumatology Will Roll Up To Pediatrics: General Pediatrics: Urology Will Roll Up To UrologyDocument47 pagesPediatrics: Rheumatology Will Roll Up To Pediatrics: General Pediatrics: Urology Will Roll Up To UrologydasbosiNo ratings yet
- Credit To: Shamjith KMDocument19 pagesCredit To: Shamjith KMRocel Mae PalianaNo ratings yet
- Bhakti Unit4Document3 pagesBhakti Unit4Shantanu DashNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet: Three Phase Induction Motor - Squirrel Cage RotorDocument1 pageData Sheet: Three Phase Induction Motor - Squirrel Cage Rotorasdsd dsdaNo ratings yet
- HackMaster QuickStart GuideDocument41 pagesHackMaster QuickStart Guidesullivbt100% (3)
- Wildlife SanctuariesDocument10 pagesWildlife SanctuariesSamia LatifNo ratings yet
- BIO 354 - Final Exam - Fall 2013 SBUDocument18 pagesBIO 354 - Final Exam - Fall 2013 SBUNerdy Notes Inc.No ratings yet
- Land NavigationDocument7 pagesLand NavigationElijah Dave BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- Monuments of The Kathmandu Valley - John Sanday@Comics4nostalgiaDocument117 pagesMonuments of The Kathmandu Valley - John Sanday@Comics4nostalgiaBipin Bazracharya100% (1)
- Panadol Osteo Product InformationDocument5 pagesPanadol Osteo Product Informationsalema2No ratings yet
- Mindfulness With BreathingDocument6 pagesMindfulness With BreathinggreenboyNo ratings yet
- 2021 Summer Season Club Turban Thermal Fac Sheet - EngDocument12 pages2021 Summer Season Club Turban Thermal Fac Sheet - EngPENA LAURANo ratings yet
- Shipmate GN30 Mk2 Manual enDocument103 pagesShipmate GN30 Mk2 Manual entoumassis_pNo ratings yet
- 5th Edition Manual 080120Document126 pages5th Edition Manual 080120Maria TudorieNo ratings yet