Professional Documents
Culture Documents
A Center Lathe
Uploaded by
Arfan KhanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
A Center Lathe
Uploaded by
Arfan KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
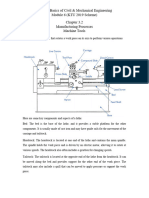
A center lathe, also known as a conventional lathe, is a type of machine tool that is
commonly used for various metalworking operations. It is designed to remove
material from a rotating workpiece, also known as the stock, to create cylindrical or
conical shapes.
The center lathe consists of a headstock, bed, tailstock, and carriage. The headstock
contains the spindle, which holds the workpiece and rotates it at high speeds. The
tailstock is used to support the other end of the workpiece, and the carriage moves
along the bed to position the cutting tool.
The center lathe can perform various operations, including turning, facing, drilling,
boring, reaming, tapping, and threading. Turning is the most common operation,
which involves removing material from the outer surface of the workpiece to create a
cylindrical shape. Facing is an operation that removes material from the end of the
workpiece to create a flat surface.
Drilling is an operation that creates a hole in the workpiece, while boring enlarges an
existing hole. Reaming is an operation that finishes a hole to a precise size, and
tapping creates internal threads in a hole. Threading is an operation that creates
external threads on a cylindrical or conical surface.
The center lathe is a versatile machine tool that is widely used in various industries,
including automotive, aerospace, and manufacturing. It requires skilled operators
who can set up and operate the machine to produce high-quality parts.
In summary, the center lathe is a type of machine tool that is used for various
metalworking operations, including turning, facing, drilling, boring, reaming, tapping,
and threading. It consists of a headstock, bed, tailstock, and carriage and requires
skilled operators to produce high-quality parts.
You might also like
- Traditional Toolmaking: The Classic Treatise on Lapping, Threading, Precision Measurements, and General ToolmakingFrom EverandTraditional Toolmaking: The Classic Treatise on Lapping, Threading, Precision Measurements, and General ToolmakingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Lathe MachineDocument7 pagesLathe MachineJacTomlinNo ratings yet
- Machine Shop ManualDocument6 pagesMachine Shop ManualManoj KumarNo ratings yet
- BME Unit IV Machine ToolsDocument41 pagesBME Unit IV Machine ToolsArvind BhosaleNo ratings yet
- Lathe ReportDocument16 pagesLathe ReportMuhammad Aisamuddin88% (8)
- Metal Cutting ProcessesDocument67 pagesMetal Cutting ProcessesAbhay SontakkeNo ratings yet
- LATHE - WriteupDocument21 pagesLATHE - WriteupMERISH GURU100% (1)
- Machine Tools NotesDocument16 pagesMachine Tools NotesKarNo ratings yet
- For More Presentation Go To: Metal Cutting LatheDocument74 pagesFor More Presentation Go To: Metal Cutting Lathebabu319No ratings yet
- Chucks: Clamp Radial Symmetry Cylindrical Drill Bit Power Tool Bar Spindle LatheDocument14 pagesChucks: Clamp Radial Symmetry Cylindrical Drill Bit Power Tool Bar Spindle LatheIrtaza Husnain100% (1)
- Machine ShopDocument22 pagesMachine Shopanurag6866No ratings yet
- Machine WorskopDocument20 pagesMachine WorskopnaemaNo ratings yet
- Lathe Machine Lab Report 1Document14 pagesLathe Machine Lab Report 1regassa rajiNo ratings yet
- Machine Tools LAB Manual PDFDocument77 pagesMachine Tools LAB Manual PDF5F2 SHAIK PALUR SAMEENANo ratings yet
- Turning - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesTurning - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaKhateeb Ul Islam QadriNo ratings yet
- Techno International Newtown New Town, Rajarhat Workshop/Manufacturing Practices Introduction of Lathe Machine ES-ME191/292Document3 pagesTechno International Newtown New Town, Rajarhat Workshop/Manufacturing Practices Introduction of Lathe Machine ES-ME191/292Sujay Das SonuNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Lathe Machine (Machine Shop)Document25 pagesIntroduction of Lathe Machine (Machine Shop)Muhammad AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Machine Shop AlexDocument61 pagesMachine Shop AlexGojam SeyoumNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Chapter 2Document66 pagesManufacturing Chapter 2Jibril JundiNo ratings yet
- Machine ShopDocument6 pagesMachine ShopAmarjeet Singh (Assistant Professor- Mechanical Engineer)No ratings yet
- Lathe MachineDocument16 pagesLathe MachineM Arslan AshrafNo ratings yet
- Lathe and Drilling MachineDocument99 pagesLathe and Drilling Machinesagar0% (1)
- Machine Tools PDFDocument13 pagesMachine Tools PDFgiacomo meliconiNo ratings yet
- Unit III LatheDocument27 pagesUnit III Lathesayan duttaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Milling Machine and Its RigidityDocument9 pagesBasics of Milling Machine and Its RigidityshubhamNo ratings yet
- Lathe MachineDocument4 pagesLathe MachineIman SadeghiNo ratings yet
- Lathe Machines & OperationsDocument43 pagesLathe Machines & OperationsInder Jeet Kori100% (1)
- Department of Petrochemical Engineering College of Technical Engineering University of Polytechnic-DuhokDocument21 pagesDepartment of Petrochemical Engineering College of Technical Engineering University of Polytechnic-DuhokWalid AdnanNo ratings yet
- Machine ShopDocument5 pagesMachine Shopkainat latifNo ratings yet
- BMEDocument23 pagesBMELawanbha LyngdohNo ratings yet
- CH-5.6 Lathe OperationDocument11 pagesCH-5.6 Lathe OperationBARUN BIKASH DENo ratings yet
- Machine Lab - ReportDocument11 pagesMachine Lab - Reportsaiq kamranNo ratings yet
- Machine Shop: Principal Parts of A LatheDocument7 pagesMachine Shop: Principal Parts of A LatheArchika YaduNo ratings yet
- LatheDocument39 pagesLatheDominador Lozano Jr.No ratings yet
- Machining: Machining Is Any of Various Processes in Which A Piece of RawDocument7 pagesMachining: Machining Is Any of Various Processes in Which A Piece of RawAshwin KumarNo ratings yet
- 2 - Machining Processes and Machine ToolsDocument69 pages2 - Machining Processes and Machine ToolsWajih HasnainNo ratings yet
- Machine ShopDocument11 pagesMachine Shop18-QADEER AHMADNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document15 pagesModule 2mohammedgousmujahidNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Part 2 Bme-1Document17 pagesModule 6 Part 2 Bme-1joeste965No ratings yet
- MPR (22446) ManualDocument31 pagesMPR (22446) Manualsiddiquimuzammil876No ratings yet
- Chapter Two Traditional Material Removal Processes MachiningDocument21 pagesChapter Two Traditional Material Removal Processes MachiningkidusNo ratings yet
- Unit-4 Machine ToolsDocument77 pagesUnit-4 Machine ToolsSOURABH GANGWARNo ratings yet
- Study and Operation of An Engine Lathe.: Course No: Ipe-108 Course Title: Workshop PracticeDocument9 pagesStudy and Operation of An Engine Lathe.: Course No: Ipe-108 Course Title: Workshop PracticeSazzadNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Engineering-1 - DPME-304Document27 pagesManufacturing Engineering-1 - DPME-304Vikas YadavNo ratings yet
- Presentation Jig and FixturesDocument11 pagesPresentation Jig and FixturesFan Ted LeeNo ratings yet
- Malwa Institute of Science & Technology, Indore: Experiment No-7Document9 pagesMalwa Institute of Science & Technology, Indore: Experiment No-7Thulasi RamNo ratings yet
- Lab 1 Fareez (Turning Machine)Document24 pagesLab 1 Fareez (Turning Machine)s231311024No ratings yet
- Lathe Machine Lab ReportDocument18 pagesLathe Machine Lab Reportregassa rajiNo ratings yet
- Lathe MachineDocument8 pagesLathe MachineAtrayee Das ME, 2026No ratings yet
- Lathe MachineDocument18 pagesLathe MachineCRAZY INDIAN XYZ100% (1)
- LatheDocument6 pagesLatheRavichandran GNo ratings yet
- To Oldies Moulds ReportDocument15 pagesTo Oldies Moulds ReportArpit JayswalNo ratings yet
- Machine Shop: Assignment No. 5Document16 pagesMachine Shop: Assignment No. 5Abdur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Quad Processing MachineDocument6 pagesQuad Processing MachineSulfikkar100% (1)
- Lathe Machine AssignmentDocument23 pagesLathe Machine AssignmentChristopher Rohrer100% (1)
- BME Module 3 Part 2Document13 pagesBME Module 3 Part 2Ajith KumarNo ratings yet
- MC-MT R16 - Unit-2Document56 pagesMC-MT R16 - Unit-2Anonymous GEHeEQlajbNo ratings yet
- Assignment No 1Document8 pagesAssignment No 1abhijeet bhosaleNo ratings yet
- Turning and Boring A specialized treatise for machinists, students in the industrial and engineering schools, and apprentices, on turning and boring methods, etc.From EverandTurning and Boring A specialized treatise for machinists, students in the industrial and engineering schools, and apprentices, on turning and boring methods, etc.No ratings yet
- Berbice High School Information Technology: Transmission MediaDocument11 pagesBerbice High School Information Technology: Transmission MediaArfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Spanner Drawing PDFDocument1 pageSpanner Drawing PDFArfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Edpm Assignment 2Document4 pagesEdpm Assignment 2Arfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Machine Cutting Is A Manufacturing Process That Involves The Controlled Removal of Material From A Larger Piece To Achieve A Desired Shape or PartDocument1 pageMachine Cutting Is A Manufacturing Process That Involves The Controlled Removal of Material From A Larger Piece To Achieve A Desired Shape or PartArfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Drawing 1Document1 pageDrawing 1Arfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Schematic Diagram 3Document4 pagesSchematic Diagram 3Arfan KhanNo ratings yet
- Here Are Some Interesting Facts and Quotes That Might Be HelpfulDocument3 pagesHere Are Some Interesting Facts and Quotes That Might Be HelpfulArfan KhanNo ratings yet