Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Magnetic Field Around A Solenoid Display Poster A4
Uploaded by
librahimliOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Magnetic Field Around A Solenoid Display Poster A4
Uploaded by
librahimliCopyright:
Available Formats
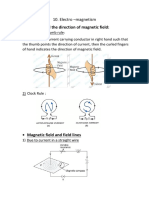
The Magnetic Field
around a Solenoid
Twisting a wire into a coil creates a solenoid.
A solenoid is a coil of wire that produces a magnetic field when a current flows through it.
The magnetic fields around each loop of the coil combine to form a single, uniform magnetic field
which is stronger than that of the same piece of wire when straightened.
Inside the solenoid Outside the solenoid
◣ parallel field lines ◥ looped field lines
◣ strongest magnetic field ◥ weaker magnetic field
◣ field lines are ◥ field lines are
close together further apart
solenoid
magnetic field line
direction of conventional current
The strength of the magnetic field around a solenoid can be increased by increasing the current
flowing through the coil of wire.
The direction of the magnetic field can be reversed by reversing the current flowing through the
loop of wire.
The direction of the conventional current through the solenoid can be used to determine the location
of its magnetic poles.
At the north pole
At the south pole
of a solenoid,
of a solenoid,
conventional
conventional current
current flows in
flows in a clockwise
an anticlockwise
direction.
direction.
You might also like
- Magnetic Field Around An Electromagnet Display Poster A4Document1 pageMagnetic Field Around An Electromagnet Display Poster A4librahimliNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: Grade 10 - Topic 6Document2 pagesElectromagnetism: Grade 10 - Topic 6Lobi RybgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 ElectromagnetismDocument30 pagesChapter 26 ElectromagnetismYash RamlakhansinghNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic: What Can We Learn From The Experiment Above?Document2 pagesElectromagnetic: What Can We Learn From The Experiment Above?Bonita DesiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 ElectromagnetismDocument29 pagesChapter 26 ElectromagnetismReef WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 ElectromagnetismDocument29 pagesChapter 26 ElectromagnetismGiovanni SlackNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class Notes - Mind Map - Class 10thDocument27 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class Notes - Mind Map - Class 10thsyedyaseen39375No ratings yet
- MagnetisumDocument20 pagesMagnetisumPpppNo ratings yet
- Attachment PHPDocument7 pagesAttachment PHPKunal Bagade.No ratings yet
- Electromagnetism Short NotesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetism Short Notespadhaai karoNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Current (Sreehas)Document3 pagesMagnetic Effects of Current (Sreehas)Sridhar NNo ratings yet
- Electro Magnetism: The Magnetic Effect of A CurrentDocument7 pagesElectro Magnetism: The Magnetic Effect of A CurrentShaikh IradNo ratings yet
- Magnetics Main Part 1 PDFDocument11 pagesMagnetics Main Part 1 PDFAnonymousNo ratings yet
- MagnetismDocument10 pagesMagnetismIvan TzNo ratings yet
- MAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT - Class Notes - Foundation Mind-MapDocument25 pagesMAGNETIC EFFECTS OF CURRENT - Class Notes - Foundation Mind-Mapmegha rohillaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Ec-Part1Document6 pagesMagnetic Effects of Ec-Part1Prisoner FFNo ratings yet
- Notes of CH - 13Document10 pagesNotes of CH - 13Shabad SinghNo ratings yet
- Nota Padat Fizik F5 ElectromagnetDocument36 pagesNota Padat Fizik F5 Electromagnetslokkro100% (40)
- Chapter-13 Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument19 pagesChapter-13 Magnetic Effect of CurrentSuhani GosainNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class 10Document6 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric Current - Class 10rachna chhabraNo ratings yet
- MagneticsDocument1 pageMagneticsHüseyin Murat PolaterNo ratings yet
- Physics 33 - Electromagnetic Effects 2Document80 pagesPhysics 33 - Electromagnetic Effects 2Hakim AbbasNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument7 pagesMagnetic Effect of CurrentgoyalnahveNo ratings yet
- Notes of Magnetic Effects of Current Class XDocument14 pagesNotes of Magnetic Effects of Current Class Xskshiarora12No ratings yet
- CH 13Document12 pagesCH 13charanNo ratings yet
- Elect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldDocument8 pagesElect Roma Gneti SM: How Electric Current Produce A Magnetic FieldIsmail MzavaNo ratings yet
- Relay OperationDocument26 pagesRelay Operationapi-3842326No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument18 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentMayurItankarNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current NotesDocument16 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current NotesNistha GuptaNo ratings yet
- Notes For Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument9 pagesNotes For Magnetic Effects of Electric Currenttanishq.sonar03No ratings yet
- Science Chapter 13 - 1Document10 pagesScience Chapter 13 - 1Radha SahachariNo ratings yet
- Q1: What Is A Magnet?Document7 pagesQ1: What Is A Magnet?Lulun NeithamNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Currentdrphysics256No ratings yet
- Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument14 pagesMagnetic Effects of Electric CurrentREHANNo ratings yet
- ch4 CL 10Document6 pagesch4 CL 10jaiathihyadNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism - Oersted DiscoveryDocument4 pagesElectromagnetism - Oersted DiscoveryMaden betoNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument3 pagesPhysicsMohit TiwariNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Electric Current Notes Chpt2Document11 pagesMagnetic Effect of Electric Current Notes Chpt2Sarathrv Rv100% (2)
- CLASS-10 Subject: ScienceDocument62 pagesCLASS-10 Subject: ScienceZeonNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Elctric CurrentDocument47 pagesMagnetic Effect of Elctric Currentrahul.op0001opNo ratings yet
- Phy Topic 2 F4Document12 pagesPhy Topic 2 F4Kandrossy GlassNo ratings yet
- Electromag Netism: C. MuisDocument85 pagesElectromag Netism: C. MuisMat MinNo ratings yet
- Phy - Magnetic Effects of Current WsDocument11 pagesPhy - Magnetic Effects of Current Wsburramokshitha88No ratings yet
- Physics 502 - Electromagnetic EffectsDocument101 pagesPhysics 502 - Electromagnetic EffectsMaissaNo ratings yet
- 10th Standard Science: Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentDocument18 pages10th Standard Science: Chapter 13 - Magnetic Effects of Electric CurrentNANDANA BSNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field: - A Magnetic Field Is A Region in Which A Body With Magnetic Properties Experiences A ForceDocument39 pagesMagnetic Field: - A Magnetic Field Is A Region in Which A Body With Magnetic Properties Experiences A ForceKartikeya Shukla100% (1)
- A Single Wire That Has Current Passing ThroughDocument3 pagesA Single Wire That Has Current Passing Throughrajkumar karjeeNo ratings yet
- Magnetic FieldsDocument2 pagesMagnetic FieldsMarie SollanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 AnsDocument3 pagesChapter 10 Anslimcheehin3No ratings yet
- Collective Oscillations in a Plasma: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyFrom EverandCollective Oscillations in a Plasma: International Series of Monographs in Natural PhilosophyNo ratings yet
- Physics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPhysics for Kids : Electricity and Magnetism - Physics 7th Grade | Children's Physics BooksRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Magnetic Fields, Special Relativity and Potential Theory: Elementary Electromagnetic TheoryFrom EverandMagnetic Fields, Special Relativity and Potential Theory: Elementary Electromagnetic TheoryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- How Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandHow Do Electric Motors Work? Physics Books for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- The Effects of a Magnetic Field on Radiation -Memoirs by Faraday Kerr and ZeemanFrom EverandThe Effects of a Magnetic Field on Radiation -Memoirs by Faraday Kerr and ZeemanNo ratings yet
- Foundation-Workbook - SkillshareDocument169 pagesFoundation-Workbook - SkillsharelibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Quiz Set 2Document14 pagesMultiple Choice Quiz Set 2librahimliNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Quiz Set 4 (Physics Only)Document14 pagesMultiple Choice Quiz Set 4 (Physics Only)librahimliNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Quiz Set 3 (HT Only)Document14 pagesMultiple Choice Quiz Set 3 (HT Only)librahimliNo ratings yet
- Sound Progress Record 1Document1 pageSound Progress Record 1librahimliNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Quiz Set 1Document14 pagesMultiple Choice Quiz Set 1librahimliNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Field Around Current-Carrying Wires Display Poster A4Document1 pageMagnetic Field Around Current-Carrying Wires Display Poster A4librahimliNo ratings yet
- Higher - Evolution of The Earths AtmosphereDocument6 pagesHigher - Evolution of The Earths AtmospherelibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Evolution of The Earths Atmosphere Reading ComprehensionDocument3 pagesEvolution of The Earths Atmosphere Reading ComprehensionlibrahimliNo ratings yet
- LOtI Reading ComprehensionDocument3 pagesLOtI Reading ComprehensionlibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Cornflour Slime Awe and Wonder Prompt Card EditableDocument1 pageCornflour Slime Awe and Wonder Prompt Card EditablelibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions Answer SheetDocument1 pageMultiple Choice Questions Answer SheetlibrahimliNo ratings yet
- (IELTS at Writing Task 1) The BOOK by Mastership (Skillshare)Document394 pages(IELTS at Writing Task 1) The BOOK by Mastership (Skillshare)Yung BuiNo ratings yet
- Coral Reef Ecosystem Reading ComprehensionDocument2 pagesCoral Reef Ecosystem Reading ComprehensionlibrahimliNo ratings yet
- LOtI Vocabulary SheetDocument1 pageLOtI Vocabulary SheetlibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Paper Towel Colour Mixing Awe and Wonder Science ActivityDocument1 pagePaper Towel Colour Mixing Awe and Wonder Science ActivitylibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Polar Animal Adaptations Information SheetsDocument4 pagesPolar Animal Adaptations Information SheetslibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Foundation - Evolution of The Earths AtmosphereDocument4 pagesFoundation - Evolution of The Earths AtmospherelibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Coral Reef Ecosystem Comprehension Questions HADocument4 pagesCoral Reef Ecosystem Comprehension Questions HAlibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Fizzy Colours Awe and Wonder Prompt Card EditableDocument1 pageFizzy Colours Awe and Wonder Prompt Card EditablelibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Animal Adaptations Display PostersDocument4 pagesAnimal Adaptations Display PosterslibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Active Transport Reading Comprehension Questions FoundationDocument4 pagesActive Transport Reading Comprehension Questions FoundationlibrahimliNo ratings yet
- IB Eassessment N20 Biology MarkschemeDocument11 pagesIB Eassessment N20 Biology MarkschemelibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Cornflour Slime Awe and Wonder Prompt CardDocument1 pageCornflour Slime Awe and Wonder Prompt CardlibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Fizzy Colours Awe and Wonder Science ActivityDocument1 pageFizzy Colours Awe and Wonder Science ActivitylibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Cornflour Slime Awe and Wonder Science ActivityDocument1 pageCornflour Slime Awe and Wonder Science ActivitylibrahimliNo ratings yet
- N19 Biology (English) MarkschemeDocument12 pagesN19 Biology (English) MarkschemelibrahimliNo ratings yet
- M22 Biology (English) MarkschemeDocument15 pagesM22 Biology (English) Markschemelibrahimli100% (1)
- Worksheet ElectrolysisDocument3 pagesWorksheet ElectrolysislibrahimliNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment Tasks For MYP ArtsDocument9 pagesFormative Assessment Tasks For MYP ArtslibrahimliNo ratings yet