Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Atomic Structure
Uploaded by
onlooker.eternity0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageOriginal Title
atomic structure
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views1 pageAtomic Structure
Uploaded by
onlooker.eternityCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Chap3_atomic structure
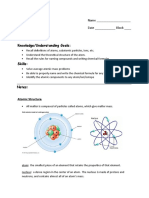
Atom
- The smallest part of an element that has the chemical properties of that
element
- Made up of empty spaces
- Nucleus = at the centre of each atom (very tiny and dense region)
- Around the nucleus is a could of moving particles = electrons
Atom
Consists:
Proton p Inside the 1 +1
nucleus
Neutron n Inside the 1 0
nucleus
Electron e- Moving 1/1836 (0) -1
around the
nucleus
Atomic number and mass number
- The atomic number of an atom is the number of protons in the atom
- The mass number of an atom is equal to the sum of the number of protons
and neutrons in the atom
Isotopes
- Atoms of the same elements with the same number of protons but different
numbers of neutrons
- Have similar physical properties (depend on the mass and their masses
are different)
- Same chemical properties (depending on the number of electrons and they
have some of electrons)
Relative masses
● Relative atomic mass
- The atomic mass is the average mass of an atom, taking into account the
amount of each isotope present in a naturally occurring sample of an
element
You might also like
- Chapter 3: Atomic Structure: Atoms MoleculesDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Atomic Structure: Atoms Moleculesonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- G9 ChemistryDocument3 pagesG9 ChemistryMustafaNo ratings yet
- 3.1. Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument3 pages3.1. Atomic Structure and The Periodic Tableahmed5030 ahmed5030No ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics - 1Document61 pagesNuclear Physics - 1Rose MusariraNo ratings yet
- Chem ModuleDocument20 pagesChem Modulekeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Notes02HTdDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure Notes02HTdAssem MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Notes - LectureDocument19 pagesAtomic Structure Notes - LecturealexandremoutonNo ratings yet
- UNIT 3 y 4 ATOMSDocument3 pagesUNIT 3 y 4 ATOMSLucia OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Atoms ElementsDocument8 pagesLecture 1 Atoms ElementsshanecarlNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure & The Periodic Table Unit 1Document15 pagesAtomic Structure & The Periodic Table Unit 1Mikaelia NesbethNo ratings yet
- c3 3 AtomicstructureandtheperiodictableDocument8 pagesc3 3 AtomicstructureandtheperiodictableIshan DixitNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure 1Document35 pagesAtomic Structure 1Jeprox Martinez0% (1)
- Physical ScienceDocument27 pagesPhysical ScienceCarlos MasikaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument6 pagesChemistryJessa Mae AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsDocument28 pagesAtoms, Isotopes, Ions, and Molecules: Key PointsCandyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- 12 S080201e Structure of An Atom1Document13 pages12 S080201e Structure of An Atom1api-262111293No ratings yet
- Structure 1.2 The Nuclear AtomDocument31 pagesStructure 1.2 The Nuclear AtomomaramrgoudaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemistry: Class ObjectivesDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Chemistry: Class ObjectivesSebastian VillegasNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Structure of The Atom and PTDocument4 pages3.1 Structure of The Atom and PTRoldan Delapa PachecoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry I Handout 2Document5 pagesGeneral Chemistry I Handout 2Roxan Oxima ClabriaNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument1 pageChemistryhi nameNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and The Periodic TableDocument6 pagesAtomic Structure and The Periodic TablecalimagandaNo ratings yet
- New Subatomic Particles ResearchDocument2 pagesNew Subatomic Particles ResearchNaeem MohammedNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument1 pageAtomic Structureapi-350245383No ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 1Document7 pagesChemistry Unit 1Natasha Liliane LootNo ratings yet
- g9 ChemistryDocument3 pagesg9 ChemistryMustafaNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument19 pagesAtomJoey PotterNo ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument6 pagesAdditional Mathematicslonydon23No ratings yet
- The Atom For AnatomyDocument106 pagesThe Atom For AnatomyAlexandra B. FloresNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument28 pagesAtomic StructureJohn Vince Ramos PapNo ratings yet
- 3.1 AtomsDocument17 pages3.1 AtomsAnisha Syazwana Binti RoslyNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Atoms and Bonding + Some Extra ChemistryDocument61 pagesTopic 3 - Atoms and Bonding + Some Extra Chemistryxtralargee.mbaNo ratings yet
- Radiation Production and Characteristics Lecture2021 22Document188 pagesRadiation Production and Characteristics Lecture2021 22Lei ClamorNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry NotesDocument342 pagesInorganic Chemistry NotesJanesh SumadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry FactsheetsDocument415 pagesChemistry FactsheetsAmbrose Aaron DavidNo ratings yet
- Atomic ParticlesDocument3 pagesAtomic Particlesanas subhanNo ratings yet
- Concept of Atomic StructureDocument23 pagesConcept of Atomic StructureMd. Mujahid HasanNo ratings yet
- (TC) C2 Atomic Structure and Electronic ConfigurationDocument5 pages(TC) C2 Atomic Structure and Electronic Configurationthanat amornratchnondNo ratings yet
- AtomsDocument2 pagesAtomsJullienne Noreen AnchetaNo ratings yet
- Structure of An AtomDocument6 pagesStructure of An AtomJust HeyNo ratings yet
- 1.1. A Simple Model of The Atom, Symbols, Relative Atomic Mass, Electronic Charge and Isotopes PDFDocument4 pages1.1. A Simple Model of The Atom, Symbols, Relative Atomic Mass, Electronic Charge and Isotopes PDFUloko ChristopherNo ratings yet
- All Notes ChemistryDocument205 pagesAll Notes ChemistrySeif MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Gen ChemDocument10 pagesChapter 2 Gen ChemJennifer MalunaoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument18 pagesAtomic StructureSue Gray (International School of Bologna)No ratings yet
- 12 S080201E Structure of An Atom1Document13 pages12 S080201E Structure of An Atom1chardemie alvarezNo ratings yet
- A. Atoms and Atomic StructureDocument40 pagesA. Atoms and Atomic StructurewasimsabriNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and IonsDocument63 pagesAtoms, Molecules and IonsRenato Jr. FariñasNo ratings yet
- KBAT Chemi CHAP 1Document15 pagesKBAT Chemi CHAP 1Chong HyenNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes - Teacher 2Document13 pagesUnit 2 Notes - Teacher 2noNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure - Chapter 4: Studying Atoms - 4.1Document29 pagesAtomic Structure - Chapter 4: Studying Atoms - 4.1XRKhaloodiNo ratings yet
- Simple Model of An Atom: IsotopesDocument4 pagesSimple Model of An Atom: IsotopesLilaNo ratings yet
- Be Sure To Read The Law of Definite Proportions and Multiple ProportionsDocument6 pagesBe Sure To Read The Law of Definite Proportions and Multiple ProportionsMahdi MiaNo ratings yet
- L2-Atoms and Atomic StructureDocument49 pagesL2-Atoms and Atomic Structurekoladejoy49No ratings yet
- Unit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthDocument218 pagesUnit 5 Materials and Cycles On EarthBlopNo ratings yet
- Mojza-AS-Chemistry-Notes CompressedDocument64 pagesMojza-AS-Chemistry-Notes CompressedNoor MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Atoms and ElementsDocument18 pagesAtoms and ElementsJACK CAMPBELLNo ratings yet
- Class-8-General Science-Chapter-5 - Inside The AtomDocument8 pagesClass-8-General Science-Chapter-5 - Inside The AtomONE CLICK COMPUTERNo ratings yet
- 2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Document12 pages2021 - GR 8 - Chemistry (230620)Keshia KatarinaNo ratings yet
- Your Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2From EverandYour Journey To The Basics Of Quantum Realm Volume II: Your Journey to The Basics Of Quantum Realm, #2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Marriage, Divorce and Remarriage: Book A 3.2.1, 3.2.6 Book B 1.2.1Document32 pagesMarriage, Divorce and Remarriage: Book A 3.2.1, 3.2.6 Book B 1.2.1onlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- Family Structure and ResponsibilitiesDocument23 pagesFamily Structure and Responsibilitiesonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Sexual Relationships: Book B 1.2.2 Book A 3.2.2Document17 pages2.4 Sexual Relationships: Book B 1.2.2 Book A 3.2.2onlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- St. Paul's Convent School F.4 IGCSE Chapter 6 &12 QuizDocument5 pagesSt. Paul's Convent School F.4 IGCSE Chapter 6 &12 Quizonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- RS ContraceptionDocument3 pagesRS Contraceptiononlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- RS ChildlessnessDocument7 pagesRS Childlessnessonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- Metallic BondingDocument2 pagesMetallic Bondingonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- Marriage, Divorce and RemarriageDocument5 pagesMarriage, Divorce and Remarriageonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- Church Celebration - Christmas and EasterDocument18 pagesChurch Celebration - Christmas and Easteronlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
- The Teachings of JesusDocument20 pagesThe Teachings of Jesusonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet
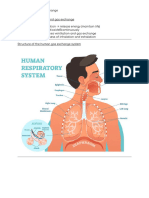
- Breathing, Ventilation and Gas ExchangeDocument5 pagesBreathing, Ventilation and Gas Exchangeonlooker.eternityNo ratings yet