Professional Documents
Culture Documents
rohini_95497885348
Uploaded by
Pugazhendhi Viru MarleyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
rohini_95497885348
Uploaded by
Pugazhendhi Viru MarleyCopyright:
Available Formats
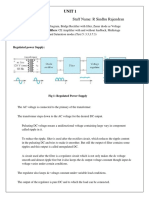
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
1.3 RECTIFIERS
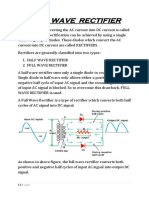
Rectifiers are classified according to the period ofconduction. They are
Half Wave Rectifier
Full Wave Rectifier
Half Wave Rectifier:
The half wave rectifier is a type of rectifier that rectifies only half cycle of the
waveform. This describes the half wave rectifier circuit working. The half rectifier
consist a step down transformer, a diode connected to the transformer and a load
resistance connected to the cathode end of the diode. The circuit diagram of half wave
transformer is shown below:
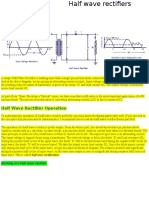
Figure: 1.3.1 Half wave Rectifier
[Source: “Electronic devices and circuits” by “Balbir Kumar, Shail.B.Jain, and Page: 252]
Figure: 1.3.2 Half wave Rectifier Wave Form
[Source: “Electronic devices and circuits” by “Balbir Kumar, Shail.B.Jain, and Page: 253]
EC8353 ELECTRONICS DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
The main supply voltage is given to the transformer which will increase or decrease
the voltage and give to the diode. In most of the cases we will decrease the supply
voltage by using the step down transformer here also the output of the step down
transformer will be in AC. This decreased AC voltage is given to the diode which is
connected serial to the secondary winding of the transformer, diode is electronic
component which will allow only the forward bias current and will not allow the reverse
bias current. From the diode we will get the pulsating DC and give to the load resistance
RL.
Working of Half Wave Rectifier:
The input given to the rectifier will have both positive and negative cycles. The
half rectifier will allow only the positive half cycles and omit the negative half cycles.
So first we will see how half wave rectifier works in the positive half cycles.
Positive Half Cycle:
In the positive half cycles when the input AC power is given to the
primary winding of the step down transformer, we will get the decreased
voltage at thesecondary winding which is given to the diode.
The diode will allow current flowing in clock wise direction from anode
to cathode in the forward bias (diode conduction will take place in
forward bias)which will generate only the positive half cycle of the AC.
The diode will eliminate the variations in the supply and give the pulsating
DCvoltage to the load resistance RL. We can get the pulsating DC at the
Load resistance.
Negative Half Cycle:
In the negative half cycle the current will flow in the anti-clockwise
direction and the diode will go in to the reverse bias. In the reverse bias
the diode will not conduct so, no current in flown from anode to cathode,
and we cannot getany power at the load resistance.
Only small amount of reverse current is flown from the diode but this
current is almost negligible. And voltage across the load resistance is
also zero.
EC8353 ELECTRONICS DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Characteristics of Half Wave Rectifier:
There are some characteristics to the half wave rectifier they are
Efficiency: The efficiency is defined as the ratio of input AC to the
output DC. Efficiency, Ƞ = P dc / Pac
DC power delivered to the load, Pdc = I2dc RL = ( Imax/pi ) 2 RL
AC power input to the transformer, Pac = Power dissipated in junction of
diode + Power
Dissipated in load resistance RL= I2rms RF + I2rms RL = {I2MAX/4} [RF + RL]
Rectification Efficiency, Ƞ = Pdc / Pac = {4/ 2} [RL/ (RF + RL)] =
0.406/{1+ RF/RL }
If RF is neglected, the efficiency of half wave rectifier is 40.6%.
Ripple factor: It is defined as the amount of AC content in the output DC.
It nothingbut amount of AC noise in the output DC. Less the ripple factor,
performance of the rectifier is more. The ripple factor of half wave
rectifier is about 1.21 (full wave rectifier has about0.48). It can be
calculated as follows:
The effective value of the load current I is given as sum of the rms
values of harmonic currents I1, I2, I3, I4 and DC current Idc.
I2 =I2dc+I21+I22+I24 = I2dc +I2ac
Ripple factor, is given as γ = I ac / Idc = (I2 – I2dc) / Idc = {( I rmdcs /
I 2)-1} = Kf2 – 1) Where Kf is the form factor of the input
voltage. Form factor is given as
Kf = Irms /Iavg = (Imax/2)/ (Imax/pi) = pi/2 = 1.57
So, ripple factor, γ = (1.572 – 1) = 1.21
Peak Inverse Voltage: It is defined as the maximum voltage that a diode
can with stand in reverse bias. During the reverse bias as the diode do not
conduct total voltage drops across the diode. Thus peak inverse voltage
is equal to the input voltage Vs.
EC8353 ELECTRONICS DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
ROHINI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Transformer Utilization Factor (TUF): The TUF is defined as the ratio
of DC power is delivered to the load and the AC rating of the transformer
secondary. Half wave rectifier has around 0.287 and full wave rectifier
has around 0.693.
Half wave rectifier is mainly used in the low power circuits. It has very
low performance when it is compared with the other rectifiers.
EC8353 ELECTRONICS DEVICES AND CIRCUITS
You might also like
- NBME 22 OfflineDocument200 pagesNBME 22 OfflineGautham Kanagala86% (14)
- Half Wave Rectifier PDFDocument23 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier PDFArjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Rectifier Efficiency - Half and Full Wave PDFDocument4 pagesRectifier Efficiency - Half and Full Wave PDFTitsarosal ThomasNo ratings yet
- Half and Full Wave RectifierDocument12 pagesHalf and Full Wave Rectifierlucy lucy50% (2)
- Bhagvender Singh XII-A Physics Project PDFDocument15 pagesBhagvender Singh XII-A Physics Project PDFvoid50% (4)
- Hepatitis Learning GuideDocument71 pagesHepatitis Learning Guidequimico clinico 27100% (10)
- Introduction of RectifierDocument4 pagesIntroduction of RectifierSuraj100% (1)
- Half Wave RectifierDocument12 pagesHalf Wave Rectifierutkarsh devNo ratings yet
- HALF WAVE RECTIFICATIONDocument23 pagesHALF WAVE RECTIFICATIONezekiel makandwaNo ratings yet
- Rectifiers Explained: Single Phase and Three Phase Rectifier CircuitsDocument30 pagesRectifiers Explained: Single Phase and Three Phase Rectifier CircuitsMuhammad Kashif BhuttoNo ratings yet
- Half wave rectifiers explainedDocument7 pagesHalf wave rectifiers explainedSurajNo ratings yet
- AimDocument12 pagesAimkarakeriNo ratings yet
- Case Study On Rectifier (8054)Document13 pagesCase Study On Rectifier (8054)SUNKARA TEJA SRI 7396078109No ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument33 pagesUnit 1 NotesAer ZNo ratings yet
- Download Full Wave Rectifier Circuits and FiltersDocument10 pagesDownload Full Wave Rectifier Circuits and FiltersVenkata PavanNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument9 pagesHalf Wave RectifierAtul Namdeo100% (1)
- Half Wave RectifiersDocument3 pagesHalf Wave RectifiersSaurabhYadav100% (1)
- RectifiersDocument17 pagesRectifiersChantayya Badugu BNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument6 pagesPhysics ProjectRaj58% (19)
- Getting Started with Multisim Circuit SimulationDocument16 pagesGetting Started with Multisim Circuit SimulationSourav MahatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9.Pptx FEEDocument9 pagesChapter 9.Pptx FEEk tine23No ratings yet
- AC to DC Conversion with RectifiersDocument16 pagesAC to DC Conversion with RectifiersJaiom JoshiNo ratings yet
- A Full Wave Rectifier Is A Circuit Arrangement Which Makes Use of Both Half Cycles of Input Alternating CurrentDocument9 pagesA Full Wave Rectifier Is A Circuit Arrangement Which Makes Use of Both Half Cycles of Input Alternating CurrentKaran SoniNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RactifierDocument3 pagesHalf Wave RactifierGAMMA GAMINGNo ratings yet
- DC Power SuppliesDocument21 pagesDC Power SuppliesIan MutugiNo ratings yet
- Half wave and full wave rectification explainedDocument5 pagesHalf wave and full wave rectification explainedHuidrom SharatNo ratings yet
- Full Wave Rectifier Guide: Circuit, Theory & UsesDocument7 pagesFull Wave Rectifier Guide: Circuit, Theory & UsesArun PratapNo ratings yet
- 5 (A) - Half Wave Rectifier - Docx - 20231127 - 143415 - 0000Document4 pages5 (A) - Half Wave Rectifier - Docx - 20231127 - 143415 - 0000smrtyfaizan786No ratings yet
- L6 Diodes and Applications(New2024)Document44 pagesL6 Diodes and Applications(New2024)Aron DionisiusNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Rectifier Physics Project PDF VinilDocument12 pagesHalf Wave Rectifier Physics Project PDF Vinilteamboys536No ratings yet
- Project Report On RectifierDocument10 pagesProject Report On RectifierHArsh90% (10)
- Full Wave Bridge RectifierDocument5 pagesFull Wave Bridge RectifierChennaiSuperkingsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Part-dIIDocument60 pagesChapter 2 Part-dIIAbdul RehmanNo ratings yet
- gunja eds pptDocument10 pagesgunja eds pptsmritibhardwaz4No ratings yet
- Basic ElectronicsDocument8 pagesBasic Electronicsengineer.chiranjitNo ratings yet
- EXP2 Half Wave RectifierDocument3 pagesEXP2 Half Wave RectifierMohammed Dyhia Ali50% (2)
- Unit 3Document40 pagesUnit 3Venkat ChadalavadaNo ratings yet
- A Document To Download PDFDocument9 pagesA Document To Download PDFreyansh.keshavaNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument5 pagesFull Wave Rectifierसूरज कुमारNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1: Introduction To Electronic Systems and DesignDocument23 pagesLesson 1.1: Introduction To Electronic Systems and DesignNoel TeporaNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument9 pagesFull Wave RectifierPUNEET BATRA0% (1)
- Full Wave RectifierDocument9 pagesFull Wave RectifierJoshua Bernardo100% (1)
- Converts Alternating Current Directcurrent InverterDocument10 pagesConverts Alternating Current Directcurrent InverterDevansh SinghNo ratings yet
- Name Quantity: Diodes1N4007 (Si) 1 Resistor 1K 1 Capacitor 100 F 1Document5 pagesName Quantity: Diodes1N4007 (Si) 1 Resistor 1K 1 Capacitor 100 F 1avinash_yuvarajNo ratings yet
- BEEE Precise NotesDocument56 pagesBEEE Precise Noteskurubamailagani ravaliNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument8 pagesHalf Wave Rectifierropef82117No ratings yet
- CH2Document55 pagesCH2Shantha KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 RectifiersDocument30 pages3 RectifiersYahya MareiNo ratings yet
- Half Wave RectifierDocument3 pagesHalf Wave Rectifiertkarpagam6No ratings yet
- Electronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)Document14 pagesElectronic Components Circuits: (Diode Characteristies - Rectifier - Clipper)em2200139No ratings yet
- power supplyDocument25 pagespower supplyaryan.bhosale002No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument11 pagesPhysics ProjectBoves AlexNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyDocument56 pagesTopic 1 Linear DC Power SupplyKu AliyaNo ratings yet
- RectifiersDocument13 pagesRectifiersInfidragon GAMINGNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgAWFJN6bnsHFT3hGk6UWSm5Zh HIwYdjEq4gcXWNBV2T1zjxGhxUwNWeMSa1ReBR-8o0PS1DNj1uxg4-UiAtZq AouLGc5W1RQTUUf sznCCr3w9eswe2Jtpg1EyvzbHj Dt7NaTVDm5Z53Document4 pagesACFrOgAWFJN6bnsHFT3hGk6UWSm5Zh HIwYdjEq4gcXWNBV2T1zjxGhxUwNWeMSa1ReBR-8o0PS1DNj1uxg4-UiAtZq AouLGc5W1RQTUUf sznCCr3w9eswe2Jtpg1EyvzbHj Dt7NaTVDm5Z53BakchodiNo ratings yet
- 3 Applications of PN Junction DiodeDocument5 pages3 Applications of PN Junction DiodeIrishNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices: Can You Recall?Document40 pagesSemiconductor Devices: Can You Recall?RAVINDRA WAYKOLENo ratings yet
- rectifier pptDocument26 pagesrectifier ppthemnphysic91No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Psychedelic Drugs-A New Era in Psychiatry?Document9 pagesPsychedelic Drugs-A New Era in Psychiatry?PeterNo ratings yet
- General Psychology Mid Term ExamDocument2 pagesGeneral Psychology Mid Term Examapi-534780597No ratings yet
- 4 WP 2013Document8 pages4 WP 2013TUTORKIMNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Technology for Food Preservation and ProcessingDocument47 pagesFermentation Technology for Food Preservation and ProcessingAhmad Syamil Muhamad ZinNo ratings yet
- Answers To Extra PracticeDocument5 pagesAnswers To Extra PracticesaraNo ratings yet
- Compabloc Heat Exchangers Cut Downtime at Nynäs RefineryDocument2 pagesCompabloc Heat Exchangers Cut Downtime at Nynäs RefinerylaythNo ratings yet
- Yoga & Diet To Prevent DepressionDocument5 pagesYoga & Diet To Prevent DepressionDietician Mrunmayee DixitNo ratings yet
- MMDST PDFDocument50 pagesMMDST PDFChristopher OlipasNo ratings yet
- 311970536Document1 page311970536Codrut RadantaNo ratings yet
- Checklist PDFDocument84 pagesChecklist PDFJeremiah Miko LepasanaNo ratings yet
- Plane Bearings: Material Indicator Shape or SeriesDocument4 pagesPlane Bearings: Material Indicator Shape or SeriesJuan LoaizaNo ratings yet
- 2020 End Year 6 PenulisanDocument8 pages2020 End Year 6 PenulisanZulhillmi ZainuddinNo ratings yet
- Accessibility POC: October 26, 2017Document7 pagesAccessibility POC: October 26, 2017Ramesh BodukaniNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 12Document12 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Class 12shivanginirai7No ratings yet
- 03 Open Merit MBBSPrivate 2019Document149 pages03 Open Merit MBBSPrivate 2019Hasnain ZahoorNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Procrastination Impact On Academic PerformanceDocument2 pagesLiterature Review On Procrastination Impact On Academic Performancemomi100% (1)
- DatasheetDocument112 pagesDatasheetStuxnetNo ratings yet
- Sound Level MeterDocument11 pagesSound Level MeterFityatal HasanahNo ratings yet
- Symbol High Low R5 R4 R3 R2: DailyDocument8 pagesSymbol High Low R5 R4 R3 R2: Daily257597 rmp.mech.16No ratings yet
- RESOLUTION 2022-08 Denial of Setback VarianceDocument5 pagesRESOLUTION 2022-08 Denial of Setback VarianceMatt McKinneyNo ratings yet
- SECTION 03380 Post-Tensioned Concrete Rev 1Document30 pagesSECTION 03380 Post-Tensioned Concrete Rev 1Abdalrahman AntariNo ratings yet
- Folder Hexa EngDocument8 pagesFolder Hexa EngMuresan MVNo ratings yet
- Jane EyreDocument165 pagesJane EyreSana AbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- WorkbookEdition 12 A Theory of HumorismDocument4 pagesWorkbookEdition 12 A Theory of HumorismMabel Ferr50% (2)
- Different Surgical Modalities For Management of Postburn FL Exion Contracture of The ElbowDocument6 pagesDifferent Surgical Modalities For Management of Postburn FL Exion Contracture of The ElbowMadhuchandra HirehalliNo ratings yet
- Kristeva On Melanie Klein's "Oresteia"Document6 pagesKristeva On Melanie Klein's "Oresteia"danthetoasterNo ratings yet
- E 242 - 95 R00 - Rti0mi1sruq - PDFDocument5 pagesE 242 - 95 R00 - Rti0mi1sruq - PDFLeón SuárezNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Breathing Exercise On Reducing Pain Perception and State Anxiety Among Primi ParturientsDocument8 pagesEffectiveness of Breathing Exercise On Reducing Pain Perception and State Anxiety Among Primi ParturientsPutra SpNo ratings yet