Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mitutoyo Hardness Minimum Thickness Specimen
Uploaded by
Isaac MartinezOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mitutoyo Hardness Minimum Thickness Specimen
Uploaded by
Isaac MartinezCopyright:
Available Formats
Quick Guide to Precision Hardness Testing Machines
Measuring Instruments
Methods of Hardness Measurement
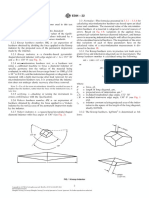
(1) Vickers (2) Knoop
Vickers hardness is a test method that has the widest application range, As shown in the following formula, Knoop hardness is a value obtained
allowing hardness inspection with an arbitrary test force. This test has by dividing test force by the projected area A (mm2) of an indentation,
an extremely large number of application fields particularly for hardness which is calculated from the longer diagonal length d (mm) of the
tests conducted with a test force less than 9.807 N (1 kgf). As shown indentation formed by pressing a rhomboidal diamond indenter (oppo-
in the following formula, Vickers hardness is a value determined by sing edge angles of 172˚30' and 130˚) into a specimen with test force F
dividing test force F (N) by contact area S (mm2) between a specimen applied. Knoop hardness can also be measured by replacing the Vickers
and an indenter, which is calculated from diagonal length d (mm, mean indenter of a microhardness testing machine with a Knoop indenter.
of two directional lengths) of an indentation formed by the indenter
F F F F F: N
(a square pyramidal diamond , opposing face angle θ=136˚) in the HK=k =0.102 =0.102 2 =1.451 2 d: mm
specimen using a test force F (N). k is a constant (1/g =1/9.80665). A A cd d c: Constant
F F
HV=k =0.102 =0.102 2Fsin 2 F
=0.1891 2
q
F: N (3) Rockwell and Rockwell Superficial
S S d2 d d: mm
To measure Rockwell or Rockwell Superficial hardness, first apply a
preload force and then the test force to a specimen and return to the
The error in the calculated Vickers hardness is given by the following preload force using a diamond indenter (tip cone angle: 120˚, tip radius:
formula. Here, Dd1, Dd2, and ‘a’ represent the measurement error that 0.2 mm) or a sphere indenter (steel ball or carbide ball). This hardness
is due to the microscope, an error in reading an indentation, and the value is obtained from the hardness formula expressed by the difference
length of an edge line generated by opposing faces of an indenter tip, in indentation depth h (µm) between the preload and test forces.
respectively. The unit of Dq is degrees. Rockwell uses a preload force of 98.07 N, and Rockwell Superficial
29.42 N. A specific symbol provided in combination with a type of
DHV DF Dd1 Dd2 a2
-2 -2 - 2 3.5×10 -3Dq indenter, test force, and hardness formula is known as a scale. Japanese
HV F d d d
Industrial Standards (JIS) define various scales of related hardness.
Relationship between Vickers Hardness and the Relationship between Rockwell/Rockwell Superficial
Minimum Allowable Thickness of a Specimen Hardness and the Minimum Thickness of a Specimen
Hardness symbol Test force
F: N 1.8 3.3 1.4
HV0.0005 4.903×10 -3 1.7 3.15
Minimum thickness of specimen (mm)
Minimum thickness of specimen (mm)
Minimum thickness of specimen (mm)
1.6 3 1.2
Minimum thickness Diagonal length 0.001 9.807×10 -3 1.5 2.85
of specimen of indentation 1.4 1.0
0.002 1.3 2.7
t: mm d: mm 19.61×10 -3
1.2 2.55 0.8
0.001 0.003 29.42×10 -3 1.1 2.4
0.001 0.005 49.03×10 -3 1.0 2.25 0.6
0.002 0.9 2.1
d Vickers hardness 0.003 0.002 0.01 98.07×10 -3 0.8 1.95 0.4
HV 0.003 0.7
0.005 0.02 0.1961 0.6 1.8
0.2
2000 0.005 0.03 0.2942 0.5 1.65
0.01 0.4 1.5 0
1000 0.01 0.05 0.4903 0.3 1.35 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
h
0.02
t
0.2 1.2
500 0.03 0.02 0.1 0.9807 0.1 1.05
300 0.05 0.03 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
0.2 1.961 0.9
F 200 0.05 0.3 2.942 0.75
HV=0.1891 2 0.1 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
t>1.5d d 0.1 0.5 4.903
100
h≒ d/7 0.2
50 0.3 0.2 1 9.807
t : Thickness of specimen (mm) 0.3
30 0.5 2 19.61
d: Diagonal length (mm) 20 0.5 3 29.42 Rockwell hardness
h: Depth of indentation (mm) 1
1 5 49.03
[Example] 2 Rockwell Superficial hardness
Specimen thickness t: 0.15 mm 3 2 10 98.07
Specimen hardness: 185 HV1 20 196.1
Test force F: 9.807 N (1 kgf) 30 294.2 Rockwell hardness
Diagonal length d: 0.1 mm 50 490.3
M
Rockwell Hardness Scales Rockwell Superficial Hardness Scales
Scale Indenter Test force Application Scale Indenter Test force Application
A 588.4 N Carbide, sheet steel 15-N 147.1 N
Thin surface-hardened layer on steel such
D Diamond 980.7 N Case-hardened steel 30-N Diamond 294.2 N
Steel (100 HRB or more to 70 HRC or less) as carburized or nitrided
C 1471 N 45-N 441.3 N
F Sphere of 588.4 N Bearing metal, annealed copper 15-T Sphere of 147.1 N
B 1.5875 mm 980.7 N Brass 30-T 1.5875 mm 294.2 N Sheet of mild steel, brass, bronze, etc.
G diameter 1471 N Hard aluminum alloy, beryllium copper, phosphor bronze 45-T diameter 441.3 N
H Sphere of 588.4 N Bearing metal, grinding wheel 15-W Sphere of 147.1 N
E 3.175 mm 980.7 N Bearing metal 30-W 3.175 mm 294.2 N Plastic, zinc, bearing alloy
K diameter 1471 N Bearing metal 45-W diameter 441.3 N
L Sphere of 588.4 N 15-X Sphere of 147.1 N
M 6.35 mm 980.7 N Plastic, lead 30-X 6.35 mm 294.2 N Plastic, zinc, bearing alloy
P diameter 1471 N 45-X diameter 441.3 N
R Sphere of 588.4 N 15-Y Sphere of 147.1 N
S 12.7 mm 980.7 N Plastic, lead 30-Y 12.7 mm 294.2 N Plastic, zinc, bearing alloy
V diameter 1471 N 45-Y diameter 441.3 N
M-9 Mitutoyo reserves the right to change any or all aspects of any product specification, including prices, designs and service content, without notice.
You might also like
- ASTM E384 (2022) - Part2Document1 pageASTM E384 (2022) - Part2david4231993No ratings yet
- ASTM E384 (2022) - Part7Document1 pageASTM E384 (2022) - Part7david4231993No ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument15 pagesHardness TestHossam SallamNo ratings yet
- Micro Hardness Tester Manual Book HVD-1000AP MPDocument38 pagesMicro Hardness Tester Manual Book HVD-1000AP MPDaisy HeNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material Lab Manual: Mechanical Engineering Second Year Section B, B - 2Document27 pagesStrength of Material Lab Manual: Mechanical Engineering Second Year Section B, B - 2Satvik YelluriNo ratings yet
- Hardness Test: I.e., Brinell Hardness Test, Rockwell Hardness Test, and Vickers Hardness Test. TheyDocument4 pagesHardness Test: I.e., Brinell Hardness Test, Rockwell Hardness Test, and Vickers Hardness Test. Theykostas.sierros9374No ratings yet
- MCE12L Activity No. 4 Hardness DeterminationDocument7 pagesMCE12L Activity No. 4 Hardness DeterminationAlex XanderNo ratings yet
- Indian Institute of Technology, Guwahati: Laboratory SheetDocument6 pagesIndian Institute of Technology, Guwahati: Laboratory SheetKamini GoyalNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestsDocument12 pagesHardness TestsHossam SallamNo ratings yet
- Table of Hardness of SteelsDocument48 pagesTable of Hardness of SteelsRicardo F.A.No ratings yet
- ASTM E92 Vickers Hardness of Metallic MaterialsDocument9 pagesASTM E92 Vickers Hardness of Metallic MaterialsUNAQ ManufacturaNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Hardness TesterDocument22 pagesInstruction Manual: Hardness TesterAziz OstencoNo ratings yet
- Hardness Test: NO: 3 Supervised By: Dr. OsmanDocument9 pagesHardness Test: NO: 3 Supervised By: Dr. Osmanwrya hussainNo ratings yet
- Hardness Test MethodsDocument7 pagesHardness Test MethodsParveen (Atam Valves)No ratings yet
- Yarmouk University Hijjawi Faculty For Engineering Technology Department of Industrial EngineeringDocument7 pagesYarmouk University Hijjawi Faculty For Engineering Technology Department of Industrial EngineeringMohmmad P.AlshormanNo ratings yet
- Hardness TheoryDocument4 pagesHardness Theorykostas.sierros937491% (11)
- Astm E92 PDFDocument9 pagesAstm E92 PDFoscar_sm77No ratings yet
- Nano IndentationDocument43 pagesNano Indentationportakal0660No ratings yet
- Hardness TestingDocument11 pagesHardness TestingJeyakumar JamesNo ratings yet
- Macro and Micro Hardness Testing: A.R.G Sreekar, M M 1 2 B 0 0 2Document6 pagesMacro and Micro Hardness Testing: A.R.G Sreekar, M M 1 2 B 0 0 2Arg SreekarNo ratings yet
- 穆賢 K1006117 HardnessTestDocument18 pages穆賢 K1006117 HardnessTestMuhammad AbizardNo ratings yet
- Vickers Test PresentationDocument21 pagesVickers Test PresentationnailamushNo ratings yet
- Vickers Hardness TestDocument3 pagesVickers Hardness TestAkhil KSNo ratings yet
- Brinell Hardness Test: Name: Amishasharon Rajavijai Sahidha Roll Number: 111120011Document7 pagesBrinell Hardness Test: Name: Amishasharon Rajavijai Sahidha Roll Number: 111120011Amisha SharonNo ratings yet
- HardnessDocument11 pagesHardnessglorialidwin.b dace mechNo ratings yet
- Input Data: Package: Bridge Name: Pier Name: 1. General Input DataDocument7 pagesInput Data: Package: Bridge Name: Pier Name: 1. General Input DataTuanNo ratings yet
- Vickers Hardness Test: Strength-Of-Materials Lab (../index - HTML)Document3 pagesVickers Hardness Test: Strength-Of-Materials Lab (../index - HTML)Ivan Camilo Joya PaezNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual For Tensile TestDocument7 pagesLab Manual For Tensile TestJIA PERN TANNo ratings yet
- Material and Design Vickers Hardness Test HardnessDocument2 pagesMaterial and Design Vickers Hardness Test HardnessDhinesh KarthickNo ratings yet
- Input Data: Package: Bridge Name: Pier Name: 1. General Input DataDocument7 pagesInput Data: Package: Bridge Name: Pier Name: 1. General Input DataTuanNo ratings yet
- Determining Permitivity and Force Between Parallel PlatesDocument2 pagesDetermining Permitivity and Force Between Parallel PlatesTumzangwanaNo ratings yet
- HSDD AppxCDocument31 pagesHSDD AppxCSharifNo ratings yet
- Torsion TestingDocument10 pagesTorsion TestingSean BruegmanNo ratings yet
- ENG - 7 - Electrical Resistance Strain Gages PDFDocument16 pagesENG - 7 - Electrical Resistance Strain Gages PDFBogdan BumbaceaNo ratings yet
- Torque Reference Transducer: Special FeaturesDocument6 pagesTorque Reference Transducer: Special FeaturesdabafiNo ratings yet
- Standard Test Method For Vickers Hardness of Metallic MaterialsDocument10 pagesStandard Test Method For Vickers Hardness of Metallic MaterialsSanjay RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Temple FACILITY Circular Slab DesignDocument1 pageTemple FACILITY Circular Slab Designselvakumar sNo ratings yet
- R WK YOs ADjbn 5 VSL FIv JFDocument15 pagesR WK YOs ADjbn 5 VSL FIv JF9bshrutiyadav16No ratings yet
- Finalized Panaflex of Vickers Hardness TestDocument2 pagesFinalized Panaflex of Vickers Hardness TestMohsin QaziNo ratings yet
- Vickers Hardness Test: Indian Institute of Space Science and TechnologyDocument5 pagesVickers Hardness Test: Indian Institute of Space Science and TechnologySarath Krishnan SNo ratings yet
- Complementary XRD-Prof. GolestanifardDocument28 pagesComplementary XRD-Prof. Golestanifardmohammad zareNo ratings yet
- Design of Trade Off III Precast ConcreteDocument9 pagesDesign of Trade Off III Precast ConcretemateojullieanneNo ratings yet
- Connections With DowelsDocument5 pagesConnections With DowelsmathuNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument6 pagesLab ReportDulshan uddeepanaNo ratings yet
- Hardness TestDocument5 pagesHardness TestkoteangNo ratings yet
- School of Mechanical EngineeringDocument50 pagesSchool of Mechanical EngineeringCrank OBSNo ratings yet
- Calculation Table For Bridge Approach Slab: I.LoadsDocument7 pagesCalculation Table For Bridge Approach Slab: I.LoadsNguyễn Duy TânNo ratings yet
- Hardness Test and Mechanical PropertiesDocument15 pagesHardness Test and Mechanical PropertiesMitzySolòrzanoNo ratings yet
- Hardness Test: Hardness Is A Measure of The Resistance To Localized Plastic Deformation Induced by EitherDocument6 pagesHardness Test: Hardness Is A Measure of The Resistance To Localized Plastic Deformation Induced by EitherApril FlowerNo ratings yet
- ME 215 - Engineering Materials I: Hardness and Hardness Testing (Part I) Hardness and Hardness Testing (Part I)Document17 pagesME 215 - Engineering Materials I: Hardness and Hardness Testing (Part I) Hardness and Hardness Testing (Part I)Emrecan LuşNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics MCQDocument138 pagesClass 11 Physics MCQTushar RanaNo ratings yet
- 200 THK Grade Slab-50kn Variable Load-With FibreDocument7 pages200 THK Grade Slab-50kn Variable Load-With FibreFazilat Mohammad Zaidi0% (1)
- BMT Lab ManualDocument75 pagesBMT Lab Manualnenu localNo ratings yet
- ET Lab ManualDocument14 pagesET Lab ManualANANDKUMAR SNo ratings yet
- Alat Uji Kekerasan VickersDocument3 pagesAlat Uji Kekerasan VickersVania AmandaNo ratings yet
- Hardness Test-Dr - Mona LectureDocument19 pagesHardness Test-Dr - Mona LecturehusseinNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Ship Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesFrom EverandShip Magnetism and the Magnetic Compass: The Commonwealth and International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Liberal Studies: Navigation and Nautical CoursesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Pro DrugDocument4 pagesPro DrugIbnu SinaNo ratings yet
- Toksikologi MerkuriDocument31 pagesToksikologi MerkuriRisvy MokoalungNo ratings yet
- Aqa 74083ba QP Jun22Document16 pagesAqa 74083ba QP Jun22tzg163No ratings yet
- Santhosh P Nano Technology PPT 1Document7 pagesSanthosh P Nano Technology PPT 1ASHWIN MNo ratings yet
- Gyroscope ReportDocument3 pagesGyroscope ReportSam DrydenNo ratings yet
- KLM Refining Technical Rev 3Document6 pagesKLM Refining Technical Rev 3Muhammad Abdul RaufNo ratings yet
- How Elements in The Universe Are FormedDocument19 pagesHow Elements in The Universe Are FormedMary Joy Llosa RedullaNo ratings yet
- Gas Treating Products and ServicesDocument16 pagesGas Treating Products and ServicesphantanthanhNo ratings yet
- Zinc Clad Ii PlusDocument4 pagesZinc Clad Ii Plusjdiaz87No ratings yet
- Food TestsDocument2 pagesFood TestsRheynel NietesNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic WavesReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- SAIOH 1 Tutorial Ventilation PDFDocument25 pagesSAIOH 1 Tutorial Ventilation PDFAbhishek C MNo ratings yet
- Mcq-1 (Work, Energy and Power)Document3 pagesMcq-1 (Work, Energy and Power)Fluorine ToxicNo ratings yet
- Chemical Design of Heat Exchanger TerdesakDocument22 pagesChemical Design of Heat Exchanger TerdesakNor Ain100% (4)
- INDMAX Technology: Light Olefins From Petroleum Residue: Background Process DescriptionDocument2 pagesINDMAX Technology: Light Olefins From Petroleum Residue: Background Process DescriptionChakravarthy BharathNo ratings yet
- Ferraro, Nakamoto, Brown - 2003 - Introductory Raman Spectroscopy Second EditionDocument4 pagesFerraro, Nakamoto, Brown - 2003 - Introductory Raman Spectroscopy Second EditionMax Jordan DooleyNo ratings yet
- Formula Writing and Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds Involving Rare Earth ElementsDocument2 pagesFormula Writing and Nomenclature of Inorganic Compounds Involving Rare Earth ElementsReinette MelodiaNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics CompiledDocument127 pagesThermodynamics CompiledShane Buraga100% (3)
- Casting DefectsDocument57 pagesCasting DefectsFajar SiradzNo ratings yet
- Mya Mya Khin M.eng ThesisDocument142 pagesMya Mya Khin M.eng ThesisAvinash VankadaruNo ratings yet
- EN - Panlube S 37Document4 pagesEN - Panlube S 37Vinodh Kanna100% (1)
- Etm 22 05 10750Document9 pagesEtm 22 05 10750Trần Thị Nguyên KhaiNo ratings yet
- Paclitaxel-Nanodiamond Nanocomplexes Enhance Aqueous Dispersibility and Drug Retention in CellsDocument35 pagesPaclitaxel-Nanodiamond Nanocomplexes Enhance Aqueous Dispersibility and Drug Retention in CellsMarcos Lopez-CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Anachem AnalysisDocument1 pageAnachem AnalysisdanicaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kimia Sains Dan AplikasiDocument3 pagesJurnal Kimia Sains Dan AplikasiMelinaNo ratings yet
- Lunar Surface Colony U of Houston 1972Document529 pagesLunar Surface Colony U of Houston 1972Aaron RizzioNo ratings yet
- Lab Report (Exp 1)Document11 pagesLab Report (Exp 1)NorfaizahNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PDF (16-19) PDFDocument21 pagesCurrent Electricity PDF (16-19) PDFCed HernandezNo ratings yet
- Biomolcules (Week 3) (AutoRecovered)Document6 pagesBiomolcules (Week 3) (AutoRecovered)JoshRobertD.ObaobNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Comprehensive ExaminationDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology - Comprehensive ExaminationDiana Jean Alo-adNo ratings yet