Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry
Uploaded by
pcgurukotari9Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry
Uploaded by
pcgurukotari9Copyright:
Available Formats
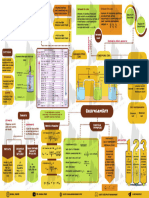
Electrode potential
Bridge
U shaped inverted Faraday 2nd Law
Salt
Also know
n as D tube connecting two Faraday 1st Law
Potential difference aniel Cell:
between electrode and electrolyte solution • Amount of chemical reactions • Amount of substance deposited
at electrodes during Nature of
electrolyte. which occurs at any electrode
Cathode: Copper electrolysis is proportional to Electrode
Ecell = Eright – Eleft during electrolysis by a current is
o o
Anode
Anode: Zinc proportional to the quantity of their chemical equivalent
Negatively charged
Salt bridge: Agar-Agar
Oxidation takes place electricity passed weights → W W W Medium of
Electrolyte: ZnSO4 , CuSO4 through electrolyte → 1 = 2 = 3 Electrolyte
Cell reaction: E1 E2 E3
Zn+ CuSO4 ZnSO4 + Cu W = zit
Cathode
Cell representation: Positively charged Faraday
Zn(s)| ZnSO4(Sol) || CuSO4(sol) | Cu (s) Laws
Quantitative
reduction takes place
Qualitative aspect depend on
Aspects
Device converting chemical
energy into electrical energy.
Electrochemical series
The arrangement of various electrodes in the
Corrosion increasing order of standard reduction Galvanic/Voltic
Standard Hydrogen Electrode potentials. Cell Electrolytic Cell
Electrochemical (SHE) Reduction Half-Reaction E°(V) Device converting
phenomenon in which Stronger F2(g) + 2e − →
2F−(aq) 2.87 Weaker electrical energy
metal oxide of metal oxidizing H2O2(aq) + 2H+(aq) + 2e − →
2 H2 O (l) 1.78 reducing
agent MnO4− (aq) + 8H +(aq) + 5e − →
Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2 O(l) 1.51 agent into chemical energy.
forms coating on Cl 2(g) + 2e − →
2Cl −(aq) 1.36 Salt Bridge
metal surface. Hydrogen gas Cr 2O22− (aq) + 14H+(aq) + 6e − →
2Cr 3+ (aq) + 7H2O (l) 1.33
at 1 atm
O2(g) + 4H+(aq) + 4e − →
2H2O(l) 1.23
Prevention Br 2(aq) + 2e − →
2Br −(aq) 1.09
Ag (aq) + e
+ − →
Ag(s) 0.80 Anode Anode
• Painting, barrier Fe3+(aq) + e − →
2Fe2+ (aq) 0.77 Electrode Cathode
Cathode
protection, rust Platinum foil +
O2(g) + 2H (aq) + 2e − →
H2O2 (aq) 0.70 Electrodes Anode → Positively charged;
solutions. Hydrogen ion I2(s) + 2e − →
2I (aq)
−
0.54
oxidation occurs
O2(g) + 2H2O(l) + 4e− →
4OH−(aq) 0.40
Cu2+(aq) + 2e − →
Cu(s) 0.34 Cathode → Negetively charged;
Example
Sn 4+(aq) + 2e − →
Sn 2+(aq) 0.15 Reduction occurs
0 2H (aq) + 2e
+ − →
H2(g) 0 Electrolyte
For SHE, E cell = 0
Pb2+(aq) + 2e − Pb(s) 0.13
• Rusting of iron.
→ −
Ni 2+(aq) + 2e − →
Ni(s) −
0.26
• tarnishing of Electrolyte
Cd (aq) + 2e
2+ − →
Cd(s) 0.40
−
Silver. Fe2+(aq) + 2e − →
Fe(s) 0.45
Zn 2+(aq) + 2 e− →
Zn(s) −
0.76
2H2O(l) + 2e− →
H2(g) + 2OH−(aq) −
0.83
Al 3+(aq) + 3e − →
Al(s) 1.66
Cell representation
Weaker
Mg2+(aq) + 2e −
oxidizing Na +(aq) + e −
→
→
Mg(s)
Na(s)
−
−
2.37
2.71
Stronger
reducing
Electrochemistry Oxidation Reduction
Battery agent
Li+(aq) + e − →
Li(s) −
3.04
agent
half half
Primary Battery secondary Battery
• reaction occurs Can be recharged Nernst Equation Electrical
only once. by passing current
Properties
• cannot be reuse. in opposite direction.
• For reaction: Mn + + ne − → M(s)
2.303 RT 1
E = E° − log n Kohlrausch's
nF [M + ] APPLICATION
1 law of Independent
• Conductance [G] = Resistance Migration of Ions
Mercury Leclanche Lead storage • For reaction: aA + bB cC + dD unit: Ohm-1 or Siemens
cell battery 2.303RT [C]c [D]d l l At infinite
(dry cell) (Ni-cd cell) Ecell = Ecell
− log a b • Specific conductivity (K) = G = cell constant dilution the To To To
nF [A] [B] a a
-1 molar determine calculate calculate
unit: Ohm-1 cm or S cm-1
conductivity Λm & Λeq degree dissociation
• At Equilibrium Ecell = 0
• Molar conductance (Λm) = 1000 × K of electrolyte of weak of constant
ANODE: Zn - Hg ANODE; Zn ANODE; Pb
1 M is given by sum electrolyt dissociatio of weak
CATHODE; Graphite CATHODE; Pb + PbO
2.303 RT unit: Scm- mol-1 of ionic -es at n: (α) Electrolye
CATHODE:
ELECTROLYTE: ELECTROLYTE; E° cell = log Kc
paste of HgO & C nF • Equivalent conductance (Λeq) = 1000 × K conductivities infinite c
H2SO4 (38% By mass) Λm
α2
kc = c
Powderd MnO2 + C + dilution. α=
of cation & 0
ELECTROLYTE: N Λm
Paste of NH4Cl + ZnCl2 unit: cm2 ohm−1 g − eq−1 anions. 1- α
paste of KOH + ZnO
0
• ∆G = −nFEcell or ∆G = − nFEcell
0 0 0
Λ m = ν +λ + + ν− λ−
anand_mani16 DR. Anand Mani https://www.anandmani.com/ https://discord.io/anandmani t.me/anandmani001
You might also like
- Electrochemistry 2022 by Bharat PanchalDocument15 pagesElectrochemistry 2022 by Bharat PanchalMuskan somkunwar92% (12)
- ASTM A453 Grade 660 - Class A/B/C/D PDF Edition 2017Document7 pagesASTM A453 Grade 660 - Class A/B/C/D PDF Edition 2017ASTM A453 Grade 660 TorqboltNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Kinetics: Theoretical AspectsFrom EverandElectrochemical Kinetics: Theoretical AspectsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- ACEGrid® Uniaxial Geogrid TDS PDFDocument1 pageACEGrid® Uniaxial Geogrid TDS PDFJuan MansillaNo ratings yet
- Chem U5 A2 EdexcelDocument48 pagesChem U5 A2 EdexcelReez SinhaNo ratings yet
- Catalogo Compressores EmbracoDocument41 pagesCatalogo Compressores EmbracoTabulla GamesNo ratings yet
- Vendor List IMP DataDocument25 pagesVendor List IMP DataSuraj RajputNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument1 pageElectrochemistryNishant SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- B3 ElectrochemistryDocument1 pageB3 ElectrochemistryGurwinder Singh 10 jasmineNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry NotesDocument18 pagesElectrochemistry NotesYahya RajputNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument33 pagesElectrochemistryAli SaqibNo ratings yet
- Lecture 15.1 - Electrochemical CellsDocument7 pagesLecture 15.1 - Electrochemical CellsLiam DoranNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 1 AVLD55rb4eu8ODpKDocument20 pagesElectrochemistry 1 AVLD55rb4eu8ODpKakshitrajesh2020No ratings yet
- Biopotential Electrodes: Subjects Covered in Chapter 5Document14 pagesBiopotential Electrodes: Subjects Covered in Chapter 5Francy Irudaya Rani ENo ratings yet
- The Potential Profile in Electrochemical Cells: Does The Current Flow Backwards Inside A Battery?Document30 pagesThe Potential Profile in Electrochemical Cells: Does The Current Flow Backwards Inside A Battery?Felipe Cepeda SilvaNo ratings yet
- ElectrolysisDocument17 pagesElectrolysisMUHAMAD ASHRAF BIN NORDINNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument23 pagesElectrochemistryStarsNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Term 2Document12 pagesElectrochemistry Term 2shivaniNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School Class 12 - Chemistry Chapter 3:electrochemistryDocument9 pagesDelhi Public School Class 12 - Chemistry Chapter 3:electrochemistryAvishi OjNo ratings yet
- BM6504U1LS02 Electrode Electrolyte InteraceDocument24 pagesBM6504U1LS02 Electrode Electrolyte InteracePrasidha PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5 - ElectrodesDocument30 pagesLecture-5 - ElectrodesMurali krishnan.MNo ratings yet
- BS MME 2024 Lec#9Document20 pagesBS MME 2024 Lec#9maqsood3982No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Notes EditedDocument22 pagesElectrochemistry Notes EditedKrrish GehlotNo ratings yet
- Ec Notes-1Document11 pagesEc Notes-1Adithyan & AnandNo ratings yet
- Redox Equilibria: N GoalbyDocument12 pagesRedox Equilibria: N GoalbyImmanuel LashleyNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 2023Document16 pagesElectrochemistry 2023Arush GautamNo ratings yet
- Electro ChemistryDocument5 pagesElectro ChemistryPRanavNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: Quick RevisionDocument31 pagesElectrochemistry: Quick Revisionfakeheartattack8kNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes 2 ED 2023-2024 16914091918462134464d0db27939a2Document8 pagesLecture Notes 2 ED 2023-2024 16914091918462134464d0db27939a2rama09092006No ratings yet
- Physics Electric CurrentDocument11 pagesPhysics Electric CurrentYoNo ratings yet
- Ionic and Electronic DC Conduction - ElectrochemistryDocument27 pagesIonic and Electronic DC Conduction - ElectrochemistryWilliam Sin Chau WaiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry G12 U4 Section 1Document53 pagesChemistry G12 U4 Section 1kalayouNo ratings yet
- Omd551 Bbi Notes Unit-1Document52 pagesOmd551 Bbi Notes Unit-1Krishnan GnanasekarNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument6 pagesElectrochemistryGovind ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Biopotential ElectrodesDocument45 pagesBiopotential ElectrodesEnjitaJiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document45 pagesLecture 5nanda1369100% (1)
- ElectrochemistryDocument9 pagesElectrochemistryTharki SaitamaNo ratings yet
- IAL Topic 16 NotesDocument11 pagesIAL Topic 16 NotesCharlotte NgaiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Potentiometry 2013Document52 pages2 - Potentiometry 2013KurniaAnisaNo ratings yet
- Summary of Photoelectric Effect, Dual Nature, X RaysDocument44 pagesSummary of Photoelectric Effect, Dual Nature, X RaysBadri MishraNo ratings yet
- Electochemistry Vedantu TATVADocument13 pagesElectochemistry Vedantu TATVAPRAVIN SNo ratings yet
- 30 Minutes ElectrochemistryDocument28 pages30 Minutes ElectrochemistryDharmikNo ratings yet
- Redox Equilibria: Electrochemical CellsDocument9 pagesRedox Equilibria: Electrochemical Cells谭智林No ratings yet
- Qdoc - Tips - 118462525 Bgas Level 2 3 Q A Monday To FridaypdfDocument32 pagesQdoc - Tips - 118462525 Bgas Level 2 3 Q A Monday To Fridaypdf9440864459No ratings yet
- Lecture 2-3Document30 pagesLecture 2-3ghidaaNo ratings yet
- Conduct o Me TryDocument111 pagesConduct o Me Tryimdevil1206No ratings yet
- NotesDocument202 pagesNotessaikarthick023No ratings yet
- Chap 2-1. OverpotentialDocument21 pagesChap 2-1. Overpotential맛있는감자No ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapapi-506717172No ratings yet
- Redox Equilibria: Electrochemical CellsDocument10 pagesRedox Equilibria: Electrochemical CellsKanishq GoswamiNo ratings yet
- Electrodes CH 5Document45 pagesElectrodes CH 5shilgiri100% (1)
- Basic Concepts in ElectrochemistryDocument19 pagesBasic Concepts in Electrochemistrynoor saqibNo ratings yet
- Article Careers360 20220319230040Document17 pagesArticle Careers360 20220319230040Sharon singhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7 Electrodes CH 5Document52 pagesLecture 7 Electrodes CH 5api-27535945100% (1)
- A2 Chem Unit 5Document47 pagesA2 Chem Unit 5Bill CipherNo ratings yet
- ELEC E8174 Homework 3 2019Document4 pagesELEC E8174 Homework 3 2019Joshua LunguNo ratings yet
- Electro ChemistryDocument30 pagesElectro ChemistryPower booster100% (1)
- 2 e Lech Tro ChemistryDocument39 pages2 e Lech Tro ChemistryrahmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Electrogravimetry and CoulometryDocument36 pagesUnit 5 Electrogravimetry and CoulometryAzzah Dyah Pramata67% (3)
- Life ELNA Technical NoteDocument9 pagesLife ELNA Technical NotejohnNo ratings yet
- CTSC Matric Masterclasses Electrochemistry 2020-1Document17 pagesCTSC Matric Masterclasses Electrochemistry 2020-1Nika ReleniNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument66 pagesElectrochemistryDeepti JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Atomic BondingDocument23 pagesChapter 1 Atomic BondingLatisha AnthonyNo ratings yet
- EcosystemDocument7 pagesEcosystempcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- Prayas 3.0 Anatomy of PlantsDocument47 pagesPrayas 3.0 Anatomy of Plantspcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Q.Document45 pagesAnimal Kingdom Q.pcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- PW Physics 12th MarathonDocument503 pagesPW Physics 12th Marathonpcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- 001 Optics and Modern PhysicsDocument70 pages001 Optics and Modern Physicspcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- FGFDocument15 pagesFGFpcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- HgyDocument22 pagesHgypcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- Tym Test Planner Phase 2Document8 pagesTym Test Planner Phase 2pcgurukotari9No ratings yet
- Energy-Changes-And-Rates-Of-Reaction CheatsheetDocument4 pagesEnergy-Changes-And-Rates-Of-Reaction CheatsheetMaryam SameerNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kai HPLCDocument16 pagesJurnal Kai HPLCdenanurbaniazharNo ratings yet
- El-Lene-H1000pc Resina Ingresa 24.06.14 Confirmar Hoja Tec Con ProveedorDocument1 pageEl-Lene-H1000pc Resina Ingresa 24.06.14 Confirmar Hoja Tec Con ProveedorJose BustosNo ratings yet
- Dowex-Marathon-A RESINA ANIÔNICADocument3 pagesDowex-Marathon-A RESINA ANIÔNICAMarcus FreitasNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Manufacturing ReportDocument30 pagesAluminum Manufacturing ReportmalynNo ratings yet
- Marley Superior Double-Sided Radiant BarrierDocument5 pagesMarley Superior Double-Sided Radiant BarrierDozer122No ratings yet
- JIGGYDocument5 pagesJIGGYAyxiahmei MirandoNo ratings yet
- GC Detector Design Troubleshooting Flame Ionization Fid Theory Basics Gas Flows July212020Document34 pagesGC Detector Design Troubleshooting Flame Ionization Fid Theory Basics Gas Flows July212020Anonymous w7gZFE8No ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument49 pagesChemistryAnam FNo ratings yet
- Cannabis Sativa Bioactive Compounds and TheirDocument15 pagesCannabis Sativa Bioactive Compounds and TheirSORIN AVRAMESCUNo ratings yet
- "Paints Version 2.6" Certification Criteria: Eco Mark Product Category No.126Document11 pages"Paints Version 2.6" Certification Criteria: Eco Mark Product Category No.126Hengchhorn PhaiNo ratings yet
- Carboline Carbothane 133 HBDocument5 pagesCarboline Carbothane 133 HBArturo SalinasNo ratings yet
- CtfileDocument90 pagesCtfileAnda AndutzaNo ratings yet
- Aits 1718 CRT I Jeea Paper 2 PDFDocument20 pagesAits 1718 CRT I Jeea Paper 2 PDFShreyansh SaxenaNo ratings yet
- MSC Exam Spectroscopy 2018 FINALDocument2 pagesMSC Exam Spectroscopy 2018 FINALPaige MunroeNo ratings yet
- Shrinkage Losses - 2 PDFDocument5 pagesShrinkage Losses - 2 PDFManisha ShewaleNo ratings yet
- AIEEEMainPaper Code ADocument37 pagesAIEEEMainPaper Code ArohitrtNo ratings yet
- Aqa 8464C1F QP Jun18 PDFDocument24 pagesAqa 8464C1F QP Jun18 PDFMustafa NabeihNo ratings yet
- Coa CV - BpuDocument3 pagesCoa CV - BpuTKM PKYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Matter and Change: Taken From Modern Chemistry Written by Davis, Metcalfe, Williams & CastkaDocument42 pagesChapter 1 - Matter and Change: Taken From Modern Chemistry Written by Davis, Metcalfe, Williams & CastkaRawan YounisNo ratings yet
- PH 107.1 Final Laboratory ActivitiesDocument22 pagesPH 107.1 Final Laboratory ActivitiesRay MclifeNo ratings yet
- Theoretical and Examples Summary of Intro To Civil - MidTermDocument11 pagesTheoretical and Examples Summary of Intro To Civil - MidTermYou channelNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Atomic StructureDocument9 pagesTopic 1 Atomic StructurearyanNo ratings yet
- Sikagard 740W (CE)Document4 pagesSikagard 740W (CE)libyanengineerNo ratings yet
- Botany J-Adhikary Enzymology 4Document9 pagesBotany J-Adhikary Enzymology 4Dharmesh R.DNo ratings yet
- Ensuring Purity and Health: A Comprehensive Study of Water Quality Testing Labs in Solapur District For Community Well-BeingDocument11 pagesEnsuring Purity and Health: A Comprehensive Study of Water Quality Testing Labs in Solapur District For Community Well-BeingInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet