Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Amendments New
Uploaded by
santalicartoonwalaa0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views24 pagesOriginal Title
Amendments new
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views24 pagesAmendments New
Uploaded by
santalicartoonwalaaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 24
Constitutional Development of India
Constitution adopted and enacted on– 26 Nov 1949
Constitution came into force – 26 Jan 1950
Preamble was accepted on – 22 January 1947
National flag adopted on – 22 July 1947
National Song (Vande Matram) adopted on– 24 Jan 1950
Dr.Rajendra Prasad elected as first President of India
on - 24 Jan 1950
National Anthem (Jana Gana Mana) Adopted on– 24
Jan 1950
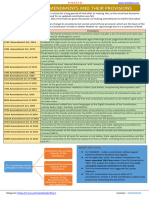
Recent Amendments
101 ST CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENT ACT 2016
GST was introduced
102 ND CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENT ACT 2018
Inserted Article 338B (NCBC) & 342A- OBC list Maintained
by President & Central Govt.
Constitutional Status was granted to The National
Commission for Backward Classes
103RD CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENT ACT 2019
Reservation For Economically Weaker Section
10% reservation to EWS in central govt. & private
educational institutions & central govt. jobs
104TH CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENT ACT 2019
Extension Of Reservation For SC/ST in Lok Sabha and
State Legislative Assembly For10 Years (Till 25th Jan
2030),
Abolished the Reservation for Anglo Indian in Lok
Sabha - Article 334
105TH CONSTITUTIONAL AMENDMENT ACT
15th August 2021
OBC Act
Amends provisions added by102nd Amendment
Which part of the Constitution deals with the
amendment to the Constitution and it’s procedure?
a) Part 19
b) Part 20
c) Part 21
d) Part 22
GST was introduced through which amendment act?
a) 101
b) 102
c) 103
d) 104
Which of the following constitutional amendments
provided for the Right to Education?
a) 88th
b) 87th
c) 87th
d) 86th
Who has the authority to amend the Indian
Constitution?
a) The President of India
b) The Prime Minister of India
c) The Parliament of India
d) The Supreme Court of India
The 10th Schedule of the Indian Constitution,
popularly known as the "Anti-Defection Law," was
added by which amendment?
a) 52nd Amendment
b) 61st Amendment
c) 73rd Amendment
d) 91st Amendment
The "basic structure" doctrine,which limits the
amending power of the Indian Parliament, was
established in which case?
a) Kesavananda Bharati v. State of Kerala
b) IndiraGandhi v. Raj Narain
c) MinervaMills v.UnionofIndia
d) Golaknathv. State of Punjab
Which amendment established the National Judicial
Appointments Commission (NJAC) for the
appointment of judges?
a) 99th Amendment
b) 100th Amendment
c) 101st Amendment
d) 102nd Amendment
Who can initiate the process of amending the Indian
Constitution?
a) Only the President of India
b) Only the Prime Minister of India
c) Only Members of Parliament
d) Any member of the Parliament
From Constitution of which country, Indian
Constitution borrowed the provision for ‘Procedure
for amendment of the Constitution’?
a) USA
b) Japan
c) Australia
d) South Africa
A constitutional amendment bill can be introduced in
which house of Parliament?
a) Rajya Sabha (Council of States)
b) Lok Sabha (House of the People)
c) Either Rajya Sabha or Lok Sabha
d) Both houses simultaneously
c) Either Rajya Sabha or Lok Sabha
Which of the following is not a part of the
amendment process of the Indian Constitution?
a) Introduction of the bill
b) Presidential assent
c) State ratification
d) Public referendum
Important Amendments
1ST AMENDMENT 1951
✓ added 9th schedule in Constitution
7TH AMENDMENT 1956
➢ Reorganization on of States
21ST AMENDMENT 1967
➢ Sindhi language was added in 8th schedule
42ND AMENDMENT 1976 – Mini Constitution
Added the words –Socialist, Secular, Integrity(SIS) in the
Preamble
Transferred from the state list to the concurrent list
1. Education
2. Forest
3. Weight & measure
4. Protection of wild animals and birds
5. Administration of justice
44TH AMENDMENT 1978
Right to property – Art 31 placed in Article 300-A as
legal right
52ND AMENDMENT 1985
➢ Anti defection law (10th schedule added)
61ST AMENDMENT 1989
➢ Age limit of voting reduced from 21 to 18
71ST AMENDMENT 1992
➢ Konkani, Manipuri& Nepali languages were added
73RD AND 74TH AMENDMENT 1992 & 1993
➢ Panchayats and Municipality
86TH AMENDMENT 2002
➢ Rightto education under Article 21-A
92ND AMENDMENT 2003
➢ Bodo,Dogri, Maithili & Santhali languages were
added in constitution Increases 18 to 22 (onwards)
Question For You My Dear All
Which of the following constitutional amendments
provided for the Right to Education?
a) 88th
b) 87th
c) 87th
d) 86th
You might also like
- Trusts & Estates Guide: Colorado MaterialsDocument5 pagesTrusts & Estates Guide: Colorado Materialsgerardchan0% (1)
- Exhibit 4 - Deed of Extrajudicial Settlement of Estate BDO (Joint)Document2 pagesExhibit 4 - Deed of Extrajudicial Settlement of Estate BDO (Joint)neilmijares23100% (1)
- Writ of Mandamus: Alleged Case No: 20 CR 599Document2 pagesWrit of Mandamus: Alleged Case No: 20 CR 599Alahdeen Moroc BeyNo ratings yet
- Ic MCQDocument27 pagesIc MCQChinnasamy100% (1)
- Legal GK QuestionsDocument32 pagesLegal GK QuestionsSanjana Dhankhar75% (24)
- Dean Navarro Lecture NotesDocument91 pagesDean Navarro Lecture NotesmayaNo ratings yet
- Indian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsFrom EverandIndian Polity with Indian Constitution & Parliamentary AffairsNo ratings yet
- Management of TrustsDocument4 pagesManagement of Trustsnikhil jkcNo ratings yet
- Indian PolityDocument67 pagesIndian PolityAshokkumar GanesanNo ratings yet
- Affidavit: Bashoy Located at Pulag, Bashoy, Kabayan, BenguetDocument1 pageAffidavit: Bashoy Located at Pulag, Bashoy, Kabayan, BenguetRoboan Bugtong Alvarez100% (1)
- Trust Deed SharesDocument4 pagesTrust Deed SharesIntanRiz100% (8)
- Constitution Worksheet KeyDocument3 pagesConstitution Worksheet KeyDanielle Praul50% (2)
- Succession EditedDocument134 pagesSuccession EditedRio AborkaNo ratings yet
- SSC CGL 2020 21 General Awareness Capsule For Tier 1 ExamDocument497 pagesSSC CGL 2020 21 General Awareness Capsule For Tier 1 ExamZahid WaniNo ratings yet
- Statutory Construction There Is A Need To Study This SubjectDocument33 pagesStatutory Construction There Is A Need To Study This SubjectAngel MeiNo ratings yet
- Major Amendments of Indian ConstitutionDocument35 pagesMajor Amendments of Indian ConstitutionlegitpreplawNo ratings yet
- AmendmentsDocument4 pagesAmendmentsyashvermaNo ratings yet
- 60 Amendments of Indian Constitution Q&ADocument17 pages60 Amendments of Indian Constitution Q&AVeeraVenkataSaiDurgaPrasad GubbalaNo ratings yet
- Important AmendmentsDocument1 pageImportant AmendmentsAmit 786No ratings yet
- Important Mcqs For Revision: Constitutional Amendments and ArticlesDocument29 pagesImportant Mcqs For Revision: Constitutional Amendments and Articlesangel angelNo ratings yet
- List of Important Amendments of The Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesList of Important Amendments of The Indian ConstitutionpreetamdasNo ratings yet
- Amendment Act (Top MCQ)Document25 pagesAmendment Act (Top MCQ)Anil YadavNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument10 pagesQuizbhanusree1312No ratings yet
- Amendments of The ConstitutionDocument22 pagesAmendments of The ConstitutionSAUMYAJIT SABUINo ratings yet
- Important Constitutional AmendmentsDocument3 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmentsNavya AroraNo ratings yet
- List of Imp Ammendments in Indian ConstitutionDocument9 pagesList of Imp Ammendments in Indian ConstitutionParveen SainiNo ratings yet
- Up PT Test-Ii 05-01-2023Document55 pagesUp PT Test-Ii 05-01-2023piyush ranjanNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments To The ConstitutionDocument6 pagesImportant Amendments To The ConstitutionprinceNo ratings yet
- DU Constitution of India 2018Document14 pagesDU Constitution of India 2018Vicky KumarNo ratings yet
- Indian Constitutional AmendmentsDocument2 pagesIndian Constitutional AmendmentsKESHAV BAHETI 12RNo ratings yet
- 60 Amendments of Indian Constitution MCQsDocument17 pages60 Amendments of Indian Constitution MCQsVeeraVenkataSaiDurgaPrasad GubbalaNo ratings yet
- Untitled DocumentDocument16 pagesUntitled Documentgagangautamedu.officialNo ratings yet
- Constitution of IndiaDocument45 pagesConstitution of Indiasagar gnNo ratings yet
- AmendmentsDocument13 pagesAmendmentsHot BoyNo ratings yet
- Important AmendmentDocument30 pagesImportant Amendmentomkumar7349No ratings yet
- Polity SSC CGL 2021 TIER 1Document13 pagesPolity SSC CGL 2021 TIER 1Atul AnandNo ratings yet
- Amendments in Indian Constitution:: First Amendment Act, 1951Document16 pagesAmendments in Indian Constitution:: First Amendment Act, 1951zahawaahmadNo ratings yet
- (Coi) Constitution of India Notes 2020. Cs ExamsquadDocument35 pages(Coi) Constitution of India Notes 2020. Cs ExamsquadRittik PrakashNo ratings yet
- Important Constitutional AmendmentsDocument6 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmentsAAYUSH SAXENANo ratings yet
- Indian Constitution and Constitutional History 2: Amendment C) 43Document5 pagesIndian Constitution and Constitutional History 2: Amendment C) 43api-3860791No ratings yet
- Important Constitutional AmendmantsDocument4 pagesImportant Constitutional AmendmantsShiva Shankar PandianNo ratings yet
- Work Sheet-2 Legal GK: D) Jana Gana ManaDocument6 pagesWork Sheet-2 Legal GK: D) Jana Gana ManaAnil BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Polity Set 1Document42 pagesPolity Set 1Manish ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Nice WorkDocument4 pagesNice WorkArif khanNo ratings yet
- INDIAN CONSTITUTION MCQsDocument103 pagesINDIAN CONSTITUTION MCQsDivya JagwaniNo ratings yet
- Important Amendments in Indian ConstitutionDocument7 pagesImportant Amendments in Indian Constitutionkrishnasantana1988No ratings yet
- Polity 4Document10 pagesPolity 4vishalbharati10230No ratings yet
- INDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)Document6 pagesINDIAN CONSTITUTION (Article & Amendment)workprofile440No ratings yet
- 2018 PolDocument16 pages2018 Polnitin pandeyNo ratings yet
- Constitution-1 With AnsDocument2 pagesConstitution-1 With AnsRajuNo ratings yet
- Indian Constituition 1 WordsDocument9 pagesIndian Constituition 1 WordsChinnasamy100% (1)
- Ambika Final 57th AMENDMENTDocument4 pagesAmbika Final 57th AMENDMENTAnkit KumarNo ratings yet
- QuizDocument6 pagesQuizOmkarAnnegirikarNo ratings yet
- Imp Article PolityDocument28 pagesImp Article PolityAshitosh RathodNo ratings yet
- Polity by D.K. Chaudharysir: Constitutional AmendmentDocument30 pagesPolity by D.K. Chaudharysir: Constitutional AmendmentNitin Dangi100% (1)
- Polity-Important AmendmentsDocument4 pagesPolity-Important AmendmentsNithish KumarNo ratings yet
- Clat 2012 Sample, Model Paper, Legal Reasoning, Legal AptitudeDocument16 pagesClat 2012 Sample, Model Paper, Legal Reasoning, Legal AptitudeM.a. RashidNo ratings yet
- Constitution Objective PDFDocument16 pagesConstitution Objective PDFAYYANAR RAJANo ratings yet
- Constitutional Law MCQDocument7 pagesConstitutional Law MCQommshreecreationNo ratings yet
- MC 18001Document1 pageMC 18001071 ROHETH S ITNo ratings yet
- What Is Constitution 95th Amendment Bill 2003?Document4 pagesWhat Is Constitution 95th Amendment Bill 2003?Vijay KumbharNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For Cie 1 Unit 1 18hs42 4thsemDocument10 pagesImportant Questions For Cie 1 Unit 1 18hs42 4thsemLaxman KuddemmiNo ratings yet
- Creation of New States in India: Mr. Suvir RaghuvanshDocument9 pagesCreation of New States in India: Mr. Suvir RaghuvanshVishakaRajNo ratings yet
- Important GK Questions With Answers Related To Indian ConstitutionDocument46 pagesImportant GK Questions With Answers Related To Indian ConstitutionbabuganeshNo ratings yet
- CONSTITUTIONDocument38 pagesCONSTITUTIONTanu SinghNo ratings yet
- Legal ????Document9 pagesLegal ????Niranjan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- T CardDocument1 pageT CardsantalicartoonwalaaNo ratings yet
- Science Set 9Document30 pagesScience Set 9santalicartoonwalaaNo ratings yet
- Best GK 3 For Fireman Lsi ForesterDocument30 pagesBest GK 3 For Fireman Lsi ForestersantalicartoonwalaaNo ratings yet
- Articles New For OssscDocument30 pagesArticles New For OssscsantalicartoonwalaaNo ratings yet
- DISGRACED Former Protectees ActDocument2 pagesDISGRACED Former Protectees ActTommyNo ratings yet
- Civil Tutorial by Kasych & CoDocument20 pagesCivil Tutorial by Kasych & CoParimitaaNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of EXTRAJUDICIAL SETTLEMENT OF ESTATEDocument3 pagesAffidavit of EXTRAJUDICIAL SETTLEMENT OF ESTATECyrill L. MarkNo ratings yet
- (G.R. No. 229010, November 23, 2020) IN THE MATTER OF THEDocument14 pages(G.R. No. 229010, November 23, 2020) IN THE MATTER OF THEGodwin CabacunganNo ratings yet
- Acain v. IACDocument3 pagesAcain v. IACKatrina Dominica FregillanaNo ratings yet
- Rule of LawDocument11 pagesRule of LawAishwarya SudhirNo ratings yet
- JUDICIAL REVIEW AssignmentDocument12 pagesJUDICIAL REVIEW AssignmentShubham PathakNo ratings yet
- Trust WrittenDocument14 pagesTrust Writtenizzah wahidaNo ratings yet
- Kalwant Singh A/l Ujagar Singh & Anor V Jaswant Kaur A/p Ujagar Singh & OrsDocument19 pagesKalwant Singh A/l Ujagar Singh & Anor V Jaswant Kaur A/p Ujagar Singh & OrscasanopiaNo ratings yet
- This Judgement Ranked 1 in The Hitlist.: 1950 AIR (SC) 163: 1950 SCR 566Document4 pagesThis Judgement Ranked 1 in The Hitlist.: 1950 AIR (SC) 163: 1950 SCR 566Nitin SherwalNo ratings yet
- Affidavit of acknowledgmentDENSODocument2 pagesAffidavit of acknowledgmentDENSOFinch AtticusNo ratings yet
- Santander Branch Closures UKDocument9 pagesSantander Branch Closures UKFuzzy_Wood_PersonNo ratings yet
- Petitioner MemorialDocument20 pagesPetitioner MemorialMahadevi MhetreNo ratings yet
- Internal and External Aids To InterpretationDocument4 pagesInternal and External Aids To InterpretationNimrat kaurNo ratings yet
- Anti RaggingDocument3 pagesAnti RaggingAbhay PradhanNo ratings yet
- CSEET Important QuestionDocument7 pagesCSEET Important QuestionArabinda SahooNo ratings yet
- Case Analysis: Maneka Gandhi v. Union of India: Ms. Kuhu TiwariDocument22 pagesCase Analysis: Maneka Gandhi v. Union of India: Ms. Kuhu TiwariShubhankar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Case Digest TANADA v. TUVERA, GR L-63915, April 24, 1985, Per J. Escolin, en BancDocument1 pageCase Digest TANADA v. TUVERA, GR L-63915, April 24, 1985, Per J. Escolin, en BancMonica LlenaresasNo ratings yet
- U.S. ConstitutionDocument17 pagesU.S. ConstitutionLucas HuidobroNo ratings yet
- Joy Wills NotesDocument76 pagesJoy Wills NotesMichael Vincent BautistaNo ratings yet