Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Rev 5
Uploaded by
MARIBEL MAGAYONOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rev 5
Uploaded by
MARIBEL MAGAYONCopyright:
Available Formats
Concrete Workability and Strength Quiz
Answers
1. Which of the following factors directly affects the workability of concrete?
A. Ambient temperature
B. Admixture type
C. Water content
D. Curing time
Answer: Water content (C)
Increasing the water content of a concrete mix increases its workability, but reduces its strength.
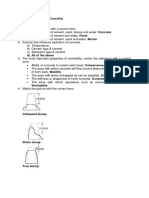
2. What is the purpose of the slump test?
A. To detect variations in the uniformity of a given concrete mix
B. To measure the density of fully compacted concrete
C. To determine the depth of penetration of a weighted ball
D. To measure the diameter of the spread after vibration
Answer: To detect variations in the uniformity of a given concrete mix (A)
The slump test is used to detect variations in the uniformity of a concrete mix with given nominal proportions.
3. What is the significance of a 'zero slump' result in the slump test?
A. It indicates a stiff mix
B. It indicates a segregated mix
C. It indicates a rich mix
D. It indicates a lean mix
Answer: It indicates a stiff mix (A)
A zero slump result in the slump test indicates a stiff mix, which is not necessarily a lean or rich mix.
4. Which test measures the depth of penetration of a weighted ball?
A. Kelly ball test
B. Slump test
C. Flow table test
D. Compacting factor test
Answer: Kelly ball test (A)
The Kelly ball test measures the depth of penetration of a weighted ball into the concrete mix, which is an indirect measure
of its workability.
5. What is the purpose of the compacting factor test?
A. To detect variations in the uniformity of a given concrete mix
B. To measure the density ratio of actual density to fully compacted density
C. To measure the diameter of the spread after vibration
D. To measure the consistency of self-consolidating concrete
Answer: To measure the density ratio of actual density to fully compacted density (B)
The compacting factor test measures the ratio of the actual recorded density of the concrete to the density of the same
concrete when fully compacted, which is an indirect measure of its workability.
6. What is the primary reason for segregation in wet concrete mixes?
A. The cement and water separate from the aggregates
B. Different particle sizes settle at different rates
C. Chemical reactions cause separation of components
D. Air bubbles rise to the surface
Answer: Different particle sizes settle at different rates (B)
Coarse particles tend to separate out since they settle more than the fine particles, leading to segregation in wet mixes.
7. What is laitance?
A. The water that rises to the surface during bleeding
B. A layer of settled coarse aggregate on the concrete surface
C. The process of compacting concrete to remove entrapped air
D. A weak, friable layer formed on the concrete surface after curing
Answer: A weak, friable layer formed on the concrete surface after curing (D)
Laitance is a weak, friable layer on the surface of concrete and sand cement screeds which appears after curing.
8. What is the purpose of curing concrete?
A. To compact the concrete and remove entrapped air
B. To increase the slump of the concrete for pumping
C. To create an environment for the concrete to harden properly
D. To remove excess water from the concrete mixture
Answer: To create an environment for the concrete to harden properly (C)
Curing of Concrete involves the creation of an environment for a period of time (suitable temperature, prevention of loss of
moisture or providing moisture).
9. What is the primary characteristic of pumped concrete?
A. It is designed to be placed underwater
B. It has a high water-cement ratio
C. It contains special admixtures for pumpability
D. It has a relatively high slump (6-8 inches)
Answer: It has a relatively high slump (6-8 inches) (D)
Pumped Concrete is a type of concrete which is designed to be pumpable with relatively high slump (6-8 inches).
10. What is the primary requirement for mixing water in concrete?
A. It must be free of impurities and contaminants
B. It must have a specific pH value
C. It must be fit for drinking
D. It must be at a specific temperature range
Answer: It must be fit for drinking (C)
The quality of mixing water is covered by saying water must be fit for drinking.
You might also like
- Workability of ConcreteDocument30 pagesWorkability of ConcreteAdnan Jadoon100% (1)
- Layout Plan For RCC Columns and FootingsDocument1 pageLayout Plan For RCC Columns and FootingsHusen GhoriNo ratings yet
- Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 pagesTutorial QuestionsHenok YalewNo ratings yet
- Consmat ReviewerDocument9 pagesConsmat ReviewerMARIBEL MAGAYONNo ratings yet
- 1 1 Merged PDFDocument59 pages1 1 Merged PDFDetroja NiharNo ratings yet
- CT MCQ BankDocument35 pagesCT MCQ BankSakshi TalmaleNo ratings yet
- Construction Material Exit ExamDocument6 pagesConstruction Material Exit Examasimamaw100% (3)
- BT Joe Quiz 1Document1 pageBT Joe Quiz 1corazon philNo ratings yet
- Masonry and ConcreteDocument3 pagesMasonry and ConcreteDarlene Daguno CabridoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 QuestionaireDocument5 pagesLecture 4 QuestionairemintclassifiedNo ratings yet
- Major 4 SoilDocument8 pagesMajor 4 SoilICE Group of Education BhopalNo ratings yet
- Class NoteDocument5 pagesClass NoteasimamawNo ratings yet
- Mock 13284 1625320792571Document13 pagesMock 13284 1625320792571mahalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionscivilDocument19 pagesMultiple Choice Questionscivilashish kushNo ratings yet
- MCQ's Concrete Technology - Fawad AhmadDocument10 pagesMCQ's Concrete Technology - Fawad AhmadFawad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Unit 1ctDocument10 pagesUnit 1ctDishantsingh RajputNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument31 pagesDocumentATHIRA UNNINo ratings yet
- Highlight in The Correct Answer in Each Item Below. Send A PDF of Complete Test To by Friday 5 November, 2020Document3 pagesHighlight in The Correct Answer in Each Item Below. Send A PDF of Complete Test To by Friday 5 November, 2020shondelB 5No ratings yet
- Geo Technical Ii Quiz QuestionsDocument11 pagesGeo Technical Ii Quiz QuestionsSukritiDanNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity # 1: Slump TestDocument12 pagesLaboratory Activity # 1: Slump TestJoyzelle JaniolaNo ratings yet
- English PDFDocument6 pagesEnglish PDFqweNo ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Slump TestDocument4 pagesExperiment 4 Slump TestZul HaswalNo ratings yet
- MCQ Concrete TechnologyDocument28 pagesMCQ Concrete TechnologySagar0% (2)
- Mdterm Comprehensive QuizDocument2 pagesMdterm Comprehensive QuizMac KYNo ratings yet
- Final Questions and Answers For Preparation To UPDA ExamDocument364 pagesFinal Questions and Answers For Preparation To UPDA ExamSameh Allaoui100% (1)
- Pre Test Dan Post Test Hydrocarbon ReservoirDocument4 pagesPre Test Dan Post Test Hydrocarbon ReservoirMochamad Kamal KatulistiwaNo ratings yet
- A. B. C. D. E.: AnswerDocument3 pagesA. B. C. D. E.: AnswerJeeva JeevaNo ratings yet
- Kerala PSC Engineering Assistant Question PaperDocument16 pagesKerala PSC Engineering Assistant Question Paperelsypeter70No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3shalona behariNo ratings yet
- Soil Mech MCQSDocument27 pagesSoil Mech MCQSUsama AhmadNo ratings yet
- BMC IV - Unit 2 & 4 - Ar - Archana & Ar - ShrijaDocument15 pagesBMC IV - Unit 2 & 4 - Ar - Archana & Ar - ShrijaIswaryaNo ratings yet
- Building Construction (Section 4) : A. B. C. DDocument12 pagesBuilding Construction (Section 4) : A. B. C. DAl RomanoNo ratings yet
- CocreteDocument62 pagesCocretesandhya rani bindhaniNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Viva QtnsDocument1 pageComprehensive Viva Qtnsచిమ్ముల సందీప్ రెడ్డిNo ratings yet
- Final Exam FINDocument8 pagesFinal Exam FINJoshua PowellNo ratings yet
- Mea Engineering College: Department of Civil ErngineeringDocument6 pagesMea Engineering College: Department of Civil ErngineeringShilji 616004100% (1)
- Concrete Technology Objective Questions: UNIT-1 Cement, Admixtures, AggregatesDocument9 pagesConcrete Technology Objective Questions: UNIT-1 Cement, Admixtures, AggregatesDilipKumarAkkaladeviNo ratings yet
- Concrete Technology: Civil EngineeringDocument24 pagesConcrete Technology: Civil EngineeringAkshay TangadiNo ratings yet
- TRB Final MaterialDocument439 pagesTRB Final MaterialAnitha MuthukumaranNo ratings yet
- Exit ExamDocument64 pagesExit ExamTadesse MegersaNo ratings yet
- New I Study CentreDocument40 pagesNew I Study Centresalapu upendraNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Report MCQDocument8 pagesGroup 2 Report MCQCristian SereñoNo ratings yet
- 2019 TNPSC Model Exam Pyramid Ias AcademyDocument17 pages2019 TNPSC Model Exam Pyramid Ias Academysubramanian0% (2)
- Meil Civil 1 (Q.P 2023)Document4 pagesMeil Civil 1 (Q.P 2023)Leela MadhuriNo ratings yet
- Correct AnswerDocument3 pagesCorrect AnswerpransuNo ratings yet
- (For Engineer) BE Concrete TechnologyDocument46 pages(For Engineer) BE Concrete Technologysuman subediNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument15 pagesAnswerMARK ARQUE LACANARIANo ratings yet
- MCQ - Cement and Concrete - ADocument8 pagesMCQ - Cement and Concrete - AdivithNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Concrete Works at The Construction SiteDocument43 pagesChapter 2 Concrete Works at The Construction SiteDdeqz Elina Bueno INo ratings yet
- Quiz Questions SoilDocument10 pagesQuiz Questions SoilnishantNo ratings yet
- 2015 SeptemberDocument15 pages2015 Septembercimpstaz100% (1)
- Concrete Technology-BitsDocument5 pagesConcrete Technology-Bitsabhiram ramNo ratings yet
- 2016 SeptemberDocument15 pages2016 SeptembercimpstazNo ratings yet
- Civil Engineering Competitive QuestionsDocument46 pagesCivil Engineering Competitive QuestionsSantosh Rai67% (3)
- CMT Test 1Document4 pagesCMT Test 1eutikol69No ratings yet
- Multiple - Unit-3Document14 pagesMultiple - Unit-3RON SAMUEL 401935No ratings yet
- MCQs Suface Tension & Interficial TensionDocument15 pagesMCQs Suface Tension & Interficial Tensionmukul sidhque100% (1)
- Building Construction (Section 2) : A. B. C. DDocument12 pagesBuilding Construction (Section 2) : A. B. C. DAl RomanoNo ratings yet
- Book 1Document20 pagesBook 1saibaNo ratings yet
- Worked Example: Checking A Steel Beam in Simple BendingDocument10 pagesWorked Example: Checking A Steel Beam in Simple BendingArianna EstructurasNo ratings yet
- Section 1800 (Flasework, Formwork and Surface Finish For Concrete Structures)Document15 pagesSection 1800 (Flasework, Formwork and Surface Finish For Concrete Structures)akvosmNo ratings yet
- The North American Port Pavement Design Manual PDFDocument15 pagesThe North American Port Pavement Design Manual PDFSi Zhang100% (1)
- Chapter 17 Light-Gauge Steel ConstructionDocument16 pagesChapter 17 Light-Gauge Steel Constructionalberttendoy2158No ratings yet
- Tihitina Siyoum PDFDocument133 pagesTihitina Siyoum PDFFahad MohamedNo ratings yet
- Failure Modes of RCC Beams Strengthened With NSM FRP TechniquesDocument9 pagesFailure Modes of RCC Beams Strengthened With NSM FRP TechniquesfelixNo ratings yet
- 4 Istructe Ec2 (Concrete) Design ManualDocument1 page4 Istructe Ec2 (Concrete) Design ManualYasonsky CaptainNo ratings yet
- Answer Scheme RC DesignDocument4 pagesAnswer Scheme RC DesignNik AliffNo ratings yet
- Bom Ilagan DemolitionDocument7 pagesBom Ilagan DemolitionJake MonteroNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2 PDFDocument10 pagesExercise 2 PDFLeong Yue HanNo ratings yet
- Metro Standard StructDwgs 080613Document41 pagesMetro Standard StructDwgs 080613rpazbNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mix Design ExampleDocument4 pagesConcrete Mix Design ExampleTheke MarkNo ratings yet
- Vernacular StructuresDocument31 pagesVernacular StructuresEr Krishan YadavNo ratings yet
- Ce 415 PDFDocument98 pagesCe 415 PDFDèfèndänt SadekNo ratings yet
- Design of BridgesDocument64 pagesDesign of BridgesSukhwinder Singh Gill89% (9)
- 9 Design of Flat Slab Column Connections As Per Aci 352-4-R89 23052014 5Document2 pages9 Design of Flat Slab Column Connections As Per Aci 352-4-R89 23052014 5Ahmad Badsha QuadriNo ratings yet
- Scaffolding, Shoring & Underpinning: Applications of ScaffoldsDocument14 pagesScaffolding, Shoring & Underpinning: Applications of Scaffoldssmugler 123100% (1)
- Specification & General Estimate For Your Villa Constructions.Document13 pagesSpecification & General Estimate For Your Villa Constructions.kanagarajodishaNo ratings yet
- Joist (BS4 Part 1@1993 Dimensions PropertiesDocument2 pagesJoist (BS4 Part 1@1993 Dimensions PropertiesAristotle MedinaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Structures Using ANSYSDocument31 pagesAnalysis of Structures Using ANSYSSaurabhMulayNo ratings yet
- Halfen Cast-In ChannelsDocument80 pagesHalfen Cast-In ChannelsGiang Thanh LamNo ratings yet
- Timber Ridge Beam Calculation Report 2Document5 pagesTimber Ridge Beam Calculation Report 2CartecSyriaNo ratings yet
- Shelf Angles For Masonry VeneerDocument17 pagesShelf Angles For Masonry VeneerJudian DuranNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Shear WallsDocument24 pagesAnalysis and Design of Shear WallsRkkodi100% (3)
- Quotation BestrackDocument3 pagesQuotation BestrackRescos KasarachiNo ratings yet
- Cc206 - Bab 4 Ibs Score NewDocument27 pagesCc206 - Bab 4 Ibs Score NewAdron LimNo ratings yet
- Concrete Structures Lecture Notes Design Stair CasesDocument21 pagesConcrete Structures Lecture Notes Design Stair CasesShikhin GargNo ratings yet
- BDC - COP-Precast Concrete Construction2016Document85 pagesBDC - COP-Precast Concrete Construction2016dexterbox1No ratings yet
- 17 Summary Premix Compaction TestDocument1 page17 Summary Premix Compaction TestKamalNo ratings yet