Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Statistics and Probability Reviewer
Uploaded by
Clover BlythOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Statistics and Probability Reviewer
Uploaded by
Clover BlythCopyright:
Available Formats
STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY - Experiment- activity in which
REVIEWER outcome cannot be predicted
- Trial- each repetition of experiment
STATISTICS- collection of methods for: - Outcome- result of experiment
- Experiments - Event- any collection of outcome
- Obtaining data - Simple Event- only one
- Analyzing possible outcome
- Conclusions - Sample Space- all possible
- Interpreting data outcomes
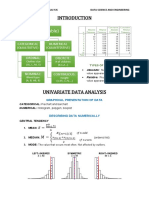
DATA- values that variables can assume
VARIABLE- characteristics that is PROBABILITY OF AN EVENT
observable or measurable Formula: 𝑃(𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡) =
𝑛(𝑒𝑣𝑒𝑛𝑡)
𝑛(𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑝𝑙𝑒 𝑠𝑝𝑎𝑐𝑒)
POPULATION- set of all values
n(event)= number of outcomes of an event
SAMPLE- subgroup of population
n(sample space)= number of all possible
outcomes
CLASSIFICATIONS OF VARIABLES:
- Qualitative Variables- represent
VARIABLES
class/category
Random- way to map outcomes of
- Quantitative Variables- represent
statistical experiment
amount/account
Discrete Random- value is obtained by
- Discrete- can be counted
counting
- Continuous- can be
Continuous Random- value is obtained by
measured (decimal)
measuring
LEVELS OF MEASUREMENT
- Nominal Level- consist of names,
DISCRETE PROBABILITY DISTRIBUTION
labels, categories
- Values of random variable can
- Ordinal Level- Arranged in orders
assume corresponding probabilities.
- Interval Level- can determine
- PROPERTIES:
amount of differences
- Sum of all
- Ratio Level- include inherent 0
probabilities should
starting point
be 1. Σ𝑃(𝑥) = 1
- Probabilities should
METHODS OF SAMPLING
be confined between
- Random- chance/ random numbers
0 and 1.
- Systematic- numbering and selecting with
0 ≤ 𝑃(𝑥) ≤ 1
number
MEAN OF A DISCRETE PROBABILITY
- Stratified- distinct groups, divide and pick
Formula: µ = Σ 𝑋 · 𝑃(𝑋)
into groups
- Cluster- intact groups
VARIANCE
- Is the in between of data sets
PROBABILITY
Formula:
- Branch of mathematics that deals
2
with chance Σ (𝑥 − µ) · 𝑃(𝑥)
STANDARD DEVIATION If positive= Add to 0.5
- Measure of amount of variation
Formula: 𝑣𝑎𝑟𝑖𝑎𝑛𝑐𝑒
𝑥 𝑃(𝑥) 𝑋 · 𝑃(𝑥) 𝑥− µ 2 2
σ (𝑥 − µ · 𝑝(𝑥)
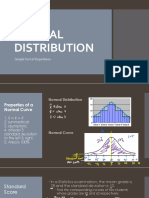
NORMAL CURVE DISTRIBUTION
- Bell curve = Subtraction
- The Normal Probability Distribution
Properties:
- Bell shaped
- Symmetrical about its center
- Mean, median, mode are equal and
at center
- Width of curve= standard deviation
=Add
- Tails are asymptotic to base line
- Area under curve=1
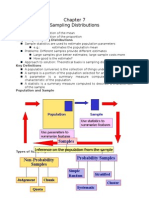
SAMPLING METHODS
STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION:
Population- group you want to generalize
µ = 0; σ = 1
(measure: parameter)
Sample- subset of population (measure:
Computing the area of curve:
statistics)
Random Sampling
- Simple Random Sampling
Each element has equal chance
= as is - Lottery/ Fishbowl Method
- Use of table of random
numbers
Slovin’s Formula
𝑁
𝑛= 2
1+𝑁𝑒
N= population size
(to the right) n= sample size
If negative= Add to 0.5 e= margin of error
If positive= Subtract to 0.5
Systematic Random Sampling
- Selecting every kth element in
population
𝑁
𝐾= 𝑛
Stratified Random Sampling
(to the left)
- Dividing into strata
If negative= Subtract to 0.5
𝑛
𝑁
then multiply the quotient to each strata
to know the number per strata
Clustered Sampling
- Dividing into clusters/groups and
pick a group for sample
mean variance St Dev
Population: µ σ
2 σ
Sample: 𝑥 𝑠
2 𝑠
FORMULAS:
Population
Σ𝑥
- Mean: µ = 𝑁
2
2 Σ(𝑥−µ)
- Variance: σ = 𝑁
2
Σ(𝑥−µ)
- StDev: σ = 𝑁
Sample:
Σ𝑥
- Mean: µ𝑥 = 𝑛
2
2 Σ(𝑥−µ𝑥)
- Variance: σ 𝑥 = 𝑛
2
Σ(𝑥−µ𝑥)
- StDev: σ𝑥 = 𝑛
CENTRAL LIMIT THEOREM
- Higher sample, more curve
You might also like
- Sample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignFrom EverandSample Size for Analytical Surveys, Using a Pretest-Posttest-Comparison-Group DesignNo ratings yet
- Stats Midterms Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesStats Midterms Cheat Sheetjibberish yoNo ratings yet
- SP ReviewerDocument4 pagesSP ReviewerMalayao, Philip Jude M.No ratings yet
- QR Midterm MemoDocument2 pagesQR Midterm MemoMarkus H.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Mathematics and Statistics B: Notes A3Document4 pagesIntroduction To Mathematics and Statistics B: Notes A3Harawa WonaNo ratings yet
- A Level Maths - Statistics Revision NotesDocument9 pagesA Level Maths - Statistics Revision NotesAftab AhmadNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistics Terms and CalculationsDocument4 pagesBasic Statistics Terms and CalculationsSagir Musa SaniNo ratings yet
- Probability Distribution: - Discrete - ContinuousDocument5 pagesProbability Distribution: - Discrete - ContinuousEavie OngNo ratings yet
- MIDTERMSDocument4 pagesMIDTERMSCarl Vincent VingnoNo ratings yet
- Stat Review NotesDocument8 pagesStat Review Notes안지연No ratings yet
- P (X) - N! - X! (N-X) ! P (1-p) : FormulaDocument6 pagesP (X) - N! - X! (N-X) ! P (1-p) : FormulaSofiaNo ratings yet
- ML Exam BHT Tough H BeeeeeeeeeDocument10 pagesML Exam BHT Tough H BeeeeeeeeeRasika DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet MidtermDocument1 pageCheat Sheet Midtermd5zb58j5dmNo ratings yet
- Cape Applied Mathematics Cheat SheetDocument6 pagesCape Applied Mathematics Cheat SheetNobody JamesNo ratings yet
- Monte Carlo SimulationDocument10 pagesMonte Carlo SimulationvyasvyasNo ratings yet
- PSYCH STATS CHAPTER 7aDocument3 pagesPSYCH STATS CHAPTER 7aNicole Rose Crave DagaleaNo ratings yet
- Stats BasicsDocument58 pagesStats BasicsRavi goelNo ratings yet
- STATSDocument4 pagesSTATSdennisalejaga08No ratings yet
- CQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DDocument15 pagesCQE Academy Equation Cheat Sheet - DAmr AlShenawyNo ratings yet
- Stat Cheatsheet (Ver.2)Document2 pagesStat Cheatsheet (Ver.2)memeNo ratings yet
- Stats 4TH Quarter ReviewerDocument2 pagesStats 4TH Quarter ReviewerKhryzelle BañagaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in StatsDocument2 pagesReviewer in StatsKirsten IguetNo ratings yet
- Math 102 Midterms Reviewer (With Mock Tests)Document3 pagesMath 102 Midterms Reviewer (With Mock Tests)Jirish RiveraNo ratings yet
- FormulasDocument2 pagesFormulasMoshiurNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability ReviewerDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability Reviewermiel noahNo ratings yet
- WK 11-Session 11 Notes-Hypothesis Testing (Two Samples) - UploadDocument12 pagesWK 11-Session 11 Notes-Hypothesis Testing (Two Samples) - UploadLIAW ANN YINo ratings yet
- Lecture 10Document13 pagesLecture 10YashikaNo ratings yet
- Math in The Modern World Stat LectureDocument3 pagesMath in The Modern World Stat LectureGylene GardonNo ratings yet
- 0826 Statistics (Class Notes) (Vanessa 2022)Document43 pages0826 Statistics (Class Notes) (Vanessa 2022)Vienne Yuen Wing YanNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics - Practice Tests and SolutionsDocument46 pagesProbability and Statistics - Practice Tests and Solutionsİlhan Burak ÖzhanNo ratings yet
- Univariate and Bivariate Data Analysis + ProbabilityDocument5 pagesUnivariate and Bivariate Data Analysis + ProbabilityBasoko_Leaks100% (1)
- QM1 Typed NotesDocument18 pagesQM1 Typed Noteskarl hemmingNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Data Analytics Cheat SheetsDocument2 pagesStatistics and Data Analytics Cheat SheetsGiova RossiNo ratings yet
- GB Academy Equation ListDocument16 pagesGB Academy Equation ListfaysalnaeemNo ratings yet
- Statistics RefresherDocument7 pagesStatistics RefresherJASMINE GOMEZNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Plotting For Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)Document2 pages2.1 Plotting For Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)RajaNo ratings yet
- 03 Statistical & Internal ValidityDocument58 pages03 Statistical & Internal ValidityAssan AchibatNo ratings yet
- Review 2 SummaryDocument4 pagesReview 2 Summarydinhbinhan19052005No ratings yet
- Instalinotes - PREVMED IIDocument24 pagesInstalinotes - PREVMED IIKenneth Cuballes100% (1)
- Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFormula SheetBlythe ButlerNo ratings yet
- Handout TA BiostatDocument4 pagesHandout TA BiostatNgọc VânNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - CH6 Normal Distribution and Other Continuous DistributionsDocument6 pagesWeek 3 - CH6 Normal Distribution and Other Continuous DistributionsAya AdelNo ratings yet
- Cambridge AS Biology 9700 Practical NotesDocument2 pagesCambridge AS Biology 9700 Practical NotesSafiya Naina100% (1)
- Sampling DistributionsDocument31 pagesSampling DistributionsdaarshiniNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Finals ReviewerDocument10 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Finals Revieweraaleah moscaNo ratings yet
- Pre Lim - Midterm HandoutsDocument3 pagesPre Lim - Midterm HandoutsJanica SamsonNo ratings yet
- Unit X - Final Review - 1 Per PageDocument30 pagesUnit X - Final Review - 1 Per PageKase1No ratings yet
- STAT Exam 1 - Review SheetDocument2 pagesSTAT Exam 1 - Review SheetSamhitha BandiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ReviewDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Reviewapi-3829767No ratings yet
- Applied Statistics II-SLRDocument23 pagesApplied Statistics II-SLRMagnifico FangaWoro100% (1)
- 2024-Lecture 09Document29 pages2024-Lecture 09Nguyễn TâmNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability: Variance of The Sample Mean Population Standard Deviation of The Sampling DistributionDocument5 pagesStatistics and Probability: Variance of The Sample Mean Population Standard Deviation of The Sampling DistributionAndrea GamutanNo ratings yet
- MMW NotesDocument10 pagesMMW Noteslpanela.21No ratings yet
- Research 9 Q3Document17 pagesResearch 9 Q3MMALTEZ, RALPH CHRISTIAN, R.No ratings yet
- Data Science Formula - Very ImpDocument6 pagesData Science Formula - Very Impcoloringcraft318No ratings yet
- Normal Distribution: Simple Test of HypothesisDocument27 pagesNormal Distribution: Simple Test of Hypothesisednalyn ladiaoNo ratings yet
- ADMS 2320 Test 1 SheetDocument1 pageADMS 2320 Test 1 SheetJustin St Louis WoodNo ratings yet
- Statistics NotesDocument44 pagesStatistics NotesAbhishek GambhirNo ratings yet
- Summary Mid Contents - 2023Document31 pagesSummary Mid Contents - 2023Tung HoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 ReviewerDocument8 pagesGeneral Biology 2 ReviewerClover BlythNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 1 ReviewerDocument6 pagesPractical Research 1 ReviewerClover BlythNo ratings yet
- Portfolio 2022 2023 3rd QuarterDocument3 pagesPortfolio 2022 2023 3rd QuarterClover BlythNo ratings yet
- Lab Activity Test On DNA Decoding BlankDocument6 pagesLab Activity Test On DNA Decoding BlankClover BlythNo ratings yet
- March 31 OnlyDocument1 pageMarch 31 OnlyClover BlythNo ratings yet
- Performance Task 3 TRACKING ALIGNING AND TESTING RADIO RECEIVERDocument3 pagesPerformance Task 3 TRACKING ALIGNING AND TESTING RADIO RECEIVERClover BlythNo ratings yet
- Group Task3 MendelDocument1 pageGroup Task3 MendelClover BlythNo ratings yet
- Calculas 1Document3 pagesCalculas 1Ishfaq ChohanNo ratings yet
- M11GM Ic 1 2Document2 pagesM11GM Ic 1 2Gemark D. Gebone100% (1)
- A Review Paper On FEA Application For Sheet Metal Forming AnalysisDocument8 pagesA Review Paper On FEA Application For Sheet Metal Forming AnalysisSagar PajankarNo ratings yet
- Math g5 m1 Full ModuleDocument249 pagesMath g5 m1 Full ModulepeppylepepperNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan ECS 228 November 2013 - April 2014 - IzziyantieDocument4 pagesLesson Plan ECS 228 November 2013 - April 2014 - IzziyantiesaifulsabdinNo ratings yet
- Great Works ListDocument10 pagesGreat Works Listsarimali2010No ratings yet
- Fundamentals in ALGEBRADocument8 pagesFundamentals in ALGEBRACarlo BiongNo ratings yet
- GLE 594: An Introduction To Applied Geophysics Magnetic MethodsDocument6 pagesGLE 594: An Introduction To Applied Geophysics Magnetic MethodsIdam. anNo ratings yet
- Universiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential CS/SEP 2011/QMT181/212/216Document10 pagesUniversiti Teknologi Mara Final Examination: Confidential CS/SEP 2011/QMT181/212/216Ahmad Nasa'ie IsmailNo ratings yet
- Portfolio IN Chemistry: Submitted By: Bianca Romualdez Iii-Beb!Document11 pagesPortfolio IN Chemistry: Submitted By: Bianca Romualdez Iii-Beb!Aaron Paul RomualdezNo ratings yet
- Full Download Problem Solving With C 10th Edition Savitch Test BankDocument32 pagesFull Download Problem Solving With C 10th Edition Savitch Test Bankarrowcornet0100% (31)
- CP and CPK SolutionDocument5 pagesCP and CPK SolutionlawtonNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3 v2Document17 pagesLab Report 3 v2Andy LapianNo ratings yet
- CHANGESDocument40 pagesCHANGESYonatan Ysrael ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Article - USBR Type IXDocument7 pagesArticle - USBR Type IXLeticia Karine Sanches BritoNo ratings yet
- ACFMDocument10 pagesACFMAnson MartinNo ratings yet
- Chen4352 PDC Lab ManualDocument26 pagesChen4352 PDC Lab ManualmohammedNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Properties and FEM Model of The Friction Welded Mild Steel-Al6061-AluminaDocument15 pagesEvaluation of Properties and FEM Model of The Friction Welded Mild Steel-Al6061-AluminaKamel FedaouiNo ratings yet
- Regression AnalysisDocument14 pagesRegression Analysispranay0% (1)
- Moodulo DsaDocument92 pagesMoodulo DsaRonaldoMaia87No ratings yet
- CLILDocument14 pagesCLILMiguel Rico Porter100% (2)
- Estimating The Shape Parameter of The Exponential-Weibull Distribution Using Bayesian TechniqueDocument11 pagesEstimating The Shape Parameter of The Exponential-Weibull Distribution Using Bayesian TechniqueProf. Madya Dr. Umar Yusuf MadakiNo ratings yet
- Demostration of Boyle's Law ReportDocument5 pagesDemostration of Boyle's Law ReportميسرةNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 Linear Data Structures - Array & StackDocument19 pagesUnit - 2 Linear Data Structures - Array & StackDarshna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9: Objective: Use Place Value Understanding To Round Multi-Digit Numbers To Any Place ValueDocument11 pagesLesson 9: Objective: Use Place Value Understanding To Round Multi-Digit Numbers To Any Place ValuejanveNo ratings yet
- Conference Proceeding.Document22 pagesConference Proceeding.ogboleobekpaNo ratings yet
- F DST 214 Cereal ProcessingDocument97 pagesF DST 214 Cereal Processingvaleria1234567890100% (1)
- Probability 1Document3 pagesProbability 1Supriti SarkerNo ratings yet
- 2000 Solutions Pascal Contest: Canadian Mathematics CompetitionDocument12 pages2000 Solutions Pascal Contest: Canadian Mathematics Competitionสฮาบูดีน สาและNo ratings yet
- Structural Design of 3-Axis CNC Machine Tool For Wood CarvingDocument100 pagesStructural Design of 3-Axis CNC Machine Tool For Wood CarvingMohamed MohamedNo ratings yet