Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mock Exam Geo
Uploaded by
origin.zerefOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mock Exam Geo
Uploaded by
origin.zerefCopyright:
Available Formats
Instructions: Basta bilugan or isulat niyo nalang sagot niyo.
Piliin ang tamang sagot, one wrong, one kitus. If wala sa
pagpipilian ang sagot, write “E”. Boom bading! Goodluck! Passing score siyempre 60% ng total alangan naman kalahati,
ayoko rin ah.
1. It is the application of laws of mechanics and hydraulics to engineering problems dealing with sediments
and other unconsolidated accumulation of solid particles.
a. Geotechnical System c. Soil Mechanics
b. Geology d. Sieve Analysis
PROBLEM 1 (for numbers 2 – 3)
Results of sieve analysis on a soil sample are shown below:
Sieve Number Size (mm) Cumulative Percent Passing
4 4.76 98
10 2.00 88
40 0.42 72
60 0.25 60
100 0.149 21
200 0.075 3
Pan 0
2. What is the effective grain size of the soil sample?
a. 0.13 b. 0.10 c. 0.08 d. 0.12
3. What is the coefficient of uniformity of the soil?
a. 2.55 b. 3.25 c. 1.45 d. 1.85
PROBLEM 2 (for numbers 4 – 6)
A sandy soil sample has a unit weight of 22.3 kN/m3 at a saturation of 80%. After the sample was oven dried, the unit
weight was reduced by 1.25 kN/m3.
4. Determine the void ratio of the sample
a. 0.45 b. 0.76 c. 0.19 d. 0.23
5. Determine the specific gravity of the soil solids
a. 2.7 b. 2.1 c. 2.55 d. 2.16
6. If the soil sample has an emax=0.85 and emin=0.10, what is the required void ratio in the site at a relative
density of 50%
a. 0.231 b. 0.546 c. 0.145 d. 0.475
PROBLEM 3 (for numbers 7 – 9)
During a lab test, a 150-cc silty sand weighing 2.75 N was found out to have a water content of 15%. Assuming
Gs=2.71,
7. Determine the percentage of air in the voids
a. 39.11% b. 23.65% c. 47.69% d. 16.67%
8. Determine the void ratio
a. 0.55 b. 0.78 c. 0.67 d. 0.21
9. Theoretically, without a change of the total volume, how much water should be added to the sample to be
fully saturated?
a. 23.49 cc b. 31.76 cc c. 12.86 cc d. 41.75 cc
10. This soil parameter quantifies the degree of packing between loosest and densest possible state of soils.
a. Relative Density c. Specific Gravity
b. Relative Compaction d. Void ratio
11. In a lab test, a clay sample conveyed a liquidity index of 1.2, what is the state of the sample?
a. Semi-solid State c. Liquid State
b. Plastic State d. Solid State
PROBLEM 4 (for numbers 12 – 14)
A soil sample was subjected to an Atterberg limit test. The plastic limit test gave three moisture content results:
18.8%, 17.9%, and 18.2%. For the sample’s liquid limit determination, the results are tabulated below.
No. of blows Bulk Unit Weight Dry Unit Weight
(kN/m3) (kN/m3)
14 125.5 105.4
20 141.4 114.8
29 132.6 109.6
32 136 113.5
12. What is the liquid limit of the soil sample?
a. 34.65% b. 20.82% c. 42.13% d. 15.74%
13. What is its plasticity index?
a. 0 b. 1.43 c. 2.52 d. 3.78
14. If the in-situ moisture content of the sample is 19%, what is its liquidity index?
a. 0.28 b. 0.68 c. 1.23 d. 1.73
15. Soils in nature commonly exist separately as gravel, sand, silt, clay, or organic matter.
a. True b. False c. Depends on the topography d. Depends on the temperature
PROBLEM 5 (for numbers 16 – 17)
Sieve analysis and Atterberg limits of a soil sample is given below.
Sieve Analysis (Percent Passing) Liquid Limit Plastic Limit
No.4 No. 10 No. 40 No. 200
70 56 48 29 33 21
16. Classify the soil using the AASHTO Sytstem
a. A-2-6 (1) b. A-2-6 (2) c. A-2-7 (1) d. A-2-7 (2)
17. Classify the soil using the USCS
a. SM (silty sand) c. GM (silty gravel)
b. SC (clayey sand with gravel) d. GW (well-graded gravel)
18. The degree of compaction of soils is measured in terms of the soils’ ____________.
a. Relative Compaction c. Shear Strength
b. Compressibility d. Dry Unit Weight
PROBLEM 6 (for numbers 19 – 22)
Laboratory compaction test results of a soil sample showed an optimum water content of 12.5% at a bulk unit weight
of 21.5 kN/m3. Sand-cone method was also performed on the field where the sample was excavated to determine the
compaction. The data used are the following:
Dry unit weight of the Ottawa sand – 15.4 kN/m3
Weight of the Ottawa sand (before use) – 0.075 kN
Weight of the Ottawa sand (after use) – 0.05 kN
Weight of the moist soil (field) – 0.03 kN
Moisture content of the soil (field) – 10.45%
19. Determine the maximum dry unit weight of the soil sample
a. 19.11 kN/m3 b. 22.78 kN/m3 c. 17.33 kN/m3 d. 20.41 kN/m3
20. Determine the degree of saturation at the maximum dry unit weight if Gs=2.7
a. 54.5% b. 67.6% c. 73.2% d. 87.4%
21. Determine the dry unit weight of the soil on the field
a. 16.73 kN/m3 b. 17.63% kN/m3 c. 13.67% d. 16.37%
22. Determine the relative compaction of the soil
a. 90.31% b. 87.55% c. 95.97% d. 88.62%
23. Which of the following is not a factor that affects hydraulic conductivity in soils?
a. Soil Type b. Void Ratio c. Specific Gravity of Soil d. Entrapped Gases
24. Which of the following statements is true?
a. Pressure head can be neglected when determining the head in the flow of water through soils
b. Seepage velocity is the property of soil which governs the flow of water through it
c. Flow of water through soils is always laminar
d. Coefficient of permeability is also called as the hydraulic gradient
PROBLEM 7 (for numbers 25 – 26)
A falling head permeability test was conducted on a clay specimen having a cross-sectional area of 50 cm2 at 25
Degrees Celsius. After 45 minutes, the water in the standpipe of diameter 0.4 cm drops from 150 cm to 98 cm.
25. What is the coefficient of permeability in cm/s per unit length?
a. 4.45 * 10-4 b. 3.96 * 10-7 c. 2.78 * 10-5 d. 1.04 * 10-6
26. What is the coefficient of permeability in cm/s per unit length at 20 Degrees Celsius?
a. 2.98 * 10-5 b. 4.21 * 10-4 c. 3.53 * 10-7 d. 3.87 * 10-6
PROBLEM 8 (for numbers 27 – 28)
A field pumping test was conducted from an aquifer of sandy soil of 8 m thickness confined between two impervious
strata. When equilibrium was established, 90 liters of water was pumped out per hour. The water elevation in an observation
well 6.0 m away from the test well was 4.1 m and another 9.0 m away was 4.7 m from the roof level of the impervious
stratum of the aquifer
27. Find the value of k of the soil in m/sec.
a. 2.02 * 10-5 b. 1.16 * 10-5 c. 3.74 * 10-5 d. 1.25 * 10-5
28. What is the discharge of water in m3/sec.
a. 2.6 * 10-3 b. 1.9 * 10-3 c. 3.3 * 10-3 d. 1.5 * 10-3
.
PROBLEM 9 (for numbers 29 – 31)
The figure below shows layers of soil in a tube that is 100mm x 100mm in cross-section. Water is supplied to
maintain a constant head difference of 400 mm across the sample. The hydraulic conductivities of the soils in the direction
of flow are as follows:
Soil K (cm/sec) Porosity (%)
A 1 * 10-2 25
B 3 * 10-3 32
C 4.9 * 10-4 22
29. Calculate the equivalent k in cm/sec
a. 2.22 * 10-2 c. 1.89 * 10-2
b. 1.06 * 10 -3 d. 2.73 * 10-3
30. Calculate the rate of water supply in cm3/hr
a. 304 c. 299
b. 340 d. 265
31. Calculate the seepage velocity through soil C in m/sec
a. 0.41 c. 0.12
b. 0.65 d. 0.38
32. It is the most common cause of levee failures in the system
a. Gravity c. Seepage
b. Poor foundation d. Flow Nets
PROBLEM 10 (for numbers 33 – 35)
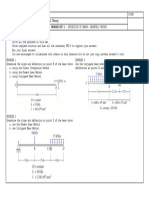
For the masonry dam below, k=5m/day
33. How many flow channels are in the figure?
a. 3 b. 4 c. 5 d. 6
34. How many head drops are in the figure?
a. 7 b. 8 c. 9 d. 10
35. Compute the seepage flow per meter width of dam in liters per minute.
a. 38.32 b. 33.64 c. 29.85 d. 27.78
You might also like
- Geotechnical QuizDocument41 pagesGeotechnical QuizAminulIslamNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Quiz Chapter 4 Form 4 @Document3 pagesChemistry Quiz Chapter 4 Form 4 @Mohd Norihwan100% (1)
- Problem Set in GEotechnical EngineeringDocument15 pagesProblem Set in GEotechnical EngineeringRachel DelosreyesNo ratings yet
- Geo 1Document57 pagesGeo 1MichaelJamesBanawisNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering ModuleDocument5 pagesGeotechnical Engineering ModuleFeigyl Faith Lanit Miro100% (3)
- SOPs For ChemicalsDocument7 pagesSOPs For ChemicalselizasunderNo ratings yet
- 100 Solved Problems in SOIL Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringDocument23 pages100 Solved Problems in SOIL Mechanics and Geotechnical EngineeringExcel Migs100% (1)
- A Soil Has A BulkDocument12 pagesA Soil Has A BulkMaverick Timbol100% (1)
- Hge Mid PreboardDocument7 pagesHge Mid PreboardChrisneil Delosreyes0% (1)
- Ricoh mpc307 407 Parts ManualDocument244 pagesRicoh mpc307 407 Parts Manualmark adams50% (2)
- 1697 Dzyan Kitabi Qedim Qutsal Oghreti Bilim Arashdirma Qurupu 1971 61sDocument67 pages1697 Dzyan Kitabi Qedim Qutsal Oghreti Bilim Arashdirma Qurupu 1971 61strametesa100% (1)
- PS2 4Document10 pagesPS2 4Karl Alexis TumibayNo ratings yet
- Cone Penetration Testing: Methods and InterpretationFrom EverandCone Penetration Testing: Methods and InterpretationRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Assignment-Ii Geotech HydraulicsDocument2 pagesAssignment-Ii Geotech Hydraulicspat cruzNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering PDFDocument83 pagesGeotechnical Engineering PDFMargaret Galang50% (2)
- 100 Solved Problems in (Soil Mechanics)Document19 pages100 Solved Problems in (Soil Mechanics)Excel Migs100% (3)
- Geotechnical Engineering I - Soil Mechanics Quiz 1 Batch 2021-2022 INSTRUCTION (S) : Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following QuestionsDocument5 pagesGeotechnical Engineering I - Soil Mechanics Quiz 1 Batch 2021-2022 INSTRUCTION (S) : Select The Correct Answer For Each of The Following QuestionsCarjez LoveNo ratings yet
- Problem Set11Document10 pagesProblem Set11Habyer47No ratings yet
- Cie - 20047 P2 - 20exam Answer - 20key 1S Sy2324Document9 pagesCie - 20047 P2 - 20exam Answer - 20key 1S Sy232424ks72xn8jNo ratings yet
- Geotechincal Engineering NotesDocument7 pagesGeotechincal Engineering NotesThesis ConsultantNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials and TestingDocument4 pagesConstruction Materials and TestingNicole May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics PlatesDocument16 pagesSoil Mechanics PlatesMarc MathieuNo ratings yet
- 01-10-15 GeotechDocument3 pages01-10-15 GeotechEj ApeloNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 - Hydro GeoDocument9 pagesExam 1 - Hydro GeoRenz PagcaliwaganNo ratings yet
- Tutorials 1-12: Tutorial Sheet 1Document11 pagesTutorials 1-12: Tutorial Sheet 1NarasimharaoNo ratings yet
- 3 Compaction - S21Document3 pages3 Compaction - S21hassanNo ratings yet
- Ecv 301 Soil Mechanics I - RevisedDocument3 pagesEcv 301 Soil Mechanics I - RevisedNatty tobieNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Problem SetDocument3 pagesSoil Mechanics Problem Setmuhammedssebatindira3No ratings yet
- Problem Set Soil Mechanics PDFDocument6 pagesProblem Set Soil Mechanics PDFDharyl Libarra BardelasNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics ExercisesDocument2 pagesSoil Mechanics ExercisesStudent555No ratings yet
- PS1 Without AnswerDocument3 pagesPS1 Without Answerbrian galangNo ratings yet
- PT 2023 Past QuestionDocument7 pagesPT 2023 Past QuestionTSOG MHNo ratings yet
- CENG 197 - CE Competency Appraisal II Problem Set 6 - Geotechnical EngineeringDocument11 pagesCENG 197 - CE Competency Appraisal II Problem Set 6 - Geotechnical EngineeringApple AterradoNo ratings yet
- Sabo Lab Prelim ExaminationDocument7 pagesSabo Lab Prelim ExaminationEllah saboNo ratings yet
- BE Civil V Soil Mechanics Tutorial 1home AsignmentDocument9 pagesBE Civil V Soil Mechanics Tutorial 1home Asignmentapple ballNo ratings yet
- Accreditation Exam 3Document12 pagesAccreditation Exam 3Andrei AlidoNo ratings yet
- Ps2 GeoDocument9 pagesPs2 GeoRio Fae BautistaNo ratings yet
- 2 Soil Classification - S21Document3 pages2 Soil Classification - S21hassanNo ratings yet
- Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and TechnologyDocument3 pagesJomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and TechnologyTinaNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document12 pagesCH 02Nadia Zaman SrutiNo ratings yet
- Soil Consolidation Solved ProblemsDocument16 pagesSoil Consolidation Solved ProblemsBurhan MNo ratings yet
- Geotech Examinee - SDocument6 pagesGeotech Examinee - SRodelNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Refresher Module PDFDocument5 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Refresher Module PDFjonilyn florentinoNo ratings yet
- Physical Soil Parameters: (Experimental Determination of Properties of Soil)Document30 pagesPhysical Soil Parameters: (Experimental Determination of Properties of Soil)Jodel ann LangresNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam 2016 2017Document4 pagesMidterm Exam 2016 2017samerNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics - Problems 1Document2 pagesSoil Mechanics - Problems 1MJ ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Exp 7 CompactionTestDocument9 pagesExp 7 CompactionTestKelvin NgugiNo ratings yet
- Evaluation Exam 7 April2023Document8 pagesEvaluation Exam 7 April2023Michael MercadoNo ratings yet
- Compaction TestDocument7 pagesCompaction TestJunrey LumangyaoNo ratings yet
- Mid QuizDocument3 pagesMid QuizRj 30No ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics RefresherDocument14 pagesSoil Mechanics Refresherfrancis bautistaNo ratings yet
- Ece 2303 - Soil Mechanics I Rat-2Document4 pagesEce 2303 - Soil Mechanics I Rat-2c.gichobiiNo ratings yet
- ProblemsetDocument6 pagesProblemsetMaryll TapiaNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering-I PDFDocument8 pagesGeotechnical Engineering-I PDFMopidevi Vijaya KishoreNo ratings yet
- The Behavior of Soil Can Be Divided Into Four Basic States A. Solid B. Semisolid C. Plastic D. LiquidDocument9 pagesThe Behavior of Soil Can Be Divided Into Four Basic States A. Solid B. Semisolid C. Plastic D. LiquidLyka Denisse CatubigNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Problems PDFDocument2 pagesSet 1 Problems PDFKristin Argosino0% (1)
- University of PeradeniyaDocument7 pagesUniversity of Peradeniyanaveen daluwattaNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Part 1Document35 pagesSoil Mechanics Part 1Marie Faye Togño Almero33% (3)
- Geotech - Plate 7Document4 pagesGeotech - Plate 7Jan Michael AbarquezNo ratings yet
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportFrom EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportNo ratings yet
- Geological Carbon Storage: Subsurface Seals and Caprock IntegrityFrom EverandGeological Carbon Storage: Subsurface Seals and Caprock IntegrityStéphanie VialleNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 4Document1 pageProblem Set 4origin.zerefNo ratings yet
- Assignment Short ColumnDocument1 pageAssignment Short Columnorigin.zerefNo ratings yet
- 6b Non Rectangular SRB - Sample Design ProblemsDocument5 pages6b Non Rectangular SRB - Sample Design Problemsorigin.zerefNo ratings yet
- 6a Non Rectangular SRB - Sample Investigation ProblemsDocument11 pages6a Non Rectangular SRB - Sample Investigation Problemsorigin.zerefNo ratings yet
- Electronics MCQsDocument17 pagesElectronics MCQslovelyosmile253No ratings yet
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesDocument2 pagesClassification of Elements and Periodicity in PropertiesShivam KumarNo ratings yet
- Spesifikasi Teknis Hyperion X9 PDFDocument4 pagesSpesifikasi Teknis Hyperion X9 PDFDjuli AgusNo ratings yet
- 1 - SetsDocument2 pages1 - SetsHerald MulanoNo ratings yet
- Evert Hoek Results CalcDocument6 pagesEvert Hoek Results CalcKanaiyalal N. ShethNo ratings yet
- Power Generation by Using Piezoelectric Transducer With Bending Mechanism SupportDocument6 pagesPower Generation by Using Piezoelectric Transducer With Bending Mechanism SupportIAES IJPEDSNo ratings yet
- Thermal Stress MonitoringDocument78 pagesThermal Stress MonitoringSIVA KAVYANo ratings yet
- Appendix 27 Alternative Requirements For Glass-Lined VesselsDocument2 pagesAppendix 27 Alternative Requirements For Glass-Lined VesselsBinay K SrivastawaNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer ProDocument7 pagesHeat Transfer ProBorse RajNo ratings yet
- PhotogrammetryDocument45 pagesPhotogrammetryValerie VictoriaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 RheologyDocument32 pagesLecture 3 Rheologybattal eduNo ratings yet
- Application of FRC in Construction of The Underground Railway TrackDocument8 pagesApplication of FRC in Construction of The Underground Railway TrackClaudio PazNo ratings yet
- FluidsDocument14 pagesFluidsRhea BakiNo ratings yet
- Applications and Interpretation Higher SpecimensDocument80 pagesApplications and Interpretation Higher SpecimensJAKE THE DOGNo ratings yet
- XII Maths Exercise 3.1 (Solution)Document11 pagesXII Maths Exercise 3.1 (Solution)mansoor100% (5)
- Origin of Voicing AlternationDocument10 pagesOrigin of Voicing AlternationCorinne D'AntonioNo ratings yet
- Full Text of "Waterproofing EngineeringDocument966 pagesFull Text of "Waterproofing Engineeringmazharul43No ratings yet
- Sample Pure PaperDocument28 pagesSample Pure PapersaNo ratings yet
- Conduction-Convection Systems: HPDX (T T)Document8 pagesConduction-Convection Systems: HPDX (T T)Nihad MohammedNo ratings yet
- FuelDocument172 pagesFuelImtiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Gas BookDocument202 pagesGas Bookomiitg67% (3)
- E 777 - Gidarakos 2005 - Ultimate - C and HDocument5 pagesE 777 - Gidarakos 2005 - Ultimate - C and HTamara Aulia RachimNo ratings yet
- Petrology NotesDocument110 pagesPetrology NotesRaj Sunil KandregulaNo ratings yet
- 05 PDFDocument1 page05 PDFdruwid6No ratings yet
- T13mra001 Mra STR 103 SLD 010 Rev B Lifting AnalysisDocument12 pagesT13mra001 Mra STR 103 SLD 010 Rev B Lifting AnalysisTannaz HadizadeNo ratings yet
- Ch7 D FFT2016Document42 pagesCh7 D FFT2016Nguyễn KhánhNo ratings yet