Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lec 2 - 2 - 1
Uploaded by
Nazmus Sakib0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views8 pagesOriginal Title
Lec 2_2_1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views8 pagesLec 2 - 2 - 1
Uploaded by
Nazmus SakibCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
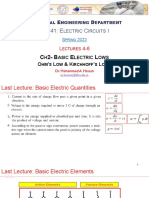
ECE 200 : Electrical Circuits I
B. Basic Laws & Resistive circuits
A d Ak
Azad Akm
Rm : UB-402,, Extn. : 4024
Email: a.azad@bracuniversity.ac.bd
© Azad Akm – BRAC University 1
B. Basic Laws & Resistive circuits
• Nodes
• Paths
• Loops
• Branches
B h
© Azad Akm – BRAC University 2
B. Basic Laws & Resistive circuits (cont.)
¾ Kirchhoff’s Current
Law:
“The algebraic sum of
the currents entering
g
any node is zero”
¾ i.e.,
ie
i A + iB + (−iC ) + (−iD ) = 0
¾ In general, N
∑
n =1
in = 0
© Azad Akm – BRAC University
↔ examples
3
B. Basic Laws & Resistive circuits (cont.)
¾ Kirchhoff’s Voltage
Law:
“The algebraic sum of
the voltages around
any closed path is
zero”
¾ i.e.,
ie
v1 + (−v2 ) + v3 = 0
¾ In general, N
∑v
n =1
n =0
© Azad Akm – BRAC University
↔ examples
4
¾ B. Basic Laws & Resistive circuits (cont.)
¾ Series and Parallel Connected Independent
Sources
© Azad Akm – BRAC University
↔ examples
5
¾B. Basic Laws & Resistive circuits (cont.)
• Resistors in Series
© Azad Akm – BRAC University 6
¾B. Basic Laws & Resistive circuits (cont.)
• Resistors in Parallel
© Azad Akm – BRAC University
↔ examples
7
THE END
© Azad Akm – BRAC University 8
You might also like
- No Nonsense General Class License Study Guide: for Tests Given Between July 2019 and June 2023From EverandNo Nonsense General Class License Study Guide: for Tests Given Between July 2019 and June 2023Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Lecture 1 and 2Document48 pagesLecture 1 and 2Mohammed ZaitounNo ratings yet
- Bee All MCQS' in 1 PDFDocument649 pagesBee All MCQS' in 1 PDFSAMAIRA SINGHNo ratings yet
- BEE All Unit MCQS'Document40 pagesBEE All Unit MCQS'GAURAV GUPTANo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - 1 - Final - FDocument19 pagesLecture 1 - 1 - Final - FNazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Unit Three - DC Circuit Analysis - Part OneDocument20 pagesUnit Three - DC Circuit Analysis - Part OneSena MekoninNo ratings yet
- CH 03 Rii Ci I Ch. 03: Resistive Circuits: Kyunghi ChangDocument52 pagesCH 03 Rii Ci I Ch. 03: Resistive Circuits: Kyunghi Chang임동훈No ratings yet
- Clases 1 3 LeydeOhmDocument23 pagesClases 1 3 LeydeOhmmanuel.zunigaNo ratings yet
- Kirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)Document7 pagesKirchhoff's Current Law (KCL)Kana Nil TorresNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Circuit Variables and Circuit Elements - Part IIDocument20 pagesChapter 2 Circuit Variables and Circuit Elements - Part IIDaniaNo ratings yet
- 2Document20 pages2Youssef HossamNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit Analysis: by Mr. Vinod Salunkhe Assistant Professor, EXTC Dept VPM's MPCOE, VelneshwarDocument46 pagesDC Circuit Analysis: by Mr. Vinod Salunkhe Assistant Professor, EXTC Dept VPM's MPCOE, Velneshwarvinod SALUNKHENo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Topic 5 Electricity Part 5 2022-2023Document14 pagesGrade 11 Topic 5 Electricity Part 5 2022-2023rhea.agarwal17No ratings yet
- 60 TOP MOST NETWORK THEOREMS - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pages60 TOP MOST NETWORK THEOREMS - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice QuestionsaftabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document6 pagesLecture 3Nazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Lecture 3 - 4Document24 pagesUnit 1 - Lecture 3 - 4Black spidey GamingNo ratings yet
- Cir2 Lect 1 Review PDFDocument21 pagesCir2 Lect 1 Review PDFKristine Benedicta Noche DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory - 1Document33 pagesCircuit Theory - 1m.cortis.mNo ratings yet
- Network TheoremsDocument13 pagesNetwork TheoremsJevan A. CalaqueNo ratings yet
- 60 TOP NETWORK THEOREMS Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersDocument12 pages60 TOP NETWORK THEOREMS Multiple Choice Questions and AnswersEarl Jenn AbellaNo ratings yet
- Lec02 DC Circuits Mod YapDocument36 pagesLec02 DC Circuits Mod YapAndrea OnglaoNo ratings yet
- Network Theorems MCQ PDF (Erexams - Com)Document11 pagesNetwork Theorems MCQ PDF (Erexams - Com)Ram RajaNo ratings yet
- Network Questions PDFDocument94 pagesNetwork Questions PDFsamyalarunNo ratings yet
- 2Document57 pages2s2-qx (s2.qx)No ratings yet
- Kirchoffs RulesDocument14 pagesKirchoffs RulesFrancis LobriñoNo ratings yet
- BEE-Unit - IDocument44 pagesBEE-Unit - Ipavankumar tvvNo ratings yet
- Electricity IDocument12 pagesElectricity IAbbasNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis (Gate Bits)Document90 pagesNetwork Analysis (Gate Bits)tvs_krishnavarma100% (3)
- Kirchhoffs LawsDocument5 pagesKirchhoffs LawsEng-Mohamed AbdelkhalekNo ratings yet
- CIRCUIT1 Lec02 Basic LawDocument29 pagesCIRCUIT1 Lec02 Basic LawChristian JavierNo ratings yet
- C1 - Fundamental of Electric CircuitDocument23 pagesC1 - Fundamental of Electric CircuitMd Imran Hossain 211-15-3964No ratings yet
- Network Theory QuestionsDocument89 pagesNetwork Theory QuestionsRam Mohan Rao Makineni100% (1)
- You Should Not Find This 2Document26 pagesYou Should Not Find This 2No OneNo ratings yet
- Clases5 hastaConexionesDeltaEstrellaDocument55 pagesClases5 hastaConexionesDeltaEstrellamanuel.zunigaNo ratings yet
- Phys502 Lect 7Document6 pagesPhys502 Lect 7MaissaNo ratings yet
- Removal Circuits1Document5 pagesRemoval Circuits1Rudinico Mariano TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - 2 - FDocument10 pagesLecture 1 - 2 - FNazmus SakibNo ratings yet
- Physics 2 Quarter 3 Module 5Document53 pagesPhysics 2 Quarter 3 Module 5Bea Lha Zandra BesingaNo ratings yet
- High Voltage Lecture 27Document24 pagesHigh Voltage Lecture 27Mansoor SarwarNo ratings yet
- CO2037 - VL01a - Basic Concepts and Resistive Circuits - 1Document12 pagesCO2037 - VL01a - Basic Concepts and Resistive Circuits - 1Lộc TrầnNo ratings yet
- ENGR204 Thevenin ChartDocument2 pagesENGR204 Thevenin ChartRezwan ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Lecture 3Document16 pagesUnit 1 - Lecture 3Abhay kushwahaNo ratings yet
- Ch02 BLawsDocument67 pagesCh02 BLawsThomas WondwosenNo ratings yet
- TRB Circuit Theory Test 1Document6 pagesTRB Circuit Theory Test 1Ragunathan NarayananNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit and Electronics NoteDocument34 pagesElectric Circuit and Electronics NoteEzekiel JamesNo ratings yet
- Lab QuestionsDocument1 pageLab QuestionsKomal Singh SheemarNo ratings yet
- Questions & Answers On Circuit Elements and Kirchhoff's LawsDocument28 pagesQuestions & Answers On Circuit Elements and Kirchhoff's Lawskibrom atsbha100% (2)
- 4 Kirchhoff's LawsDocument34 pages4 Kirchhoff's LawsNainum FAREEDNo ratings yet
- Pre InformeishonDocument3 pagesPre InformeishonAndresNo ratings yet
- Topic 1. Basic Concepts & Laws PDFDocument93 pagesTopic 1. Basic Concepts & Laws PDFkeinhuat79No ratings yet
- Case Study QuestionsDocument6 pagesCase Study Questionskabir sharmaNo ratings yet
- Ch02-Basic Laws - 副本Document73 pagesCh02-Basic Laws - 副本avishek aviNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document12 pagesLecture 4deepika yadavNo ratings yet
- Module - 1-Introduction To DC AnalysisDocument39 pagesModule - 1-Introduction To DC AnalysisananysatyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Electric Circuits: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesFrom EverandBasic Electric Circuits: Pergamon International Library of Science, Technology, Engineering and Social StudiesRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Oscillometry and Conductometry: International Series of Monographs on Analytical ChemistryFrom EverandOscillometry and Conductometry: International Series of Monographs on Analytical ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)