Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orientation in Space and Time
Uploaded by
mayana agarwalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Orientation in Space and Time
Uploaded by
mayana agarwalCopyright:
Available Formats
MYP Year: 5
Subject: Chemistry
Unit: Chemical equation and reaction
Global context: Orientation in space and Time
Task Sheet- Kinetic Theory
Criterion A – Knowing and Understanding
Task based on Kinetic theory of particle and nature of the substance which relates to their change of
states.
Name …………………………… Date ……………
Topics covered:
Kinetic theory of particles
Heating Cooling curve
1. Gases diffuse, which means that they move to occupy the total available volume.
(a) Explain, using kinetic particle theory, why gases diffuse. [2]
Diffusion is movement of particles in any direction, gases can diffuse because they have no fixed shape,
the particles are free to move wherever they want which is why they are able to move to occupty the
total available volume, however much it may be.
(b) When the colorless gases hydrogen bromide and ethylamine come into contact, a
white solid is formed.
CH3CH2NH2(g) + HBr(g) =>CH3CH2NH3Br(s)
white solid
The following apparatus can be used to compare the rates of diffusion of the two gases
ethylamine and hydrogen bromide.
PSG/MYP/CHEMISTRY/ UNIT-CHEMICAL REACTION AND EQUATION/TASK SHEET-KINETIC THEORY, HEATING
1
COOLING CURVE/VC/GS/2023-24
State at which position, A, B or C, the white solid will form. Explain your choice. [3]
A, ethylamine will diffuse faster bcz its molar mass is lesser than hydrogen bromide and lighter
molecules diffuse faster.
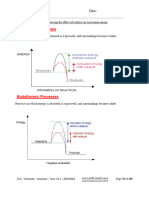
2 Ethanoic acid is a colorless liquid at room temperature. It has the typical acid properties and
forms compounds called ethanoates.
A pure sample of ethanoic acid is slowly heated from 0oC to 150oC and its temperature is
measured every minute. The results are represented on the graph below.
(i) State the change that occurs in the region D to E. = liquid to gas
[1]
(ii) Describe the difference in the region B to C if an impure sample had been used?
Could take more time if impure sample used because the melting point could increase due to more
components and higher force of attraction to break down.
[1]
PSG/MYP/CHEMISTRY/ UNIT-CHEMICAL REACTION AND EQUATION/TASK SHEET-KINETIC THEORY, HEATING
2
COOLING CURVE/VC/GS/2023-24
(iii) Draw on the graph how the line would continue if the acid was heated to a higher
temperature. [1]
(iv) Write down missing information in the following table that compares the separation and
movement of the molecules in regions C to D with those in E to F.
C to D E to F
Less
separation (distance
A lot
between particles)
movement of particles random and slow
Random and fast
yes
Can particles move apart to fill
yes
any volume?
PSG/MYP/CHEMISTRY/ UNIT-CHEMICAL REACTION AND EQUATION/TASK SHEET-KINETIC THEORY, HEATING
3
COOLING CURVE/VC/GS/2023-24
3.(a) A small amount of liquid bromine is added to a container which is then sealed.
Br2(l) Br2(g)
Explain using the ideas of the Kinetic Theory to why, after about an hour, the
bromine molecules have spread uniformly to occupy the whole container.
[3]
There is no presence of air and due to increased temperature of a container, the
liquid particles gained enough energy to break the bonds and vaporize to gas.
Bromine liquid turned into bromine gas which is how it was able to diffuse
uniformly to occupy the whole container.
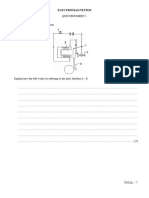
(b) The diagrams below show simple experiments on the speed of diffusion of gases.
PSG/MYP/CHEMISTRY/ UNIT-CHEMICAL REACTION AND EQUATION/TASK SHEET-KINETIC THEORY,
4
HEATING COOLING CURVE/VC/GS/2023-24
Based on the kinetic theory of particle explain the observations in the diagram -2 and 3. One has
been done for you.
The diagram -1 shows that there is air inside and outside the porous pot so the rate of diffusion of
air into the pot is the same as the rate of diffusion of air out of the pot. The pressure inside and
outside the pot is the same so the colored liquid is at the same level on each side of the tube.
Diagram-2
Diagram-3
4. The Kinetic Theory explains the properties of matter in terms of the arrangement and
movement of particles. Nitrogen is a gas at room temperature. Nitrogen molecules, N 2, which
are spread far apart move in a random manner at high speed.
(i) Explain how does the movement and arrangement of the molecules in a crystal of
nitrogen differ from those in gaseous nitrogen?
(ii) A sealed container contains nitrogen gas. The pressure of a gas is due to the molecules of the
gas hitting the walls of the container.
Explain why the pressure inside the container increases when the temperature is increased
PSG/MYP/CHEMISTRY/ UNIT-CHEMICAL REACTION AND EQUATION/TASK SHEET-KINETIC THEORY,
5
HEATING COOLING CURVE/VC/GS/2023-24
You might also like
- SS1 Chemistry 2nd Term Lesson Note PDFDocument58 pagesSS1 Chemistry 2nd Term Lesson Note PDFKelly Isaac100% (3)
- Matter Practice Worksheet 1 - 8 ChemDocument2 pagesMatter Practice Worksheet 1 - 8 ChembhaveshkhantedNo ratings yet
- Coil Tubing - IwcfDocument26 pagesCoil Tubing - IwcfWH Baloch67% (3)
- Chapter 3 Gases Lesson1 - 12Document97 pagesChapter 3 Gases Lesson1 - 12Julius Salas100% (1)
- Science 8 Q3 Periodic Exam Blooms Taxo With Answer KeyDocument6 pagesScience 8 Q3 Periodic Exam Blooms Taxo With Answer KeyPantz Revibes Pastor100% (1)
- Kinetic Molecular TheoryDocument3 pagesKinetic Molecular TheoryGarren Jude Aquino100% (1)
- Q4-Worksheet-Week 2Document7 pagesQ4-Worksheet-Week 2Gian EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Q4 M2-Chemical-EquilibriumDocument14 pagesGeneral Chemistry Q4 M2-Chemical-EquilibriumSteinerNo ratings yet
- Design of Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument42 pagesDesign of Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger3004 Divya Dharshini. MNo ratings yet
- Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter: Chapter 3 ReviewDocument8 pagesAtoms: The Building Blocks of Matter: Chapter 3 ReviewAref Dahabrah0% (1)
- Cryocap Air Liquide - BrochureDocument20 pagesCryocap Air Liquide - BrochurePriyanshi VNo ratings yet
- API 570 Piping Inspection: © Matthews Engineering Training LTDDocument35 pagesAPI 570 Piping Inspection: © Matthews Engineering Training LTDFernando Santos0% (1)
- Lecture 7 Turbulence Modeling IntroductiDocument48 pagesLecture 7 Turbulence Modeling IntroductiAnkit Dekhatawala SVNITNo ratings yet
- Introduction To LNG & Material Used in LNG ServicesDocument104 pagesIntroduction To LNG & Material Used in LNG ServicesVishaka ThekkedathNo ratings yet
- Lect-4-Material Balances With Chemical ReactionDocument23 pagesLect-4-Material Balances With Chemical ReactionBa 4xNo ratings yet
- GE Oil & Gas Aeroderivative Gas Turbine: Emission Reduction Techniques DLE1.0 SystemDocument46 pagesGE Oil & Gas Aeroderivative Gas Turbine: Emission Reduction Techniques DLE1.0 SystemJuan Manuel100% (2)
- 13 - Chapter 5 CFD Modeling and Simulation - 2Document28 pages13 - Chapter 5 CFD Modeling and Simulation - 2Zahid MaqboolNo ratings yet
- Theory of Bose-Einstein Condensation in Trapped Gases: Franco Dalfovo and Stefano GiorginiDocument50 pagesTheory of Bose-Einstein Condensation in Trapped Gases: Franco Dalfovo and Stefano Giorginibpadhi1704No ratings yet
- Thermo 02 00007Document6 pagesThermo 02 00007RunkitoNo ratings yet
- Particle View of States of Matter - Lesson 2Document16 pagesParticle View of States of Matter - Lesson 2uaeali072No ratings yet
- RMP v079 p1381Document74 pagesRMP v079 p1381buddy72No ratings yet
- Holdship17 - UCLCHEM - A Gas-Grain Chemical Code For Clouds, Cores, and C-ShocksDocument10 pagesHoldship17 - UCLCHEM - A Gas-Grain Chemical Code For Clouds, Cores, and C-ShocksYuxuan YuanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Ty 04Document7 pagesQuestion Bank Ty 04Arshad PathanNo ratings yet
- Cbse Board Examination Term-Ii: Class 11 - PhysicsDocument3 pagesCbse Board Examination Term-Ii: Class 11 - PhysicsMukeshkumar KadamNo ratings yet
- A-Physical Chemistry - BS - Chemistry - IUB-Revised-31.12.2020Document22 pagesA-Physical Chemistry - BS - Chemistry - IUB-Revised-31.12.2020Sabir Ali SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Two Multic ComponetDocument20 pagesTwo Multic ComponetFriday Niyehmi Abolorunke ChristopherNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Instability of The Hybrid Halide Perovskite Semiconductor CH NH PbiDocument7 pagesIntrinsic Instability of The Hybrid Halide Perovskite Semiconductor CH NH PbiNyau NyauNo ratings yet
- Adsorption and Desorption Process in Lab For H20, CO2, CO and Mixture of H2O-CO2 On AU SampleDocument39 pagesAdsorption and Desorption Process in Lab For H20, CO2, CO and Mixture of H2O-CO2 On AU SamplegauriNo ratings yet
- Chemistry U3 XITH2023Document4 pagesChemistry U3 XITH2023SA M MYNo ratings yet
- Benchmark VulcanDocument30 pagesBenchmark VulcanRicardo Angelo Quispe MendizábalNo ratings yet
- Dynamical Structural Science Five-Dimensional CrystallographyDocument9 pagesDynamical Structural Science Five-Dimensional CrystallographyArturo Velazquez MoralesNo ratings yet
- Combustion Unit 2 3 5Document62 pagesCombustion Unit 2 3 5shivkumarNo ratings yet
- Kurbanaliev 2022 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2373 022011Document13 pagesKurbanaliev 2022 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2373 022011life issexyNo ratings yet
- Note 28 Oct 2023Document21 pagesNote 28 Oct 2023Jihan Abou GhaddaraNo ratings yet
- Time Singularities of Correlators From Dirichlet Conditions in Ads/CftDocument30 pagesTime Singularities of Correlators From Dirichlet Conditions in Ads/CftR DaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 111/121 - Fall 2016 - Practice Term Test #1Document3 pagesChemistry 111/121 - Fall 2016 - Practice Term Test #1Nawaf AlsuhaibaniNo ratings yet
- Eksoterm EndotermDocument8 pagesEksoterm EndotermAkun FakeNo ratings yet
- Classical Fields Approximation For Bosons at Nonzero TemperaturesDocument38 pagesClassical Fields Approximation For Bosons at Nonzero TemperaturesChris RaymondNo ratings yet
- Bhairab Ganguly College: Physics DepartmentDocument2 pagesBhairab Ganguly College: Physics DepartmentUppu oopsuNo ratings yet
- Chemy102 Lab ManualDocument53 pagesChemy102 Lab ManualGhazanfar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Chem-Phys-Lett-2008-Delocalisation in Conjugated Triazene Chromophores-Insigth From TheoryDocument6 pagesChem-Phys-Lett-2008-Delocalisation in Conjugated Triazene Chromophores-Insigth From TheoryELKIN ALFONSO RODRIGUEZ AGUALIMPIANo ratings yet
- 2A Matter EXAMDocument4 pages2A Matter EXAMCarla MinghettiNo ratings yet
- The Structure of 13-Butadiene ClustersDocument20 pagesThe Structure of 13-Butadiene Clusterssof chimisteNo ratings yet
- Ut 4 Class Xi PhyDocument3 pagesUt 4 Class Xi PhyMohan SuyalNo ratings yet
- Modeling Ignition and Thermal Wave Progression in Binary Granular Pyrotechnic CompositionsDocument11 pagesModeling Ignition and Thermal Wave Progression in Binary Granular Pyrotechnic CompositionsShofi MuktianaNo ratings yet
- POGIL: Kinetic Molecular Theory: Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesPOGIL: Kinetic Molecular Theory: Learning ObjectivesSir JoshNo ratings yet
- 10 - HW PDFDocument3 pages10 - HW PDFnazeco tanjeroNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review Packet With QuestionsDocument58 pagesMidterm Review Packet With Questionszoohyun91720No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0016236122032987 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S0016236122032987 MainApri WiyonoNo ratings yet
- The Polytropic Equation of State of Interstellar Gas CloudsDocument23 pagesThe Polytropic Equation of State of Interstellar Gas Cloudstestonly261No ratings yet
- Unit 6 - Thermochemistry: Ap ChemistryDocument32 pagesUnit 6 - Thermochemistry: Ap Chemistrysyafr.e.424No ratings yet
- 2023 Unification of The First Law of Quantum ThermodynamicsDocument43 pages2023 Unification of The First Law of Quantum ThermodynamicsWI TONo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document27 pagesLecture 1Anonymous BW2VsFifi9No ratings yet
- Liu 2006Document19 pagesLiu 2006raz naghizaNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Generalised HydrodynamicsDocument76 pagesLecture Notes On Generalised Hydrodynamicsسيد محمد محمد سالمNo ratings yet
- Lecture On Holography Method of CondmatphyDocument86 pagesLecture On Holography Method of Condmatphyatticus peinNo ratings yet
- 3.5 Kinetic Molecular Theory StudentDocument5 pages3.5 Kinetic Molecular Theory StudentSyed RazaNo ratings yet
- AE4ASM002 Designing Materials With Aerospace Specific Properties SummaryDocument16 pagesAE4ASM002 Designing Materials With Aerospace Specific Properties SummaryJanJNo ratings yet
- Cluster Mergers, Core Oscillations, and Cold FrontsDocument11 pagesCluster Mergers, Core Oscillations, and Cold FrontsEdwin RetanaNo ratings yet
- Feshbach Resonances in Ultracold GasesDocument62 pagesFeshbach Resonances in Ultracold GasesJuanRivasNo ratings yet
- J.M. Martínez-Val Et Al - High Density Plasmas Formation in Inertial Confinement Fusion and AstrophysicsDocument4 pagesJ.M. Martínez-Val Et Al - High Density Plasmas Formation in Inertial Confinement Fusion and AstrophysicsOlmnopNo ratings yet
- Modern Terpyridine Chemistry. by Ulrich S. Schubert: Randolph Thummel, University of HoustonDocument3 pagesModern Terpyridine Chemistry. by Ulrich S. Schubert: Randolph Thummel, University of HoustonAbbyNo ratings yet
- Thermal Characterization of Polymers (MSE LAb 7)Document2 pagesThermal Characterization of Polymers (MSE LAb 7)GhostInTheFlameNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document19 pagesLecture 2RajeshNo ratings yet
- 2 - Article Boussessi-DMCDocument8 pages2 - Article Boussessi-DMCrahma boussassiNo ratings yet
- Handout - 2021 - CHEM F111Document2 pagesHandout - 2021 - CHEM F111vishnuNo ratings yet
- Physics334 S1 2021Document11 pagesPhysics334 S1 2021shuaicheng geNo ratings yet
- Yr 9 Physics Revision 3Document4 pagesYr 9 Physics Revision 3KitanNo ratings yet
- Cavity Cooling of An Atomic Array - Oxana MishinaDocument21 pagesCavity Cooling of An Atomic Array - Oxana MishinaCambiador de MundoNo ratings yet
- 1 Use The Periodic Table On Page 2 To Help You Answer This QuestionDocument10 pages1 Use The Periodic Table On Page 2 To Help You Answer This Questionmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Periodic - Table - Revision - Sheet - 1 - Crit - ADocument5 pagesPeriodic - Table - Revision - Sheet - 1 - Crit - Amayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Revision Sheet 2-Crit ADocument6 pagesPeriodic Table Revision Sheet 2-Crit Amayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Task Sheet - Periodic Table 2023Document10 pagesTask Sheet - Periodic Table 2023mayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Extra Ques ElectromagnetismDocument20 pagesExtra Ques Electromagnetismmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Bibliography Task 1Document3 pagesBibliography Task 1mayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- MYP 4 Ext. Parabolic Tiling BCD - SADocument8 pagesMYP 4 Ext. Parabolic Tiling BCD - SAmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Stopping Distance WsDocument3 pagesStopping Distance Wsmayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Psg/Myp/Year-4 /Chemistry/Unit2/Fa/Gs/Vc 1Document6 pagesPsg/Myp/Year-4 /Chemistry/Unit2/Fa/Gs/Vc 1mayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- Average Speed and VelocityDocument6 pagesAverage Speed and Velocitymayana agarwalNo ratings yet
- US Patent 2002 Distilasi ReaktifDocument9 pagesUS Patent 2002 Distilasi ReaktifMohammad Afif PrabowoNo ratings yet
- Water Distribution SystemsDocument49 pagesWater Distribution SystemsAnonymous fE2l3Dzl100% (1)
- XM Filter ElementDocument2 pagesXM Filter ElementhafsakrknNo ratings yet
- Odlicno Za Post Cured Smola Se Strdnuva Na 50 A Se Dopekuva Na 150Document2 pagesOdlicno Za Post Cured Smola Se Strdnuva Na 50 A Se Dopekuva Na 150Oliver RisteskiNo ratings yet
- Diagram For Understanding Chemical ProcessesDocument4 pagesDiagram For Understanding Chemical ProcessesPlay DineNo ratings yet
- FluxDiag - Data 2Document2 pagesFluxDiag - Data 2Dragisa DjukicNo ratings yet
- Concentration of ReactantsDocument4 pagesConcentration of ReactantsFernalyn Elaine TabilogNo ratings yet
- Answersheet 2nd Quarter W2 (Chemistry 2)Document4 pagesAnswersheet 2nd Quarter W2 (Chemistry 2)secret maskNo ratings yet
- Practice Worksheet 7 - Malinao - FernandoDocument3 pagesPractice Worksheet 7 - Malinao - Fernandonifermalinao22No ratings yet
- 8.TF Chemical KineticsDocument6 pages8.TF Chemical KineticsrajeshwariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. Measurement of Level and FlowDocument26 pagesChapter 7. Measurement of Level and FlowNguyen NguyenNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument2 pagesUntitledwilyo juniorNo ratings yet
- Chee Assignment 1Document13 pagesChee Assignment 1TSHEGOFATSO GOTSILENGNo ratings yet
- Aug Monthly Test Chem Set ADocument2 pagesAug Monthly Test Chem Set Adeepritesh2702No ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Analysis of Optimal Condensing Temperature of Cascade-Condenser in CO /NH Cascade Refrigeration SystemsDocument9 pagesThermodynamic Analysis of Optimal Condensing Temperature of Cascade-Condenser in CO /NH Cascade Refrigeration Systemslog duongNo ratings yet
- Kinetics of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polystyrene (PS) Dynamic PyrolysisDocument9 pagesKinetics of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) and Polystyrene (PS) Dynamic PyrolysissherryNo ratings yet
- Abstract Fly Ash MLPDocument2 pagesAbstract Fly Ash MLPGaya Jaya Coating IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- Chemical Process Calculations: Autumn 2021Document23 pagesChemical Process Calculations: Autumn 2021Ujjwal AnandNo ratings yet
- Flow Measurement (Sensors)Document3 pagesFlow Measurement (Sensors)josekadaNo ratings yet
- V5X VRF Service Manual 380V-3Ph-60HzgfjDocument105 pagesV5X VRF Service Manual 380V-3Ph-60HzgfjSam RVNo ratings yet