Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Jfuture 202005025
Uploaded by
devi kumarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Jfuture 202005025
Uploaded by
devi kumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Step 1: Define the Hypotheses
Null Hypothesis ( H 0): The population mean is equal to 80 ( μ=80).
Alternative Hypothesis ( H 1): The population mean is not equal to 80 ( μ ≠ 80).
Step 2: Calculate the Test Statistic
We use the formula for the t-statistic in a one-sample t-test, which measures how far the
sample mean is from the population mean in terms of the standard error of the mean:
x́−μ
t=
s/√n
Plugging in the values:
x́=77.5 (sample mean)
μ=80 (hypothesized population mean)
s=6.2 (sample standard deviation)
n=21 (sample size)
The standard error of the mean (SEM) is calculated as:
s 6.2
SEM= =
√ n √ 21
Then, calculate the t-statistic:
77.5−80
t=
SEM
Step 3: Calculate the Standard Error and the T-statistic
Let's calculate the standard error and the t-statistic.
The standard error of the mean (SEM) is approximately 1.353 , and the calculated t-
statistic is −1.848.
Step 4: Determine the Degrees of Freedom
The degrees of freedom (df) for a single-sample t-test is n−1:
df =n−1=21−1=20
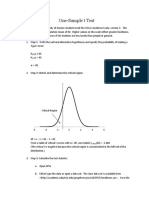
Step 5: Calculate the p-value
The p-value is the probability that under the null hypothesis ( H 0), we would observe a
statistic (in this case, the t-statistic) at least as extreme as the one calculated. Since it's a
two-tailed test (because the alternative hypothesis is μ ≠ 80), we calculate the p-value
from both tails of the t-distribution:
p-value=2 × T-distribution CDF of t statistic
Let's calculate the p-value using the degrees of freedom and the t-statistic:
The p-value for this test is approximately 0.079 . This value represents the probability of
observing a sample mean at least as extreme as 77.5 under the null hypothesis that the
true population mean is 80 , given the normal distribution of the population.
Step 6: Conclusion
The p-value to significance level (commonly α =0.05 ) to decide whether to reject or fail
to reject the null hypothesis:
If p-value≤ α , reject H 0.
If p-value>α , fail to reject H 0.
In this case, since the p-value ≈ 0.079 is greater than 0. 05, you would fail to reject the
null hypothesis. This indicates there is not enough evidence at the 5% significance level
to conclude that the population mean differs from 80.
Rounded to two decimal places, the p-value is 0.08.
You might also like
- CFA Level 1 Review - Quantitative MethodsDocument10 pagesCFA Level 1 Review - Quantitative MethodsAamirx6450% (2)
- Margin of ErrorDocument6 pagesMargin of ErrorFaith Febe AustriaNo ratings yet
- Document StatDocument5 pagesDocument StatYohannes AlemuNo ratings yet
- 1 Point Estimation: Parameter Estimation Kaustav Banerjee Decision Sciences Area, IIM LucknowDocument4 pages1 Point Estimation: Parameter Estimation Kaustav Banerjee Decision Sciences Area, IIM LucknowRajiv KumarNo ratings yet
- Statistics Hypothesis TestingDocument7 pagesStatistics Hypothesis TestingWasif ImranNo ratings yet
- TohDocument53 pagesTohY20me135 V.LokeshNo ratings yet
- Ch04le 1Document59 pagesCh04le 1Jose TrianoNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inference: Dr. Mona Hassan AhmedDocument34 pagesStatistical Inference: Dr. Mona Hassan Ahmedkareem3456No ratings yet
- One-Sample T TestDocument4 pagesOne-Sample T Testjorge9000000No ratings yet
- Calculating Standard Error Bars For A GraphDocument6 pagesCalculating Standard Error Bars For A GraphKona MenyongaNo ratings yet
- Psych Stats ReviewerDocument16 pagesPsych Stats ReviewerReycee AcepcionNo ratings yet
- Statistical TestsDocument24 pagesStatistical TestsSumit SharmaNo ratings yet
- AD3411 - 6 To11Document15 pagesAD3411 - 6 To11Raj kamalNo ratings yet
- Statistical Inference IIDocument3 pagesStatistical Inference IIshivam1992No ratings yet
- I. $E (/mu - T) 0$ Ii. $var (/mu - T) /sigma 2$ Iii. $cov (/mu - T,/mu - (T-J) ) 0 T/neq T-J$ Iv. $/mu - T /sim N (0,/sigma 2) $Document11 pagesI. $E (/mu - T) 0$ Ii. $var (/mu - T) /sigma 2$ Iii. $cov (/mu - T,/mu - (T-J) ) 0 T/neq T-J$ Iv. $/mu - T /sim N (0,/sigma 2) $Hʌɩɗɘʀ AɭɩNo ratings yet
- 9.1. Prob - StatsDocument19 pages9.1. Prob - StatsAnkit KabiNo ratings yet
- Lc07 SL Estimation - PPT - 0Document48 pagesLc07 SL Estimation - PPT - 0Deni ChanNo ratings yet
- Statistical EstimationDocument31 pagesStatistical EstimationAgung Nuza DwiputraNo ratings yet
- Module 6-1Document21 pagesModule 6-1Ho Uyen Thu NguyenNo ratings yet
- Lecture21 HypothesisTest1Document53 pagesLecture21 HypothesisTest1Sonam AlviNo ratings yet
- Handout 7Document16 pagesHandout 7farahNo ratings yet
- CHM 421 - ToPIC 3 - StatisticsDocument58 pagesCHM 421 - ToPIC 3 - StatisticsthemfyNo ratings yet
- ASPjskjkjksnkxdqlcwlDocument34 pagesASPjskjkjksnkxdqlcwlSonuBajajNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The T-Statistic: PSY295 Spring 2003 SummerfeltDocument19 pagesIntroduction To The T-Statistic: PSY295 Spring 2003 SummerfeltEddy MwachenjeNo ratings yet
- EX-Hypothesis Test of The MEANDocument5 pagesEX-Hypothesis Test of The MEANBobbyNicholsNo ratings yet
- STA101 Formula SheetDocument4 pagesSTA101 Formula SheetOlawale AwedaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: Statistical Inference by Dr. Javed IqbalDocument4 pagesLecture 5: Statistical Inference by Dr. Javed IqbalHamna AghaNo ratings yet
- Point and Interval EstimationDocument10 pagesPoint and Interval EstimationJiten BendleNo ratings yet
- Bootstrap Event Study Tests: Peter Westfall ISQS DeptDocument34 pagesBootstrap Event Study Tests: Peter Westfall ISQS DeptNekutenda PanasheNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics and Management Science NotesDocument74 pagesBusiness Statistics and Management Science Notes0pointsNo ratings yet
- Week 8:: Hypothesis Testing With One-Sample T-TestDocument18 pagesWeek 8:: Hypothesis Testing With One-Sample T-TestWillie WeiNo ratings yet
- Inferences Based On A Single Sample: Confidence Intervals and Tests of Hypothesis (9 Hours)Document71 pagesInferences Based On A Single Sample: Confidence Intervals and Tests of Hypothesis (9 Hours)Kato AkikoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Sampling Distributions: InfiniteDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Sampling Distributions: InfiniteNsy noormaeeerNo ratings yet
- Estimating Population Values PPT at BEC DOMSDocument50 pagesEstimating Population Values PPT at BEC DOMSBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)No ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Minggu 13 SimsisDocument9 pagesBahan Ajar Minggu 13 SimsisjovankaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Cheat SheetDocument23 pagesStatistics Cheat Sheetcannickg100% (2)
- Week 1 - Hypothesis Testing - Part 1Document77 pagesWeek 1 - Hypothesis Testing - Part 1Desryadi Ilyas MohammadNo ratings yet
- Topic07 WrritenDocument23 pagesTopic07 Wrritenjonathan.dinharaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Introduction To The T StatisticDocument32 pagesChapter 9 Introduction To The T StatisticdeNo ratings yet
- Review of StatisticsDocument36 pagesReview of StatisticsJessica AngelinaNo ratings yet
- Statistc in ChemistryDocument13 pagesStatistc in Chemistrycinvehbi711No ratings yet
- STA101 Formula SheetDocument4 pagesSTA101 Formula SheetConner BiekerNo ratings yet
- Testing of Hypothesis: 1 Steps For SolutionDocument8 pagesTesting of Hypothesis: 1 Steps For SolutionAaron MillsNo ratings yet
- PSYCH 240: Statistics For Psychologists: Interval Estimation: Understanding The T DistributionDocument44 pagesPSYCH 240: Statistics For Psychologists: Interval Estimation: Understanding The T DistributionSatish NamjoshiNo ratings yet
- Multiple Regression Analysis - InferenceDocument34 pagesMultiple Regression Analysis - InferenceAndre Mitsuo AkamineNo ratings yet
- Hypothesis HandoutsDocument17 pagesHypothesis HandoutsReyson PlasabasNo ratings yet
- Ed Inference1Document20 pagesEd Inference1shoaib625No ratings yet
- QueDocument13 pagesQueSatish G KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Hypotheses Test 1 HandoutDocument15 pagesHypotheses Test 1 HandoutTabbara MohamedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 2014 Statistical Data Treatment and EvaluationDocument44 pagesLecture 3 2014 Statistical Data Treatment and EvaluationRobert EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 Statistics 2Document47 pagesChapter 08 Statistics 2aymanNo ratings yet
- Basic Monte Carlo TechniquesDocument10 pagesBasic Monte Carlo TechniquesMobeen AhmadNo ratings yet
- MathDocument24 pagesMathNicole Mallari MarianoNo ratings yet
- Braun Bootstrap2012 PDFDocument63 pagesBraun Bootstrap2012 PDFJoe OgleNo ratings yet
- P1.T2. Quantitative AnalysisDocument23 pagesP1.T2. Quantitative Analysisruthbadoo54No ratings yet
- 02data Part2Document34 pages02data Part2baigsalman251No ratings yet
- Consent FormDocument2 pagesConsent FormMegNo ratings yet
- Refelction Essay 3Document3 pagesRefelction Essay 3api-709105209No ratings yet
- Hotel Clarks Avadh - Sales PromotionDocument69 pagesHotel Clarks Avadh - Sales PromotionSujay Vikram Singh0% (1)
- Cost Comparison On Industrialized Building System (IBS) and Conventional Method For School Construction ProjectDocument7 pagesCost Comparison On Industrialized Building System (IBS) and Conventional Method For School Construction ProjectJudy TanNo ratings yet
- Math7 q4 ReviewerDocument13 pagesMath7 q4 ReviewerShanelle SalmorinNo ratings yet
- CH 6Document31 pagesCH 6MabelNo ratings yet
- Iip Final Report FormatDocument2 pagesIip Final Report FormatKASTURI P (Marketing 21-23)No ratings yet
- RSPO GHG Assessment Procedure For New Development, V3-EnglishDocument68 pagesRSPO GHG Assessment Procedure For New Development, V3-EnglishChong Yi KokNo ratings yet
- Sa3 - 2Document72 pagesSa3 - 2Cherry JaraNo ratings yet
- Body Scan AnalysisDocument9 pagesBody Scan AnalysisAmaury CosmeNo ratings yet
- The Coffee Shop Dining ExperieDocument18 pagesThe Coffee Shop Dining ExperieFelisitas AgnesNo ratings yet
- Bhavani PPT On SynopsisDocument12 pagesBhavani PPT On SynopsisAnkitha KavyaNo ratings yet
- Chartier Toolkit - forLeadershipandLearningDocument109 pagesChartier Toolkit - forLeadershipandLearningKacper RucińskiNo ratings yet
- Contour MappingDocument3 pagesContour MappingvikaskamalNo ratings yet
- Perceptions of Nurses Towards The Adoption of A Computerized Documentation SystemDocument12 pagesPerceptions of Nurses Towards The Adoption of A Computerized Documentation SystemTrixia RiveraNo ratings yet
- RM Module 2-1Document20 pagesRM Module 2-1mansiNo ratings yet
- 4 Pretest and Posttest AnalysisDocument6 pages4 Pretest and Posttest AnalysisRonnie NaagNo ratings yet
- Of K-Pop Fandom (Yia, 2012), Media Dependency TheoryDocument23 pagesOf K-Pop Fandom (Yia, 2012), Media Dependency TheoryJoseph Lorenzo Acosta CerilloNo ratings yet
- 444 Brickell Ave Phase I Report 5-15-21Document39 pages444 Brickell Ave Phase I Report 5-15-21the next miami100% (1)
- A Strategic Human Resource Approach To Leading Diversified Teams: A Case Study of The U.S. MilitaryDocument59 pagesA Strategic Human Resource Approach To Leading Diversified Teams: A Case Study of The U.S. MilitaryIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- What Is Research?: Research Methods For ArchitectureDocument9 pagesWhat Is Research?: Research Methods For ArchitectureshanNo ratings yet
- Self-Regulation of Action and AffectDocument27 pagesSelf-Regulation of Action and AffectClaudia AvendañoNo ratings yet
- Why and When Paradoxical Leader Behavior Impact Employee Creativity: Thriving at Work and Psychological SafetyDocument12 pagesWhy and When Paradoxical Leader Behavior Impact Employee Creativity: Thriving at Work and Psychological SafetyImran KhanNo ratings yet
- The Less Americans Know About Ukraine's Location, The More They Want U.S. To InterveneDocument3 pagesThe Less Americans Know About Ukraine's Location, The More They Want U.S. To InterveneThavamNo ratings yet
- A Study On The Estimation of Cost Functions For The Trucking Industry in KoreaDocument10 pagesA Study On The Estimation of Cost Functions For The Trucking Industry in KoreaDinesh PoudelNo ratings yet
- TS101 PDFDocument33 pagesTS101 PDFHafizAhmadNo ratings yet
- Physics 3 May 2007Document12 pagesPhysics 3 May 2007Sheena ShahNo ratings yet
- Half-Cell Potential Test From The Upper-Side and The Lower-Side of Reinforced Concrete Slabs: A Comparative StudyDocument6 pagesHalf-Cell Potential Test From The Upper-Side and The Lower-Side of Reinforced Concrete Slabs: A Comparative StudyANNADURAINo ratings yet
- An Investigation Into Employee Job Satisfaction and Its Impact On Organizational EffectivenessDocument8 pagesAn Investigation Into Employee Job Satisfaction and Its Impact On Organizational EffectivenessAhmad Nurhadi Al-GhazaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter VI Communication For Academic PurposeDocument59 pagesChapter VI Communication For Academic PurposeJohn Michael Gaoiran GajotanNo ratings yet