Professional Documents
Culture Documents
C H O + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 P 2 Pyruvic Acid, (CH (C O) Cooh + 2 Atp + 2 Nadh + 2 H+
C H O + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 P 2 Pyruvic Acid, (CH (C O) Cooh + 2 Atp + 2 Nadh + 2 H+
Uploaded by
Terefe Tsegaye BogaleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
C H O + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 P 2 Pyruvic Acid, (CH (C O) Cooh + 2 Atp + 2 Nadh + 2 H+
C H O + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 P 2 Pyruvic Acid, (CH (C O) Cooh + 2 Atp + 2 Nadh + 2 H+
Uploaded by
Terefe Tsegaye BogaleCopyright:
Available Formats
Cellular respiration or aerobic respiration is a series of chemical reactions which begin with the reactants
of sugar in the presence of oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water as waste products.
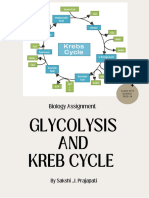
Cellular respiration has four stages
The first metabolic pathway during cellular respiration is glycolysis. Coming from the Greek word
―glyk‖ which means ―sweet‖ and ―lysis‖ which means ―dissolution―, glycolysis is the breakdown of
one molecule of glucose (sugar) into two molecules of pyruvate.
As shown in the above diagram, glycolysis takes place in the cytosol.
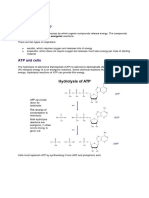
C6H12O6 + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 P → 2 pyruvic acid, (CH3(C=O) COOH + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+
Glycolysis produce two ATP molecules, four molecules are actually produced during the entire process.
However, two molecules are consumed during the preparatory phase, hence, resulting to a net of just two
ATP molecules.
The second stages is so-called ―link reaction” that occurs. Pyruvate from glycolysis is oxidized
(converted) to acetyl coA, one molecule of NADH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), and one molecule
of carbon dioxide.
The third stage is called as the Tricarboxylic Acid (TCA) cycle, or simply the Citric Acid cycle, the
Krebs cycle (identified by Hans Adolf Krebs)
The Krebs cycle, which occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion, includes a series of oxidation-
reduction reactions that result in the oxidation of the acetyl group to two carbon dioxide molecules
You might also like
- Lab 5 Alcoholic Fermentation in YeastDocument15 pagesLab 5 Alcoholic Fermentation in YeastFilipe GoncalvesNo ratings yet
- 12 RespirationDocument3 pages12 RespirationSan Siddz100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration Process: C H O + 6O + 6H O 12H O + 6 CoDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration Process: C H O + 6O + 6H O 12H O + 6 CoCatherine Rose Villarin AlferezNo ratings yet
- Far Eastern University: Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis and Citric Acid CycleDocument6 pagesFar Eastern University: Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis and Citric Acid CycleAnne Nicole ZalamedaNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesCellular RespirationErnest Nuñez LoquinarioNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesCellular RespirationErnest Nuñez LoquinarioNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleDocument10 pagesDifference Between Glycolysis and Krebs CycleKuresh RabidNo ratings yet
- Fermentation and TypesDocument3 pagesFermentation and TypesJared AllenNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration SummaryDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Summarylady ann jimenezNo ratings yet
- 2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoDocument6 pages2 Glucose Is in Phase TwoLucas BuSheaNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Notes - StudentDocument3 pagesCellular Respiration Notes - StudentjoisbastaNo ratings yet
- Biology Assignment - 20231106 - 003633 - 0000Document17 pagesBiology Assignment - 20231106 - 003633 - 0000vikashjejusar1No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument18 pagesCellular RespirationrhaineNo ratings yet
- C 4 - 1 - Cellular Respiration ProcessDocument114 pagesC 4 - 1 - Cellular Respiration ProcessNGỌC TRẦN NGUYỄN BẢONo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds GlucoseDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds Glucosemegamega11No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration - Aerobic and AnaerobicDocument5 pagesCellular Respiration - Aerobic and AnaerobicJeaña Despi DaguismolNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Metabolism Glycolysis and T.C.A. CycleDocument23 pagesIntroduction To Metabolism Glycolysis and T.C.A. Cycleمحمد جانNo ratings yet
- Respiration-Glycolysis and Krebs CycleDocument17 pagesRespiration-Glycolysis and Krebs CycleTwinkle MounamiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration PDFDocument10 pagesCellular Respiration PDFAnonymous HXLczq3No ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration 1Document28 pagesCellular Respiration 1Maria Flor PabeloniaNo ratings yet
- Las Q4 WK3.1Document8 pagesLas Q4 WK3.1Perlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- What Is Respiration?Document10 pagesWhat Is Respiration?Yana LouisseNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy and Physiology II: Biology 1414 Unit 8 Metabolism and NutritionDocument103 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology II: Biology 1414 Unit 8 Metabolism and Nutritionciroj25No ratings yet
- Bioenergetic 2 Report 85%finishDocument11 pagesBioenergetic 2 Report 85%finishYap StainleyNo ratings yet
- JacobDocument10 pagesJacobJaysley Jacob Mazala MazalaNo ratings yet
- Fermentationprocess 150129034150 Conversion Gate02Document14 pagesFermentationprocess 150129034150 Conversion Gate02skNo ratings yet
- Respiration CycleDocument1 pageRespiration CycleEy KaguriNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On Cellular RespirationDocument16 pagesLecture Notes On Cellular RespirationBhillee Agas ValdezNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeDocument8 pagesCellular Respiration Is A Set of Metabolic Reactions and Processes That TakeashNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesCellular RespirationNiña Jennifer Potter Vergara100% (2)
- Gen Bio Reviewer 2nd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio Reviewer 2nd QuarterauroraroderosNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesGlycolysis and Cellular RespirationAlessandro IevaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Notes: Cellular RespirationDocument34 pagesChapter 9 Notes: Cellular RespirationJevon Freshness EllisNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid CycleDocument22 pagesCitric Acid CycleSteph VeeNo ratings yet
- Biological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of FoodDocument13 pagesBiological Oxidation. JP: Caloric Value of Foodsagar sagu100% (1)
- Respiratory System and Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesRespiratory System and Cellular Respirationalexandra.munozNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Respiration NotesDocument1 pagePhotosynthesis and Respiration NotesjazsloanNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument3 pagesBioenergeticslai weng hongNo ratings yet
- GB1 Q2 Week-3bDocument10 pagesGB1 Q2 Week-3bAnnejhel Mae PoralanNo ratings yet
- Lab.3 PhysicsDocument4 pagesLab.3 Physicsksoo5118No ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument6 pagesCellular RespirationBrian Reyes GangcaNo ratings yet
- Week 7 PhotosynthesisDocument5 pagesWeek 7 PhotosynthesisCarl Brian L. MonteverdeNo ratings yet
- Class 11 - Biology - Respiration in PlantsDocument13 pagesClass 11 - Biology - Respiration in PlantsDivyansheeNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesisjeankayzelrodelasNo ratings yet
- C6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O +ATP: RespirationDocument2 pagesC6H12O6 + 6O2 - 6CO2 + 6H2O +ATP: RespirationHarleen BalNo ratings yet
- CO2 H2O: Light Reacti On Calvin CycleDocument4 pagesCO2 H2O: Light Reacti On Calvin Cycleyazi08No ratings yet
- C H O + 6O 6CO + 6H O: Cellular RespirationDocument7 pagesC H O + 6O 6CO + 6H O: Cellular RespirationKristi IvanovaNo ratings yet
- Module 3C - Cellular RespirationDocument9 pagesModule 3C - Cellular RespirationDiane Balaba OsingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cell RespirationDocument12 pagesChapter 5 Cell Respirationaznknight323No ratings yet
- CH 7 Notes Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesCH 7 Notes Cellular RespirationCJ100% (1)
- Bio CH09 L01Document9 pagesBio CH09 L01MrMidoo2020No ratings yet
- Palco Aimee Nicole A. 11 Abm E What Is Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesPalco Aimee Nicole A. 11 Abm E What Is Cellular RespirationRonalou PalcoNo ratings yet
- Palco Aimee Nicole A. 11 Abm E What Is Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesPalco Aimee Nicole A. 11 Abm E What Is Cellular RespirationRonalou PalcoNo ratings yet
- Fermentation and RespirationDocument45 pagesFermentation and RespirationNedhal Mahmoud KaleefahNo ratings yet
- Four Stages of Respiration: What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?Document1 pageFour Stages of Respiration: What Is The Formula For Cellular Respiration?AqilahNo ratings yet
- 5 - Lab 5 - Alc Ferm in Yeast - F2009Document15 pages5 - Lab 5 - Alc Ferm in Yeast - F2009Odhiambo HenryNo ratings yet
- Answer 2) : Cellular RespirationDocument2 pagesAnswer 2) : Cellular RespirationNabeel ZahurNo ratings yet
- Cellular Respiration PetaDocument2 pagesCellular Respiration PetaChloue DavidNo ratings yet
- Part II: Match Items Given in Column B' With Items Given in Column A' A'' B''Document1 pagePart II: Match Items Given in Column B' With Items Given in Column A' A'' B''Terefe Tsegaye BogaleNo ratings yet
- English Grade 7 Teachers Guide Zero DraftDocument168 pagesEnglish Grade 7 Teachers Guide Zero DraftTerefe Tsegaye BogaleNo ratings yet
- At The End of This Unit, Learners Will Able ToDocument1 pageAt The End of This Unit, Learners Will Able ToTerefe Tsegaye BogaleNo ratings yet
- Mahts g8 Model3Document6 pagesMahts g8 Model3Terefe Tsegaye Bogale100% (1)
- AccelerantsDocument85 pagesAccelerantsTerefe Tsegaye BogaleNo ratings yet