Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Chemistry of Maple Syrup
Uploaded by
chumak.alyona.uaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Chemistry of Maple Syrup
Uploaded by
chumak.alyona.uaCopyright:
Available Formats
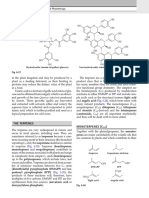
MAPLE SYRUP CHEMISTRY
Maple syrup is the largest commercially produced product derived from tree sap. The sweet
syrup has more constituents than just sugar, however. Here’s a brief look at a small selection.
SUGARS ACIDITY
HO
HO O
HO OH
O O HO
OH
HO O
OH HO
OH O OH
Sucrose is the main sugar in Maple syrup is slightly acidic
maple syrup, making up almost due to the presence of several
70% of its composition. The organic acids. The most
percentages of other sugars abundant of these is malic
are very low by comparison. acid, at around 0.5%.
PHENOLIC COMPOUNDS SOURCE OF COLOUR
HO
HO O
HO
O O
OH
N N N
O
R R R
VANILLIN (ABOVE) HO O EXAMPLE FRAGMENT OF A MELANOIDIN STRUCTURE
AND QUEBECOL (RIGHT) (Melanoidins are brown polymers formed by the Maillard reaction)
Phenolic compounds in maple syrup form from Maple syrup is graded according to its colour.
degradation of lignin in sap, though some, like However, we still don’t know the exact compounds
quebecol, form in the syrup-making process. Some behind its colouration. Maillard reactions,
contribute to the syrup’s flavour, though the exact caramelisation, and formation of polycarbonyl
combination of compounds remains unclear. compounds have all been implicated.
© COMPOUND INTEREST 2015 - WWW.COMPOUNDCHEM.COM | @COMPOUNDCHEM
C Shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives licence.
Image: CC BY-NC licence, The Wild Center, https://goo.gl/FmsdFE BY NC ND
You might also like
- Science and Cooking - Michael BrennerDocument341 pagesScience and Cooking - Michael BrennerĐại Đao Vương100% (11)
- The Chemistry of Coffee v2 PDFDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Coffee v2 PDFJanifer JohnNo ratings yet
- Casa Moriones Elite Packages 100 GuetsDocument2 pagesCasa Moriones Elite Packages 100 GuetsCarlo Juancho P. Funtanilla50% (2)
- 10 - Beer Stabilization Technology-Clearly A Matter of ChoiceDocument42 pages10 - Beer Stabilization Technology-Clearly A Matter of ChoiceGiorgi GhambashidzeNo ratings yet
- 3.4. Tannins by Betty 2016Document27 pages3.4. Tannins by Betty 2016BEHANo ratings yet
- 02 - Haze FormationDocument22 pages02 - Haze FormationGiorgi GhambashidzeNo ratings yet
- Biosynthesis of Natural Products Derived From Shikimic Acid 4.1. Phenyl-Propanoid Natural Products (C - C)Document22 pagesBiosynthesis of Natural Products Derived From Shikimic Acid 4.1. Phenyl-Propanoid Natural Products (C - C)Preeti YadavNo ratings yet
- 9-Advacnes in LigninDocument35 pages9-Advacnes in LigninHarry DouglasNo ratings yet
- TEST METHOD GUAR GUM FAO Additive-412Document4 pagesTEST METHOD GUAR GUM FAO Additive-412Sol SolNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of PoppiesDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of PoppiesShruti SinghalNo ratings yet
- Cocktail Chemistry: The Chemistry of A Mojito: O OH O OH O HODocument1 pageCocktail Chemistry: The Chemistry of A Mojito: O OH O OH O HOVicManT.MolinaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy: Tannin Containing DrugsDocument16 pagesPharmacognosy: Tannin Containing Drugsratchagar aNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Red LipstickDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Red LipstickDian Permata AdmNo ratings yet
- Honey Health Benefits and Uses in Medicine: Hana Scepankova, Jorge A. Saraiva, and Letícia M. EstevinhoDocument14 pagesHoney Health Benefits and Uses in Medicine: Hana Scepankova, Jorge A. Saraiva, and Letícia M. EstevinhoAndrés Felipe Zapata MurielNo ratings yet
- Poly Suga NateDocument2 pagesPoly Suga NatemndmattNo ratings yet
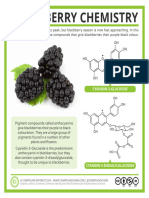
- Blackberry ChemistryDocument1 pageBlackberry Chemistrychumak.alyona.uaNo ratings yet
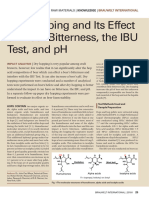
- Dry Hopping and Its Effects On Bitterness Ibu PH Brauwelt 2018 1 25 1601582140723Document5 pagesDry Hopping and Its Effects On Bitterness Ibu PH Brauwelt 2018 1 25 1601582140723louzadasamaNo ratings yet
- Senyawa Bahan Alam Bersifat RacunDocument10 pagesSenyawa Bahan Alam Bersifat RacunPriscilaNo ratings yet
- 08Document9 pages08Michele PierigéNo ratings yet
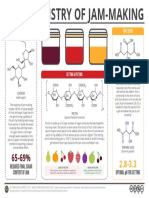
- The Chemistry of Jam Making PDFDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Jam Making PDFanton_428No ratings yet
- Vodka 2024 3Document1 pageVodka 2024 3Kicki AnderssonNo ratings yet
- 1 Hesperidin IsolationDocument5 pages1 Hesperidin IsolationSajanMaharjanNo ratings yet
- The Chemistry of Wine 2016 1Document1 pageThe Chemistry of Wine 2016 1Stephane HelfgotNo ratings yet
- 1362 4908 1 PBDocument10 pages1362 4908 1 PBAhmad BakkorNo ratings yet
- Poly SugaMulseDocument2 pagesPoly SugaMulsemndmattNo ratings yet
- Wort Boiling and ClarificationDocument116 pagesWort Boiling and ClarificationYuri Basda100% (1)
- Figures-Facts-Benefits BENEO FinalDocument16 pagesFigures-Facts-Benefits BENEO FinalBryan TorresNo ratings yet
- Areas of Research in Green Chemistry: FeedstocksDocument58 pagesAreas of Research in Green Chemistry: FeedstocksjohnNo ratings yet
- Polyaquole284a2 2w 0414Document8 pagesPolyaquole284a2 2w 0414Ishwar LavhaleNo ratings yet
- Review Article: Structural Characterization of Lignin and Its Degradation Products With Spectroscopic MethodsDocument16 pagesReview Article: Structural Characterization of Lignin and Its Degradation Products With Spectroscopic MethodsIngrid ContrerasNo ratings yet
- TerpenosDocument4 pagesTerpenosDaniel Castillo hernándezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09Document10 pagesLecture 09CataNo ratings yet
- Symthesis of AspirinDocument9 pagesSymthesis of Aspiringamer lionNo ratings yet
- P. Shajesh, S. Smitha, P. R. Aravind, P. Krishna Pillai, K.G.K. WarrierDocument20 pagesP. Shajesh, S. Smitha, P. R. Aravind, P. Krishna Pillai, K.G.K. WarriershajeshNo ratings yet
- Lecture AZB - Stumbé 2021-2022 Introduction To PolymersDocument62 pagesLecture AZB - Stumbé 2021-2022 Introduction To PolymersФарида СултановаNo ratings yet
- Alcohols-Structure and Synthesis 2Document82 pagesAlcohols-Structure and Synthesis 2Ali Issa OthmanNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Pathways: Glycolysis Pentose Phosphate PathwayDocument1 pageMetabolic Pathways: Glycolysis Pentose Phosphate PathwayLucasLeãoNascimentoNo ratings yet
- HoneyDocument30 pagesHoneySayed Newaj ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Poly Suga BetaineDocument4 pagesPoly Suga Betainemndmatt100% (1)
- The Chemistry of Litmus and LichensDocument1 pageThe Chemistry of Litmus and LichenszartabsocialmediaNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Dietary Polyphenols and Their Therapeutic EffectsDocument15 pagesAn Overview of Dietary Polyphenols and Their Therapeutic EffectsBRUNO JOSE BRITO TEIXEIRANo ratings yet
- BV Polymer PDFDocument34 pagesBV Polymer PDFPrathamesh KumbharNo ratings yet
- Flavonoid Full 2023Document66 pagesFlavonoid Full 2023Tasya AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Classes Winter11 30CID18 LipidsCh26Document21 pagesClasses Winter11 30CID18 LipidsCh26Daniel TranNo ratings yet
- Answerstochapter7.Pdf: Ltrece Química Orgánica Biológica 4º Grado en Química Facultad de Química Universitat de ValènciaDocument8 pagesAnswerstochapter7.Pdf: Ltrece Química Orgánica Biológica 4º Grado en Química Facultad de Química Universitat de ValènciaJorge Jimenez CuencaNo ratings yet
- Lipasa CalixarenoDocument10 pagesLipasa CalixarenoNicole CollazosNo ratings yet
- AspirinDocument22 pagesAspirinNaveen PatelNo ratings yet
- The-Chemistry-Of-Condensed-TanninsDocument28 pagesThe-Chemistry-Of-Condensed-TanninsIvan Fisgativa VillarragaNo ratings yet
- Wine Mouthfeel and Texture Author Seth CohenDocument24 pagesWine Mouthfeel and Texture Author Seth CohenMiho CraftsNo ratings yet
- Diosmetin ReviewDocument9 pagesDiosmetin ReviewAshu GadewarNo ratings yet
- Myths Sorghum EnglishDocument3 pagesMyths Sorghum EnglishrbusingeNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics & Acidity: Objectives GoalDocument21 pagesThermodynamics & Acidity: Objectives GoalNahokoSatomiNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Sugars PDFDocument29 pagesAnalysis of Sugars PDFVasco BrancoNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Sugars PDFDocument29 pagesAnalysis of Sugars PDFAbu RaihanNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Sugars PDFDocument29 pagesAnalysis of Sugars PDFKhalidNo ratings yet
- What Is Organic Chemistry?Document72 pagesWhat Is Organic Chemistry?gs7514424No ratings yet
- Drug Discovery and DevelopmentDocument34 pagesDrug Discovery and DevelopmentShowmic AhmedNo ratings yet
- How to Fuel Your Vehicles With the Power of Ethanol: Introductory Manual to the Elaboration of Ethanol, Gasohol, E10, E20 and E85 FuelsFrom EverandHow to Fuel Your Vehicles With the Power of Ethanol: Introductory Manual to the Elaboration of Ethanol, Gasohol, E10, E20 and E85 FuelsNo ratings yet
- Part 1Document5 pagesPart 1ธัญชนกNo ratings yet
- Gktoday MCQ January 2023 PDFDocument56 pagesGktoday MCQ January 2023 PDFKaran Singh100% (1)
- Miss Callaghan Comes To GriefDocument149 pagesMiss Callaghan Comes To GriefSunil D. MehtaNo ratings yet
- SHN Learning Resource - PPT - NutritionDocument45 pagesSHN Learning Resource - PPT - NutritionJHOY ANDREA MARIE CRUZNo ratings yet
- Anshu Marriage ProjectDocument17 pagesAnshu Marriage Projectdeyanshu7No ratings yet
- Sikkim: An Enrichment Activity by Abhimanyu Nair, Tanmay Sharma and Arneesh Srivastava of 8Document11 pagesSikkim: An Enrichment Activity by Abhimanyu Nair, Tanmay Sharma and Arneesh Srivastava of 8Abhi NairNo ratings yet
- Drug Abuse NotesDocument10 pagesDrug Abuse NoteskenNo ratings yet
- DHDBBB43552019Document13 pagesDHDBBB43552019linh lmkNo ratings yet
- Global HungerDocument35 pagesGlobal HungerJANMATTHEW PAPANo ratings yet
- Crafting - Alchemy, Herbalism, & Poisons - GM BinderDocument1 pageCrafting - Alchemy, Herbalism, & Poisons - GM BindersaisanziNo ratings yet
- Refined Guar SplitDocument37 pagesRefined Guar SplitkashifBack upNo ratings yet
- FR 1975 11 24 PDFDocument128 pagesFR 1975 11 24 PDFArifin ZakyNo ratings yet
- Service Blueprint - Restaurant DiningDocument3 pagesService Blueprint - Restaurant DiningArvindManoharan100% (2)
- V2 - Unit 6 - English IV - OKDocument38 pagesV2 - Unit 6 - English IV - OKDICQNo ratings yet
- The Last of The MohicansDocument53 pagesThe Last of The MohicansInti LlaphaNo ratings yet
- Nitin 2Document2 pagesNitin 2Zenni KalraNo ratings yet
- Atomic Habits - 1 Hour Action Guide VFDocument26 pagesAtomic Habits - 1 Hour Action Guide VFarjungangadharNo ratings yet
- Iregular Verb: V1 V2 V3 Ving MeaningDocument2 pagesIregular Verb: V1 V2 V3 Ving MeaningTejo AllvianNo ratings yet
- Determining Vicinal Diketones in Beer Using Valve-and-Loop Headspace AnalysisDocument4 pagesDetermining Vicinal Diketones in Beer Using Valve-and-Loop Headspace Analysisbethel mekonnenNo ratings yet
- SPS Agreement Under The WTO: The Indian ExperienceDocument16 pagesSPS Agreement Under The WTO: The Indian Experiencenightangle23No ratings yet
- Business Plan AsstDocument15 pagesBusiness Plan AsstAman KemalNo ratings yet
- Region 2 Write Up Part Abc and Some of D Hehe EditDocument6 pagesRegion 2 Write Up Part Abc and Some of D Hehe EditAmabelle DuranNo ratings yet
- Multicooker RMC-M4502E User ManualDocument192 pagesMulticooker RMC-M4502E User ManualMiriamLopezNo ratings yet
- Material Safety Data SheetDocument12 pagesMaterial Safety Data SheetDEEP PATELNo ratings yet
- Operations ManagementDocument6 pagesOperations ManagementYaswanth KumarNo ratings yet
- US VERSION - ElevateYourSustainabilityStrategywiththerighpackagingDocument10 pagesUS VERSION - ElevateYourSustainabilityStrategywiththerighpackagingSaddam BousbataNo ratings yet
- Policy Brief Template 20Document9 pagesPolicy Brief Template 20Muh. SahrilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Elephant Part 1Document4 pagesAnatomy Elephant Part 1AqilahNo ratings yet