Professional Documents
Culture Documents
River Systems
River Systems
Uploaded by
nokumavhaivhaiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
River Systems
River Systems
Uploaded by
nokumavhaivhaiCopyright:
Available Formats
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
SESSION 5: RIVER SYSTEMS
KEY CONCEPTS:
In this session we will focus on the following aspects:
- Where the water in rivers come from.
- Factors influencing run-off, infiltration (and rate of erosion)
- Drainage basins
X-PLANATION:
1. WHERE DOES THE WATER IN RIVERS COME FROM?
Surface run-off / Direct run-off:
Sheet flow and stream flow after precipitation. (Meteoric water)
Ground water / Base flow:
Infiltrated water that is first stored as ground water and later seeps into
streams.
This is supplemented with juvenile water and fossil water in some regions.
Hydrological Cycle:
Brought to you by Page 1
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
2. FACTORS INFLUENCING RUN-OFF, INFILTRATION (AND RATE OF
EROSION)
Precipitation: Soft – more infiltration, Hard – less infiltration.
Winter rain – less evaporation – more infiltration, summer rain – more
evaporation less infiltration.
Soil moisture content: If soil is already saturated with water there will be
little infiltration and more run-off.
Vegetation: Dense vegetation enhances infiltration, while sparse vegetation
leads to more run-off and less infiltration.
Gradient of the slope: Steep slopes lead to more run-off, and gradual
slopes enhance infiltration.
Porosity: Porous rock allows more infiltration and reduces the run-off in the
area.
Permeability: Rock with joints and cracks allows more infiltration.
2. DRAINAGE BASINS:
Terminology:
River system: main stream and all its tributaries.
Drainage basin / Catchment area: The whole area drained by a river
system. Area from where stream gets water.
Watershed: The high lying areas that separate different drainage basins.
Interfluves: Spurs that separate different tributaries in a river system.
Tributary: Smaller stream that joins main stream.
Confluence: Where 2 tributaries meet.
River Systems:
A: Main stream / Mouth
B: Tributary
C: Watershed
D: Origin of stream
E: Interfluves
F: Main watershed
Brought to you by Page 2
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
Drainage Basin of South Africa:
Source: Geomatica Titanium – South Africa, Hydrology
3.1. Characteristic of a Drainage Basin:
3.1.1 Stream Order:
All origin streams are order 1, where 2 similar order streams meet, it goes to
the next order, e.g. 3 meets 3 = 4
The higher the order, the less of those streams that would be in a drainage
basin.
Higher order streams are longer than low order streams.
Low order streams have steeper gradients than high order streams.
Higher order streams drain larger areas of the total drainage basin.
Brought to you by Page 3
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
3.1.2. Drainage Density:
The total length of all streams in a drainage basin:
Fine – many streams / area
Medium – average amount of streams
Course – few streams / area
Factors influencing drainage density:
Precipitation: More precipitation will lead to more streams on the surface.
Gradient: Steeper gradients cause faster run-off and less surface
streams.
Vegetation: Dense vegetation causes more infiltration and thus less
surface streams.
Permeability and porosity: Rock that is porous and permeable will allow
more infiltration, and less surface streams will develop
Brought to you by Page 4
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
Low Drainage Density near Olifantshoek, Sishen and Kuruman:
Source: Geomatica Titanium – South Africa, Hydrology
Brought to you by Page 5
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
High Drainage Density East of Durban:
Source: Geomatica Titanium – South Africa, Hydrology
3.1.3. Drainage patterns
Drainage pattern refers to the shape of the river system caused by the
underlying rock.
A. Dendritic:
- tree shape, develops on uniform rock.
- Tributaries join at more obtuse angles on steeper slopes.
- A Dendritic drainage pattern in the Karoo
- These are tributaries in the upper reaches of the Gouritz River.
Source: Geomatica Titanium – South Africa,|
Hydrology
Brought to you by Page 6
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
B. Rectangular:
- main stream and tributaries has 90º angles in, develop on jointed
rock.
- Rectangular pattern along the Orange River over jointed rock.
Source: Geomatica Titanium – South
Africa, Hydrology
C. Trellis:
- Parallel main streams with short tributaries that join the main stream
at right angles.
- Develop in fold mountains, homoclinal ridges or alternating soft and
hard rock.
- A trellis pattern in another part of the Gouritz catchment area in the
Oudtshoorn area is between the Cape fold mountains.
Brought to you by Page 7
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
Source: Geomatica Titanium – South Africa, Hydrology
D. Radial / Centrifugal:
- All streams run outwards from a single high point, e.g. islands,
mesas, conical hills and buttes.
- Small first order streams run in all directions from the Matabetule
mesa (table mountain)
Source: Geomatica Titanium – Durban
local level
Brought to you by Page 8
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
E. Centripetal:
- All streams run to one central lake, e.g. inside a volcanic crater.
A centripetal drainage pattern around the Inanda dam
Source: Geomatica Titanium – Durban local level.
F. Deranged:
- No clear pattern visible.
- Develops on very flat areas or areas that had a continental glacier
on them. Many lakes and marshes.
- A Deranged drainage stream pattern near Springbok in the
Northern Cape.
- There is no clear pattern and streams do not link up or flow in a
specific direction.
Brought to you by Page 9
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
Source: Geomatica Titanium – South Africa, Hydrology
Brought to you by Page 10
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
X-AMPLE QUESTIONS:
Question 1:
1.1. Indicate whether the following statements are true or false:
1.1.1. An aquifer is a rock that is impermeable and does not allow water to move
through it.
1.1.2. A flow hydrograph records how much water passes a given point in a given
period of time.
1.1.3. A periodic river is a river that only flows in the rainy season when it receives
ground water.
1.1.4. Rocks that are uniformly resistant and exposed to the same type of weathering
will weather at different rates.
1.1.5. The water table indicates the level of water on the surface of the earth.
(5 x 2) [10]
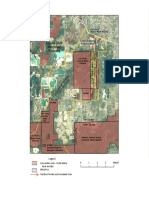
Question 2:
Refer to the extract on the following page, as well as the photograph and diagram of
rivers draining into the Hartbeespoort Dam.
Brought to you by Page 11
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
2.1. (a) Identify the drainage pattern of the Jukskei River as seen in the
figure above. (1 x 2) (2)
(b) Give ONE reason for your answer to QUESTION 2.1. (a). (1 x 2) (2)
2.2 (a) Flooding is common in Alexandra. What is a flood? (1 x 2) (2)
(b) Why do people still build shacks on the banks of the Jukskei River
if the area is threatened by constant flooding? (1 x 2) (2)
(c) Explain why there is a short lag time and a high flood peak as the
Jukskei River flows through Alexandra. (3 x 2) (6)
(d) Name any TWO consequences of flooding for the inhabitants of
Alexandra. (2 x 2) (2)
2.3 (a) Describe the locations of the sewerage works in relation to the
rivers shown in the figure above (1 x 2) (2)
(b) What are the consequences of the above for people living on the
banks of the Hartbeespoort Dam? (2 x 2) (2)
(c) State TWO measures that can be introduced by the provincial
government to ensure that all rivers flowing into the Hartbeespoort
Dam are free of sewerage effluents. (2 x 2) (2)
[22]
Brought to you by Page 12
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
Question 3:
Use the figure below which shows the different fluvial processes and characteristics
of a drainage basin to assist you to give ONE term for each of the descriptions
below. Write only the term next to the question number as an answer, for example
3.6 base flow.
3.1 Area where a river gets its water from
3.2 Area drained by a river and its tributaries
3.3 The point where a tributary meets the main stream
3.4 Section of a stream from one bank to the other
3.5 High-lying area that separates two drainage basins (5 x 2) [10]
Brought to you by Page 13
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
Question 4:
FIGURE 4 A illustrates a drainage basin. FIGURE 4 B shows the three river courses
associated with a river system. Examine both diagrams carefully.
Figure 4 A
Figure 4 B
4.1 (a) The drainage basin illustrated in FIGURE 4A shows a lo w drainage
density (coarse texture). What does this mean? (1 x 2) (2)
(b) Give TWO possible reasons why this drainage basin has a low
drainage density (coarse texture). (2 x 2) (4)
(c) Explain why the two factors mentioned in QUESTION 4.1(b) will
result in a low drainage density (coarse texture). (2 x 2) (4)
Brought to you by Page 14
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
4.2 (a) Identify the THREE main river courses labelled R, S and T in
FIGURE 4 B respectively. (3 x 2) (6)
(b) Along which ONE of the three courses labelled R, S or T will
flooding most likely occur? (1 x 2) (2)
(c) Explain how the characteristics of the river course mentioned in
QUESTION 4.2(b) will promote flooding here. (2 x 2) (4)
(d) Flooding along the river course named in QUESTION 4.2(b) can be
both a blessi ng and a curse for the people living on the adjacent
flood plain. Explain this statement. (2 x 2) (4)
(e) State ONE method that can be introduced to reduce flooding along
the river course named in QUESTION 4.2(b). (1 x 2) (2)
[28]
Question 5:
Refer to the figure above illustrating the relationship between stream type and the
water table.
Indicate whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE. Write only 'true' or
'false' next to the question number.
5.1 River X will only flow after a heavy thunderstorm.
5.2 River Y is a periodic river.
5.3 River Z will only flow during the wet season.
5.4 The water table lies at a lower level during a prolonged drought.
5.5 River Z does not receive any water from base flow to support its flow.
(5 x 2) [10]
Brought to you by Page 15
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
Question 6:
Refer to FIGURE 6.4 (A – F) representing the drainage basins of two river systems
(A and B) and flow hydrographs (C – F) to show run-off in rivers after rain showers.
Also read the extract on floods below.
Flooding occurs when water overflows its normal channels such as streams and
storm water drains. Floods may also occur when there is an accumulation of water
by drainage into areas which are not normally submerged. Floods are common in
South Africa following long periods of drought. Drought, overgrazing and the
deterioration of the land make the ecosystem vulnerable. Humans can alter the flow
characteristics of a river negatively by clearing vegetation, constructing impermeable
tar and concrete surfaces, and building on a river's flood plain.
6.1. Define the following terms referred to above:
(a) Drainage basin (1 x 2) (2)
(b) River system (1 x 2) (2)
6.2 Describe the shapes of drainage basins A and B respectively. (2 x 2) (4)
Brought to you by Page 16
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
6.3 List and explain any TWO factors that could influence the run-off in a river.
(4 x 2) (8)
6.4 Suppose a rain shower of 100 mm occurs in each of drainage basins A
and B. Which of the flow hydrographs (C – F) will most likely represent
stream flow at the point marked = in drainage basins A and B respectively?
(2 x 2) (4)
[20]
Brought to you by Page 17
Geography
Grade 12
www.learnxtra.co.za
ANSWERS TO HOMEWORK X-ERCISES
Question 1:
Brought to you by Page 18
You might also like
- Geography - Study Guide - ANSWERS - Garret Nagle and Briony Cooke - Second Edition - Oxford 2017Document44 pagesGeography - Study Guide - ANSWERS - Garret Nagle and Briony Cooke - Second Edition - Oxford 2017Felix ShaoNo ratings yet
- LaguindinganDocument12 pagesLaguindinganJessa OgUisNo ratings yet
- Rivers Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Document26 pagesRivers Cambridge IGCSE Geography (9-1)Georgina HolmesNo ratings yet
- Sabo TSGDocument121 pagesSabo TSGMark Jayson Portarcos100% (1)
- Topographic Position Index (Weiss, 2001)Document1 pageTopographic Position Index (Weiss, 2001)Aina AzlanNo ratings yet
- Lecture - The Humid Geomorphic EnvironmentDocument82 pagesLecture - The Humid Geomorphic Environmentরুবিয়াস হ্যাগ্রিড100% (1)
- RiversDocument44 pagesRiverstiyaresti31No ratings yet
- Earth Surface ProcessDocument33 pagesEarth Surface ProcessCynthia NgNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Origin of Lake and RiverDocument43 pagesLecture 2 - Origin of Lake and Riversyuhada280304No ratings yet
- GEOGRAPHY NOTES For SURVIVAL PDFDocument22 pagesGEOGRAPHY NOTES For SURVIVAL PDFmathews ismail100% (1)
- Nrivers and River Processes The Hydrological CycleDocument17 pagesNrivers and River Processes The Hydrological Cyclegazadon100% (1)
- RiversDocument32 pagesRiversmadzivirejayNo ratings yet
- Geology 800: Running Water: The Geology of Streams and FloodsDocument12 pagesGeology 800: Running Water: The Geology of Streams and FloodsManish YadavNo ratings yet
- Assignment On: Runoff and Flooding (Drainage Pattern, Stream Flow Velocity, River-Stage and Discharge.)Document15 pagesAssignment On: Runoff and Flooding (Drainage Pattern, Stream Flow Velocity, River-Stage and Discharge.)Mozakkir AzadNo ratings yet
- Unit Six: Fluvial Processes and LandformsDocument123 pagesUnit Six: Fluvial Processes and LandformsAntariksa PrianggaraNo ratings yet
- Running Waters 2Document10 pagesRunning Waters 2Janeth Villanueva Montorio WaminalNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 - STREAMS AND FLOODS OutlineDocument7 pagesCHAPTER 6 - STREAMS AND FLOODS OutlineSharaine CastilloNo ratings yet
- 6th SEM HydrologyDocument28 pages6th SEM HydrologyPankaj ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Lecture-2 - Landform Developed by PDFDocument44 pagesLecture-2 - Landform Developed by PDFMd.Minhaz UddinNo ratings yet
- Running Water and StreamsDocument13 pagesRunning Water and Streamsরুবিয়াস হ্যাগ্রিডNo ratings yet
- GS - 2965 - AnsDocument37 pagesGS - 2965 - Ansprithvi.drprithvipatelNo ratings yet
- Rivers 1652535475Document20 pagesRivers 1652535475paqurette3No ratings yet
- Esci Finals 1Document2 pagesEsci Finals 1Franz CalopeNo ratings yet
- Classification of StreamsDocument20 pagesClassification of StreamsJeremiah Algem MendezNo ratings yet
- ERTH 2403 - Introduction To Oceanography Lecture 8 - Tides TidesDocument7 pagesERTH 2403 - Introduction To Oceanography Lecture 8 - Tides TidesAndre YimNo ratings yet
- Excel in GeographyDocument204 pagesExcel in Geographyblessingtebogo86100% (1)
- 2010 GCSE Revision GuideDocument55 pages2010 GCSE Revision Guidelost_boy26No ratings yet
- River, River System & Management: Running Water Is The Most Important Agent of ErosionDocument34 pagesRiver, River System & Management: Running Water Is The Most Important Agent of Erosionabir hasan100% (1)
- Chapter OneDocument43 pagesChapter OneGetahun TadesseNo ratings yet
- Water On Land Paper 1 Physical RiversDocument14 pagesWater On Land Paper 1 Physical RiversTrevor Chad100% (1)
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesEarth Science ReviewerIcarusNo ratings yet
- DeltasDocument28 pagesDeltasMuhammad BilalNo ratings yet
- River Systems & Causes of FloodingDocument10 pagesRiver Systems & Causes of FloodingVicksy007No ratings yet
- 2 2riversDocument12 pages2 2riversLK chanellNo ratings yet
- River Systems & Causes of FloodingDocument13 pagesRiver Systems & Causes of FloodingSynthatrisma UtamiNo ratings yet
- Running WaterDocument24 pagesRunning WaterpicefeatiNo ratings yet
- Pee 322 - 3Document55 pagesPee 322 - 3FAVOUR ORUAIGHONo ratings yet
- Geography... Digest AnsDocument6 pagesGeography... Digest Ansmanorma.vishwakarma911No ratings yet
- Geography Exam NotesDocument10 pagesGeography Exam Noteslajoneee :pNo ratings yet
- Erosion and Deposition Action of Running Water and GroundwaterDocument12 pagesErosion and Deposition Action of Running Water and GroundwaterDevraj H SNo ratings yet
- The StreamsDocument37 pagesThe Streamsheychandler2023No ratings yet
- Deserts: Subtropical Deserts - The General Atmospheric Circulation Brings Dry, Subtropical Air Into MidDocument9 pagesDeserts: Subtropical Deserts - The General Atmospheric Circulation Brings Dry, Subtropical Air Into MidHarsh DevNo ratings yet
- LAS For Summative Assessment Identify The Various Water Resources On Earth (Document17 pagesLAS For Summative Assessment Identify The Various Water Resources On Earth (David Jonel RoceroNo ratings yet
- 2 Rivers-and-StreamsDocument105 pages2 Rivers-and-StreamsNino DucaNo ratings yet
- Streams and Rivers Lab: An Introduction To Fluvial GeomorphologyDocument15 pagesStreams and Rivers Lab: An Introduction To Fluvial GeomorphologyVictoria Valentina RamírezNo ratings yet
- Kegy 213Document9 pagesKegy 213PremKumarNo ratings yet
- Caie As Level Geography 9696 Core Physical Geography v1Document18 pagesCaie As Level Geography 9696 Core Physical Geography v1BrizzyNo ratings yet
- New Revision Notes On HydrologyDocument19 pagesNew Revision Notes On Hydrologylyana123480% (5)
- Landforms and Their EvolutionDocument22 pagesLandforms and Their EvolutionTsudrawsNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Geography Solutions Class 9 Chapter 10 DenudationDocument5 pagesSelina Concise Geography Solutions Class 9 Chapter 10 DenudationArgha senguptaNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Fresh Water SystemsDocument5 pagesTopic 3 - Fresh Water SystemsjleodennisNo ratings yet
- Geo Term-2 Denudation 1Document11 pagesGeo Term-2 Denudation 1Tvisha AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 GeologyDocument5 pagesQuiz 2 Geologyhaha xdNo ratings yet
- FAJANILAN JEROME C.activityno.2 Depositional Sedimentary Environment and StructuresDocument11 pagesFAJANILAN JEROME C.activityno.2 Depositional Sedimentary Environment and StructuresJerome FajanilanNo ratings yet
- Low River Flows and WetlandsDocument3 pagesLow River Flows and WetlandsHoney Grace TizonNo ratings yet
- North Caroni Plains Case StudyDocument13 pagesNorth Caroni Plains Case StudyThe Cropper Foundation100% (5)
- STORM HYDROGRAPH New Notes UpdatedDocument21 pagesSTORM HYDROGRAPH New Notes UpdatedMalia Damit100% (1)
- River Basin ProcessesDocument16 pagesRiver Basin Processes3alliumcourtNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledBB KivinesNo ratings yet
- Action of Running WaterDocument2 pagesAction of Running WaterJust A Random GuyNo ratings yet
- Rivers - Earth Processes - OneGeology Kids - EXtra - OneGeologyDocument4 pagesRivers - Earth Processes - OneGeology Kids - EXtra - OneGeologySubbareddyNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Landforms and Their Evolution 13Document16 pagesChap 5 Landforms and Their Evolution 13abhaykumarkans054No ratings yet
- Sedimentary Crisis at the Global Scale 2: Deltas, A Major Environmental CrisisFrom EverandSedimentary Crisis at the Global Scale 2: Deltas, A Major Environmental CrisisNo ratings yet
- Geography Chapter4Document21 pagesGeography Chapter4davedtruth2No ratings yet
- Class IX - Revision Assignment Chapter 2 - Geography Physical Features of IndiaDocument4 pagesClass IX - Revision Assignment Chapter 2 - Geography Physical Features of IndiaAaryan LeekhaNo ratings yet
- Physiography of India Mountain Plateaus Passes 30Document13 pagesPhysiography of India Mountain Plateaus Passes 30Renu KatiyarNo ratings yet
- Hortons Stream OrderingDocument14 pagesHortons Stream OrderingMuhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- Valuasi Ekonomi Erosi Lahan Pertanian Di Sub Daerah Aliran Sungai Keduang Kabupaten WonogiriDocument8 pagesValuasi Ekonomi Erosi Lahan Pertanian Di Sub Daerah Aliran Sungai Keduang Kabupaten WonogiriYusrina AfrohNo ratings yet
- Hydr Design of Settling Basin NewDocument51 pagesHydr Design of Settling Basin NewmukhleshNo ratings yet
- Structure Analysis Gunung Benau Karst Area by Using mSTA and FFD, North Kalimantan, IndonesiaDocument11 pagesStructure Analysis Gunung Benau Karst Area by Using mSTA and FFD, North Kalimantan, IndonesiahennyNo ratings yet
- Major Landforms - Mountains, Plateaus, and Plains - Learn Faster - ClearIASDocument11 pagesMajor Landforms - Mountains, Plateaus, and Plains - Learn Faster - ClearIASAmar SinghNo ratings yet
- ANDAMAN & NICOBAR ISLANDS Census PDFDocument252 pagesANDAMAN & NICOBAR ISLANDS Census PDFanushka kashyapNo ratings yet
- Cubrinovski Et Al. 2018 - System Response of Lique Able DepositsDocument18 pagesCubrinovski Et Al. 2018 - System Response of Lique Able DepositsLale ÖnerNo ratings yet
- Dec-01 David Dorsey WatershedMap No ContoursDocument1 pageDec-01 David Dorsey WatershedMap No ContoursNews-PressNo ratings yet
- What Are The Potential Effects of A Large Impact Event?Document8 pagesWhat Are The Potential Effects of A Large Impact Event?Eljien LumbayoNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: GEOGRAPHY 9696/11Document4 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: GEOGRAPHY 9696/11Ona N MaleteNo ratings yet
- Huggett - 1975 - Soil Landscape Systems A Model of Soil GenesisDocument22 pagesHuggett - 1975 - Soil Landscape Systems A Model of Soil GenesisAndrés David VelásquezNo ratings yet
- Geography Set-2 Indian Physical Geography: IslandDocument27 pagesGeography Set-2 Indian Physical Geography: IslandP UmaSankar SubudhiNo ratings yet
- Eden Tunstall 2006 Ecological Versus Social RestorationDocument20 pagesEden Tunstall 2006 Ecological Versus Social RestorationAna CarolinaNo ratings yet
- 08 Chapter 08 Structures 2007 RevDocument130 pages08 Chapter 08 Structures 2007 Revاسومي الوكحNo ratings yet
- A Preliminary Investigation Into The Hydrology of The Jackson/Frazier Wetland, OregonDocument54 pagesA Preliminary Investigation Into The Hydrology of The Jackson/Frazier Wetland, OregonNoah SolomonNo ratings yet
- WadiDocument2 pagesWadiyusuf mohammadNo ratings yet
- Geomorphology: Hitoshi Saito, Daichi Nakayama, Hiroshi MatsuyamaDocument9 pagesGeomorphology: Hitoshi Saito, Daichi Nakayama, Hiroshi MatsuyamaPeteris SkelsNo ratings yet
- Geography Picture DictionaryDocument4 pagesGeography Picture DictionaryEva Andersen VargaNo ratings yet
- India Physical: Chapter - 1Document11 pagesIndia Physical: Chapter - 1Ankit SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Fluvial LandformsDocument30 pagesFluvial Landformsbrighton mjuni100% (1)
- PenckDocument27 pagesPenckVivek DograNo ratings yet
- Wexford Biodiversity PlanDocument145 pagesWexford Biodiversity PlanJim HendrickNo ratings yet
- Cowell 1992Document6 pagesCowell 1992Arthur Antônio MachadoNo ratings yet
- Acting President: Philkairos, IncDocument17 pagesActing President: Philkairos, Incjubin funterNo ratings yet