Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ICNIRPUVWorkers (Page 35) - 12
Uploaded by
Madani MecheriOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ICNIRPUVWorkers (Page 35) - 12
Uploaded by
Madani MecheriCopyright:
Available Formats
Protecting Workers from Ultraviolet Radiation
2. Characteristics of UVR
2.1 Basic Concepts
Ultraviolet radiation, like visible radiation (light) and infrared radiation, is radiant energy.
Together, these forms of radiant energy are referred to as “optical radiation.” Light and other
forms of optical radiation are distinguished from each other by their wavelength (the distance
between crests in the wave that carries the energy). In the optical spectrum, wavelengths are
normally quantified in terms of nanometers (1 nm = 10–9 m) in the UVR and visible spectrum
and in terms of micrometers (1 µm = 10-6 m) in the infrared spectrum. Light is of shorter
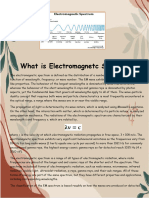
wavelengths than infrared and UVR is of shorter wavelengths than light. Figure 1 shows the
spectral band designations by wavelength for the optical spectrum. In describing the biological
effects of optical radiation, the spectrum is frequently divided into seven photobiological spectral
bands (CIE 1999). The ultraviolet spectral bands are: UVC (100-280 nm), UVB (280-315 nm),
and UVA (315-400 nm). The Sun and artificial light sources emit radiant energy within the
optical spectrum, comprising the ultraviolet, visible and infrared (Figure 1).
Figure 1. The electromagnetic spectrum and the wavelength bands.
The measurement of optical radiation is referred to as “radiometry.” There are a number of
radiometric terms that are used. The “radiant power” in watts (W) describes the rate of energy
output of an optical source (rather than the photometric quantity of luminous flux in lumens
weighted for the sensitivity of the eye that describes the output of a visible lamp designed for
lighting). For a pulsed optical source such as a flashlamp, the “radiant energy” in joules (J)
describes the output where one joule is equivalent to one watt delivered over 1 second or 1 watt-
second. Two dosimetric quantities quantify human exposure to UVR: “irradiance” and “radiant
exposure.” The irradiance is the rate of surface exposure in watts per square meter (W m-2) and
the radiant exposure is the radiant energy per unit area accumulated over a time interval in joules
per square meter (J m-2).
2.2 Solar Radiation
Sunlight has played a critical role in the development of life on Earth. The infrared and visible
regions of the solar radiation comprise 95 % of the total radiation reaching the Earth’s surface.
12
You might also like
- Lecture Notes I 2016Document38 pagesLecture Notes I 2016Edward Baleke SsekulimaNo ratings yet
- Spectmethods PDFDocument47 pagesSpectmethods PDFalexlhhcasNo ratings yet
- Practical Introduction to Laser DermatologyFrom EverandPractical Introduction to Laser DermatologyVishal MadanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Solar Radiation: 1.1 Basics of LightDocument15 pagesChapter 1: Solar Radiation: 1.1 Basics of LightYoussef KamounNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 EM Waves and UV ProtectionDocument41 pagesUnit 10 EM Waves and UV Protectiongalaxy113No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum and BandwidthDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum and BandwidthJennybabe NapolesNo ratings yet
- Lin 2007Document5 pagesLin 2007Francisco ChangoNo ratings yet
- The Language of LightDocument27 pagesThe Language of Lightmradojcin100% (1)
- The Language LightDocument26 pagesThe Language LightbahbaguruNo ratings yet
- What Is An Electromagnetic WaveDocument2 pagesWhat Is An Electromagnetic WaveMarjorie Baya BidlanNo ratings yet
- 2chapter 2.1Document15 pages2chapter 2.1John Mel DumaguitNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Solar Radiation Part 1 Principles Notes PDFDocument21 pagesLecture 5 Solar Radiation Part 1 Principles Notes PDF॰अचूक॰ Milan SubediNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry 4 Spectroscopy - 1Document43 pagesAnalytical Chemistry 4 Spectroscopy - 1PERPETUAL TAKYINo ratings yet
- The Physics of RadiationDocument10 pagesThe Physics of RadiationClaudio TesserNo ratings yet
- E Lighting: New Quantum Wave The WaveDocument1 pageE Lighting: New Quantum Wave The WavereacharunkNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument16 pagesElectromagnetic SpectrumTanish100% (1)
- Optoelecronic Devices: © Watkins 2009 Missouri S&T Page 18 of 30Document13 pagesOptoelecronic Devices: © Watkins 2009 Missouri S&T Page 18 of 30sampathkumar1980No ratings yet
- Phy 104 Atomic SpectraDocument24 pagesPhy 104 Atomic SpectraAisha abba HabibNo ratings yet
- Solar Simulation: Oriel Product TrainingDocument32 pagesSolar Simulation: Oriel Product TrainingrickNo ratings yet
- Examen Ambrosio 2 InglesDocument12 pagesExamen Ambrosio 2 InglesLadhy Guadalupe Feliciano FuentesNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Energy Sources of RsDocument10 pages2.1 Energy Sources of RsrowlinNo ratings yet
- Historical Perspective Chapter 1 PDFDocument19 pagesHistorical Perspective Chapter 1 PDFKallie FokkerNo ratings yet
- MODELDocument23 pagesMODELYakoub ChekimaNo ratings yet
- Laser Scanner Technology Laser Scanner Technology: Scholarlycommons ScholarlycommonsDocument23 pagesLaser Scanner Technology Laser Scanner Technology: Scholarlycommons ScholarlycommonsYakoub ChekimaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Spectrochemical MethodsDocument2 pagesIntroduction To Spectrochemical MethodsSean CollinsNo ratings yet
- Copy 2nd QuarterDocument30 pagesCopy 2nd QuarterLiwayway MadaliNo ratings yet
- E01 Handbook IntroductionDocument12 pagesE01 Handbook IntroductionAlexander Quebra Madeira NemchinovNo ratings yet
- TTHH FFFFDocument84 pagesTTHH FFFFkevin desaiNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing and Gis Unit - Iii Rs-IiDocument12 pagesRemote Sensing and Gis Unit - Iii Rs-Iivijjikewlguy7116No ratings yet
- Lighting Handbook 2Document263 pagesLighting Handbook 2Boris TepavacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Rad Safety, Prod of X-Rays (Essentials of Dental Assisting)Document35 pagesChapter 15 - Rad Safety, Prod of X-Rays (Essentials of Dental Assisting)mussanteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EM SpectrumDocument8 pagesIntroduction To EM SpectrumKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Basic Physics of X-Ray Imaging: Carl A Carlsson and Gudrun Alm CarlssonDocument31 pagesBasic Physics of X-Ray Imaging: Carl A Carlsson and Gudrun Alm CarlssonAyoub HaranjaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanical ModelDocument25 pagesQuantum Mechanical ModelAletheaNo ratings yet
- RS 2 - DKDocument14 pagesRS 2 - DKkaran bishtNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To: Light MeasurementDocument17 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To: Light MeasurementLê Quốc ViệtNo ratings yet
- Document (4) - 1Document9 pagesDocument (4) - 1Justin DugangNo ratings yet
- 08 PhotometryDocument17 pages08 PhotometryHelenNo ratings yet
- 2.electro Magnetic RadiationDocument38 pages2.electro Magnetic RadiationSujata SarkarNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattDocument21 pagesUnit-1 Electromagnetism: Kushal BhattKushal BhattNo ratings yet
- Lighting Ch1 2Document27 pagesLighting Ch1 2AymanNo ratings yet
- FTA ReportDocument20 pagesFTA Reportzen AlkaffNo ratings yet
- SCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLDocument42 pagesSCH 100 Notes 2013-2014 ALLErick Wangila WanyonyiNo ratings yet
- Lighting Lec 1 BDocument31 pagesLighting Lec 1 BAymanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WaveDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic WavewerewolfNo ratings yet
- Investigation Project PhysicsDocument16 pagesInvestigation Project Physicskartikdutt.08No ratings yet
- Measurement: See Also:,, andDocument6 pagesMeasurement: See Also:,, andVed NarsekarNo ratings yet
- Remote Sensing and Gis Module 1Document12 pagesRemote Sensing and Gis Module 1Shaik SulemanNo ratings yet
- 38 Lighting HandbookDocument263 pages38 Lighting HandbooktorinomgNo ratings yet
- The Light Chapter-1Document259 pagesThe Light Chapter-1walsarisNo ratings yet
- Applications of Electromagnetic WavesDocument21 pagesApplications of Electromagnetic WavesSaliu MalikNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Electromagnetic RadiationDocument14 pagesUnit 1 Electromagnetic RadiationDrSoumitra SoniNo ratings yet
- Zwinkels - 2015 - Light Electromagnetic SpectrumDocument9 pagesZwinkels - 2015 - Light Electromagnetic SpectrumFirda SyavieraNo ratings yet
- Radiometry and Photometry Units and Conversion FactorsDocument4 pagesRadiometry and Photometry Units and Conversion FactorsRazvan OnicaNo ratings yet
- Radio Wave Radio Waves Are A Type of Electromagnetic Radiation With Wavelengths inDocument8 pagesRadio Wave Radio Waves Are A Type of Electromagnetic Radiation With Wavelengths inGElla BarRete ReQuilloNo ratings yet
- What Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Document11 pagesWhat Is Electromagnetc Spectrum?Rodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One X-Ray and Gamma RayDocument65 pagesChapter One X-Ray and Gamma RayBlue JasmineNo ratings yet
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceFrom EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (51)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectFrom EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (20)
- The Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameFrom EverandThe Simulation Hypothesis: An MIT Computer Scientist Shows Whey AI, Quantum Physics and Eastern Mystics All Agree We Are In A Video GameRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (88)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseFrom EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (69)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (410)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldFrom EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (64)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyFrom EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyNo ratings yet
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Professor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellFrom EverandProfessor Maxwell's Duplicitous Demon: The Life and Science of James Clerk MaxwellRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (21)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1396)
- The Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessFrom EverandThe Quantum Screen: The Enigmas of Modern Physics and a New Model of Perceptual ConsciousnessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (37)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Untold Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (553)
- A Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itFrom EverandA Natural History of Color: The Science Behind What We See and How We See itRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Sun in a Bottle: The Strange History of Fusion and the Science of Wishful ThinkingFrom EverandSun in a Bottle: The Strange History of Fusion and the Science of Wishful ThinkingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (38)