Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Visual Vocabulary PDF
Visual Vocabulary PDF
Uploaded by
Dziugas CiucelisOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Visual Vocabulary PDF
Visual Vocabulary PDF
Uploaded by
Dziugas CiucelisCopyright:
Available Formats
Elements of Art: This is a collection of terms that are useful in visual analysis.
Not ALL are relevant to what we do in class, but if you can apply some of them to your analysis, your precision
of analysis will improve. Give it a shot.
You may be looking at an entirely visual text and examining how the design conveys meaning.
The ad exudes sensuality through the use of lines and color…
The theme of environmental preservation is conveyed through the selected color scheme and the emphasis on…
The designer’s choice to back-light the man creates a sense of …
A visual hierarchy is created by establishing the primary focal point as _____ through isolation, and then using
vertical lines to create a path of movement and guide the audience’s eyes to the image of ___ at the bottom of the
page.
In LangLit class, you are often discussing how image or the aesthetics of a piece complement or further the
meaning of the written text.
The author’s claim that ____ __ is furthered through the use of the visuals…
The design and color of the webpage also work to highlight the idea of…
The mood of the piece is conveyed both through language and design…
The image(s) in the text directly relate(s) to the author’s statement “_________” The image shows…
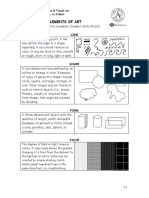
The following is a list of the most common "Elements of Art" used today.
Balance: Emphasis: by or through
symmetrical
asymmetrical dominance
radial a focal point
a center of interest
Rhythm/Movement isolation
types size
regular contrast
alternating converging lines
progressive
flowing Space
dominant path of movement open – closed
vertical filled – empty
horizontal interior – exterior
diagonal
curving Light/Color/Value
shading
Proportion: contrast
life-size primary
monumental secondary
miniature neutral color
normal color schemes: warm, cool, neutral, monochromatic
exaggerated complementary
idealized intensity: bright – dull, high key – low key
Lines/path of movement: Shape/Form
active - passive solid - void
bold - delicate concave - convex
flowing - light ambiguous - complete
straight - curved organic - geometric - free-form
thick - thin circle - sphere-
dark - light square - cube –
broken - continuous triangle - pyramid- cone
geometric - organic
implied - actual
precise – irregular
RHYTHM: repetition of line, light, shape, etc.
PROPORTION: To put in proper relation with something else.
SHAPE: 2-Dimensional objects (circle, square, triangle)
FORM: 3-Dimensional objects ( cone, cube, cylinder, sphere)
LINE-OF-ACTION: designates the movement or action of a character in a drawing
POSITIVE SPACE: area an object occupies.
NEGATIVE SPACE: area around an object.
VALUE: lightness or darkness of an color
COMPOSITION: way of arranging a drawing or painting so it is interesting to look at and equally balanced.
GOLDEN RULE OF THIRDS: a way of breaking down a composition mathematically, focusing on thirds.
BACKGROUND: area within a composition that appears further away from the viewer. Objects appear smaller
with less detail.
MIDDLE GROUND: part of a composition that appear between the foreground and back ground.
FOREGROUND: in a scene or artwork , the part that seems closest to you. Objects appear larger and more
detailed.
HUE : common name of a color ( i.e. blue, green, etc)
PRIMARY COLOR : red, blue & yellow
SECONDARY COLOR : green, orange & violet ( mix primary colors)
TERTIARY (INTERMEDIATE) : red-orange, yellow-orange, blue-green, etc.
ADVANCING COLORS : colors that appear to come towards you (warm colors)
WARM COLORS : red, orange & yellow
COOL COLORS : blue, violet & green
RECEDING COLORS : colors that appear to be in the background (generally cool colors)
COMPLEMENTARY : colors that are directly across from each other on the color wheel
INTENSITY : brightness or dullness of a color
SATURATION: intensity of a color—a bright color is highly saturated
OPAQUE : colors that you can't see through
TRANSPARENT : colors that you can see through
MONOCHROMATIC : a single color and it's tints and shades
VERTICAL : top - to - bottom. This can refer to the placement of objects within a composition or the
composition itself.
HORIZONTAL : left - to -right. This can refer to the placement of objects within a composition or the
composition itself.
LIGHT: the amount of light and dark, the source of light, back-lit, front-lit, top-lit, angle of light
TEXTURE: can be actual, like brushstrokes on canvas, or imitative of a textured surface
AESTHETICS: To experience a feeling or response to art.
DON’T IGNORE THE GAZE! Are we supposed to follow his/her eyeline to see an object they are looking at? Is
that object in the ad/artwork or is it out of the frame? Is the gaze direct or averted? Is there direct eye contact
with audience (a direct mode of address/direct appeal)? Remember that often the one watching has power and
the one being watched becomes an object, weaker. Are there two people in the ad? Are they looking at each
other, or is one watching the other? Is one being objectified?
Art Vocabulary
TOK Connect: Almost a hundred years ago, an American artist and teacher of art named Arthur Wesley Dow wanted his art students to
be able to see, describe and create visual qualities in a systematic way. Dow wrote about the “elements of art” in 1899. Over the years, it
has been changed and expanded by artists and experts. (Paraphrased from Art: Images and Ideas by Laura H. Chapman)
LANGUAGE AS A WOK:
How is this an example of shared knowledge?
Is there a need for a common language in the creation of shared knowledge?
What other AOK depend on systematic language, and is it to a greater or lesser extent than in the Arts?
You might also like
- Fantasy Artist Genius Guide Vol. 2Document196 pagesFantasy Artist Genius Guide Vol. 2Vũ Hải71% (7)
- Elements of ArtDocument3 pagesElements of ArtSerendipity FelicityNo ratings yet
- Anne Bogart and Tina Landau The Viewpoints Book PDFDocument127 pagesAnne Bogart and Tina Landau The Viewpoints Book PDFRevo Natz100% (10)
- The Elements of ArtDocument45 pagesThe Elements of ArtLaLa FullerNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. 3. Elements and Principles of ArtDocument72 pagesUnit 2. 3. Elements and Principles of ArtLuis Norbert Santiago100% (1)
- Special Subjects: Basic Color Theory: An Introduction to Color for Beginning ArtistsFrom EverandSpecial Subjects: Basic Color Theory: An Introduction to Color for Beginning ArtistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Photography Course PapersDocument12 pagesPhotography Course PapersAndrew Madkour-AliNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Line and Kinds of LineDocument11 pagesLesson 1 - Line and Kinds of LineNestyn Hanna VillarazaNo ratings yet
- 3 D Elements PrinciplesDocument2 pages3 D Elements PrinciplesvichazzNo ratings yet
- Elements and Principles of Visual ArtDocument4 pagesElements and Principles of Visual ArttapanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7. Elements and Principles of ArtDocument83 pagesLesson 7. Elements and Principles of ArtSophiaEllaineYanggatLopez100% (6)
- Elements Principles of ArtDocument49 pagesElements Principles of ArtCherilyn OchoaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Elements and Principles of DesignDocument53 pagesLesson 6 - Elements and Principles of DesignJerick FernandezNo ratings yet
- Appendix B: Elements and Principles of DesignDocument6 pagesAppendix B: Elements and Principles of DesignJennifer StraussNo ratings yet
- Art TermsDocument6 pagesArt Termsapi-546172080No ratings yet
- THEATERDocument30 pagesTHEATERDianne Rose LeeNo ratings yet
- Architecture Vs Cinema PDFDocument128 pagesArchitecture Vs Cinema PDFY'moon ZahraNo ratings yet
- Basic Photography Skills Training PlanDocument15 pagesBasic Photography Skills Training Planali_awaisNo ratings yet
- V-Ray For SketchUp Ebook - Artistic Approach For DesignersDocument37 pagesV-Ray For SketchUp Ebook - Artistic Approach For DesignersMoshe Shemesh0% (1)
- Line and Kinds of Line: Lesson 1Document104 pagesLine and Kinds of Line: Lesson 1Jodelyn JumarangNo ratings yet
- Design PrinciplesDocument50 pagesDesign PrinciplesAlma Jean SubongNo ratings yet
- Color Wheel Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesColor Wheel Lesson Planapi-310441633No ratings yet
- David Noton Composition Tutorials Preview 1Document23 pagesDavid Noton Composition Tutorials Preview 1Mario TegalNo ratings yet
- Elements of Art and Principles of DesignDocument28 pagesElements of Art and Principles of Designsarbast piro100% (1)
- Drawing Academy: The Basics of Drawing / Line and Areas of Colour / Light and Shade / PerspectiveFrom EverandDrawing Academy: The Basics of Drawing / Line and Areas of Colour / Light and Shade / PerspectiveNo ratings yet
- Graffiti Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesGraffiti Lesson PlanEx Ares100% (1)
- 7 Elements of DesignDocument4 pages7 Elements of DesignRandomizmNo ratings yet
- 7 Elements of ArtDocument82 pages7 Elements of ArtMaria YetNo ratings yet
- Ron Kasprisin - Urban Design - The Composition of Complexity (2019, Routledge)Document339 pagesRon Kasprisin - Urban Design - The Composition of Complexity (2019, Routledge)ohoud100% (1)
- Elements Principles Art PDFDocument40 pagesElements Principles Art PDFAL Qassim U ManjoorsaNo ratings yet
- Formal Properties: Elements of Art: ColorDocument11 pagesFormal Properties: Elements of Art: ColorPaula AlmeydaNo ratings yet
- Elements and Principles of ArtDocument36 pagesElements and Principles of ArtCharmaine JonesNo ratings yet
- The Elements and Principles of Art OverviewDocument33 pagesThe Elements and Principles of Art Overviewmaddiethe4thNo ratings yet
- Principles Elements-EckertDocument14 pagesPrinciples Elements-Eckertapi-487437900No ratings yet
- The Elements of ArtDocument7 pagesThe Elements of ArtAeleu JoverzNo ratings yet
- Elements Principles: of andDocument36 pagesElements Principles: of andGerardBalosbalosNo ratings yet
- Elementsofart 150928140602 Lva1 App6892Document28 pagesElementsofart 150928140602 Lva1 App6892api-372755748No ratings yet
- The Elements of Art and Principles of DesignDocument16 pagesThe Elements of Art and Principles of Designapi-500498959No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Elements Nad Principles of Design 1Document57 pagesLesson 6 Elements Nad Principles of Design 1Jelvi Maris LoyolaNo ratings yet
- Ed Arts Teaching Arts in The Elementary GradesDocument22 pagesEd Arts Teaching Arts in The Elementary Gradesmiralona relevoNo ratings yet
- Elements Principles: of andDocument36 pagesElements Principles: of andSHIRLEY M. CLARIDADESNo ratings yet
- Art Appreciation Lesson 2 Elements and Principles of ArtDocument52 pagesArt Appreciation Lesson 2 Elements and Principles of ArtbernaldcatliNo ratings yet
- 2 Exploring Art Chapter 2Document64 pages2 Exploring Art Chapter 2Michael Edward De VillaNo ratings yet
- LAS MAPEH 10 Q1 W2 ArtsDocument8 pagesLAS MAPEH 10 Q1 W2 ArtsJemalyn Hibaya LasacaNo ratings yet
- Intro To Fundamentals of ArtDocument43 pagesIntro To Fundamentals of ArtJessa CapuchinoNo ratings yet
- MAPEHDocument5 pagesMAPEHALLISONNo ratings yet
- Elements of Art and Principles of DesignDocument44 pagesElements of Art and Principles of DesignRaymond RamosNo ratings yet
- Art 1 Winter Exam 2022Document2 pagesArt 1 Winter Exam 2022Mason KlinglerNo ratings yet
- The Elements of Art and Design:: LineDocument7 pagesThe Elements of Art and Design:: LineRomeo LibanNo ratings yet
- Videography NC IIDocument117 pagesVideography NC IIAlmir BatacNo ratings yet
- Arts ReviewerDocument3 pagesArts ReviewerJerome MagdaongNo ratings yet
- GE ELECT Modules PDF VersionDocument130 pagesGE ELECT Modules PDF VersionMaureen AstherelleNo ratings yet
- Art History Review Principles of DesignDocument3 pagesArt History Review Principles of DesignAmy DengNo ratings yet
- Elements of Art Principles of Design Art Criticism - HandoutDocument4 pagesElements of Art Principles of Design Art Criticism - Handoutapi-294607284No ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Elements and Principles of The ArtsDocument40 pagesUnit 4 - Elements and Principles of The ArtsEj BeatoNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Elements and Principles of ArtDocument6 pagesUnit 4 - Elements and Principles of ArtCarla RamosNo ratings yet
- Arts ElementsDocument6 pagesArts ElementsNathalie GetinoNo ratings yet
- Cpar ReviewerDocument5 pagesCpar ReviewerADEM MARIONE C. INOVEJASNo ratings yet
- The Elements of ArtDocument7 pagesThe Elements of ArtTitus NoxiusNo ratings yet
- Elements and Principles of Visual ArtsDocument58 pagesElements and Principles of Visual ArtsFe Marie RoculasNo ratings yet
- The Elements of DesignDocument4 pagesThe Elements of DesignarchishotNo ratings yet
- Minding The Arts (By Leynes & Fajardo PDFDocument236 pagesMinding The Arts (By Leynes & Fajardo PDFPrincess Gloriani0% (1)
- The Ingredients For A Great CompositionDocument43 pagesThe Ingredients For A Great CompositionBlady PilcoNo ratings yet
- The Elements of Art 2Document61 pagesThe Elements of Art 2karlyahihNo ratings yet
- Elements and Principles of Design: Ar Suvarna Deshpande/LeleDocument63 pagesElements and Principles of Design: Ar Suvarna Deshpande/LeleCarrie BakerNo ratings yet
- Elements of ArtsDocument52 pagesElements of Artskyle022021No ratings yet
- Fine Arts Unit 1 2 2D Power PointDocument24 pagesFine Arts Unit 1 2 2D Power PointChelsea HughesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Humanities 412 Art AppreciationDocument6 pagesChapter 3 Humanities 412 Art AppreciationAlexis Ramirez67% (3)
- Lesson 2Document43 pagesLesson 2Mount CarmelNo ratings yet
- Art App. Group 1 ReportDocument43 pagesArt App. Group 1 ReportChris MacaraegNo ratings yet
- CPAR LessonDocument4 pagesCPAR LessonIekzkad RealvillaNo ratings yet
- LO 2. Describe Quality Projects/ Products of Fashion AccessoryDocument83 pagesLO 2. Describe Quality Projects/ Products of Fashion AccessoryGrace Mary Mascariñas Jao100% (3)
- EmTech Week5Document11 pagesEmTech Week5Crisanto CorpuzNo ratings yet
- And Personal: Up CloseDocument5 pagesAnd Personal: Up CloseLinda DuncanNo ratings yet
- Basic Art TermsDocument4 pagesBasic Art Termskolouch1375% (4)
- Art Grade 6 Notes Term 1Document11 pagesArt Grade 6 Notes Term 1Denis WaweruNo ratings yet
- Basic Photography CompositionDocument10 pagesBasic Photography Compositionleslie sabateNo ratings yet
- Arts Appreciation WEEK 2Document7 pagesArts Appreciation WEEK 2Andrea Nicole De LeonNo ratings yet
- Bogdan Iacob, Marius Bercea A Full Rotation of The Moon,, Accessed On The 18th of May 2017Document5 pagesBogdan Iacob, Marius Bercea A Full Rotation of The Moon,, Accessed On The 18th of May 2017Diana RoscaNo ratings yet
- Interior DecorationDocument11 pagesInterior DecorationbhuvaneswariNo ratings yet
- Q1 CPAR 12 - Module 5Document22 pagesQ1 CPAR 12 - Module 5NezelNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 4: Arts and Crafts of LuzonDocument29 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 4: Arts and Crafts of LuzonDeo GaveriaNo ratings yet
- Balace and Gravitational Curve: Activity 9Document5 pagesBalace and Gravitational Curve: Activity 9Jenz Hope Segui NovelaNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1672304520335 7014153538859903203Document23 pagesOrca Share Media1672304520335 7014153538859903203Princess ShariefNo ratings yet
- Art and Design: Paper 0400/01 Observational/Interpretative AssignmentDocument14 pagesArt and Design: Paper 0400/01 Observational/Interpretative AssignmentbonalambokNo ratings yet
- Cpar Week 5 Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions SlmsDocument25 pagesCpar Week 5 Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions SlmsGorettiNo ratings yet
- MODULE Art AppreciationDocument59 pagesMODULE Art AppreciationThrolaj Ben AbrisNo ratings yet
- The Elements and Principles of ArtDocument3 pagesThe Elements and Principles of Artnur100% (1)
- Lesson 3 - Art Elements and PrinciplesDocument40 pagesLesson 3 - Art Elements and PrinciplesHiro Jemmima RenoudNo ratings yet