Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science 10 Notes
Science 10 Notes
Uploaded by
sarmientoangelica6720 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageOriginal Title
SCIENCE 10 NOTES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageScience 10 Notes
Science 10 Notes
Uploaded by
sarmientoangelica672Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
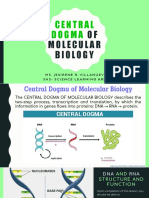
HEREDITY: INHERITANCE and A DNA is a double helix molecule composed of
complementary deoxyribonucleic units. The
VARIATION complementary base pairs of the DNA are held by
hydrogen bonds.
RNA is a single stranded.
DNA AND RNA In DNA adenine always bonds with uracil, and cytosine
bonds with guanine.
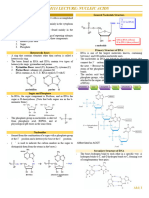
COMPONENT MOLECULES
1. The DNA molecule is composed of 3 types of component
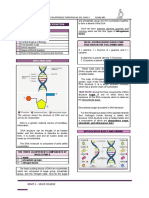
molecule: REPLICATION
Phosphate group, the sugar deoxyribose, and the bases In 1953, JAMES WATSON and FRANCIS CRICK
adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine 9 (A, T, C G) worked out that DNA is double helix like twisted
NUCLEOTIDES staircase. The two sugar phosphate backbones make up
2. There are 3 molecules that form the basic building block the sides and the base pairs make up the rungs or steps
of DNA, The nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of of the twisted staircase.
one phosphate group, one sugar molecule and one of the Deoxyribose acid is copied during interphase prior to
four bases in the example. Across the strands of the mitosis qnd theosis. It is important that new copies are
helix, A always pair with G, T with C. Ribonucleic Acid, exactly like the original molecule. The structure of the
like DNA, is a nucleic acid. How ever RNA structure DNA provides a mechanism for making accurate copies of
differs from DNA structure in 3 ways. the molecule. The process of making copies of DNA is
DIFFERENCES OF RNA AND DNA called REPLICATION. When the DNA replicates, two
identical copies of DNA molecules are produced, which
1. RNA is single strand whereas DNA is double stranded. are exactly the same as the original.
2. The sugar in RNA is ribose; DNA has deoxyribose.
3. Both DNA and RNA contains four nitrogenous bases, but
instead of thymine, RNA contains a similar base called
Uracil (u) the uracil pair with adenine. The major type of
RNA include; messenger RNA (mRNA), ribosomal RNA
(rRNA) and transfer RNA (RNA).
KEY CONCEPTS
You might also like
- DNA - RNA Introduction AssignmentDocument18 pagesDNA - RNA Introduction AssignmentIZ - 12JR 1013186 Lincoln Alexander SSNo ratings yet
- AS1182Document2 pagesAS1182Sinan ChenNo ratings yet
- DNA StructureDocument4 pagesDNA StructureMaybella PruntyNo ratings yet
- 17.1 (158 Marks) : MarkschemeDocument44 pages17.1 (158 Marks) : MarkschemeSemwezi EnockNo ratings yet
- Holes - Some Important VocabularyDocument29 pagesHoles - Some Important VocabularySomaye Salek MousaviNo ratings yet
- Castle Mendeleev WorksheetDocument2 pagesCastle Mendeleev WorksheetdavgenNo ratings yet
- Belaria® Comfort ICM (8,13) CatalogDocument35 pagesBelaria® Comfort ICM (8,13) CatalogMisterTeoNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids ChemistryDocument68 pagesNucleic Acids ChemistryAlok DhelditNo ratings yet
- What You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsDocument35 pagesWhat You'll Learn: You Will Distinguish Among Different Types of MutationsSeemaNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Molecular Biology PDFDocument32 pagesCentral Dogma of Molecular Biology PDFStephy LimboNo ratings yet
- REPLICATIONDocument9 pagesREPLICATIONdineshNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 3rd QuarterDocument6 pagesGen Bio 3rd QuarterzafmustaphaNo ratings yet
- DNA Vs RNADocument28 pagesDNA Vs RNALeilani Joy Rivera GabitoNo ratings yet
- Basic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Document38 pagesBasic Structures of Dna and Rna 2Herajen DeadoNo ratings yet
- 3 - Structure of DNA, RNA, GenesDocument206 pages3 - Structure of DNA, RNA, GenesJustina VillageNo ratings yet
- 7 - DNA Protein Synthesis Study GuideDocument2 pages7 - DNA Protein Synthesis Study Guideelursgod1No ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument8 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritancevidushipolistyaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Reviewer FinalsDocument18 pagesBiochem Reviewer Finalscha cuteNo ratings yet
- Molecular BiologyDocument2 pagesMolecular BiologyJaymark HisonaNo ratings yet
- Heredity and VariationsDocument18 pagesHeredity and VariationsLovely Syre LaysonNo ratings yet
- Polynucleotide Chain of Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)Document1 pagePolynucleotide Chain of Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)Marigold D. HermonioNo ratings yet
- Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument13 pagesMolecular Basis of InheritanceDikansha JasaiwalNo ratings yet
- LeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Document6 pagesLeaP Science 10 Q3 Week 4Tzuyu ChouNo ratings yet
- Biology Report - Nucleic AcidDocument12 pagesBiology Report - Nucleic AcidAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acid - Britannica Online EncyclopediaDocument46 pagesNucleic Acid - Britannica Online EncyclopediaBauza, Stephanie Dawn T.No ratings yet
- 04-Chemical Basis of HeredityDocument10 pages04-Chemical Basis of HeredityBen Abella100% (1)
- Deoxyribonucleic AcidDocument10 pagesDeoxyribonucleic AcidAlbert Jade Pontimayor LegariaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideDocument11 pagesChapter 12 Glencoe Biology Study GuideabdulazizalobaidiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids.Document18 pagesNucleic Acids.kasingabalyaandrewNo ratings yet
- Jeeheheb GRRDocument22 pagesJeeheheb GRRahhhyiNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesNucleic AcidsMartina BugejaNo ratings yet
- BIO 111 Lecture 8-Nucleic AcidsDocument47 pagesBIO 111 Lecture 8-Nucleic AcidsChinyamaNo ratings yet
- Biological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDocument2 pagesBiological Significance of DNA and RNA SturucturesDr.Charles BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1112 - DNA and ReplicationDocument50 pagesLecture 1112 - DNA and Replicationnizobell100% (1)
- The Genetic Material-1Document48 pagesThe Genetic Material-1Windra TrivenNo ratings yet
- WK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2Document7 pagesWK8-9 - Nucleic Acids 1 - 2opingaangelamae.opingaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and DiscoveryDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 8 - The DNA - Structure, Function, and Discoverybabylen bahalaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionDocument8 pagesLesson 2 Dna Structure and Dna ExtractionGreatel Elijah TorregosaNo ratings yet
- 1 Nucleic AcidsDocument11 pages1 Nucleic AcidsSafiya JamesNo ratings yet
- Level of Structural OrganizationDocument15 pagesLevel of Structural OrganizationahmedNo ratings yet
- Name: Muhammad Abdur Rehman Class: Bs Zoology Roll No: ZOOL51F20R019 Presented To: Sir Abdul MajidDocument5 pagesName: Muhammad Abdur Rehman Class: Bs Zoology Roll No: ZOOL51F20R019 Presented To: Sir Abdul Majidobaid ur rehmanNo ratings yet
- DNA Structure and ReplicationDocument12 pagesDNA Structure and ReplicationJhune Dominique GalangNo ratings yet
- Unit8 DnareplicationandtranscriptionDocument27 pagesUnit8 Dnareplicationandtranscriptionkramesh55107No ratings yet
- Dianne D. Mariano BSN 101Document9 pagesDianne D. Mariano BSN 101Dianne MarianoNo ratings yet
- Dna StructureDocument32 pagesDna Structurealexagano4321No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids Fact SheetDocument1 pageNucleic Acids Fact Sheetasieee chimmyNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritanceDocument10 pagesCBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of InheritancesahanaNo ratings yet
- Differences Between DNA and RNADocument2 pagesDifferences Between DNA and RNAmonishaNo ratings yet
- What Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Document5 pagesWhat Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Central DogmaDocument4 pagesCentral DogmaalxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance - WatermarkDocument31 pagesChapter - 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance - Watermarktejeshnaik026No ratings yet
- Activity 1 HeredityDocument9 pagesActivity 1 HeredityAnonymous SpjVHfNpqNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids.Document7 pagesNucleic Acids.Mujthaba AdmaniNo ratings yet
- DNA and RNADocument23 pagesDNA and RNAHazel SioseNo ratings yet
- Mol Bio-DNA-bookbasedDocument8 pagesMol Bio-DNA-bookbasedElijah Mae MundocNo ratings yet
- Nucliec AcidDocument5 pagesNucliec AcidJoyce Fraulein T. LejosNo ratings yet
- Aristotle Dna Rna ReportDocument13 pagesAristotle Dna Rna ReportSarah Joy RiveraNo ratings yet
- DNA Replication PDFDocument7 pagesDNA Replication PDFPiyush ChandraNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument6 pagesNucleic AcidsAbhijat JhaNo ratings yet
- Carry Instructions Be Copied Polynucleotides Nucleotides: Adenine Guanine Thymine Uracil CytosineDocument3 pagesCarry Instructions Be Copied Polynucleotides Nucleotides: Adenine Guanine Thymine Uracil Cytosineapi-296833859No ratings yet
- Dnarna PPTDocument32 pagesDnarna PPTgianexp123No ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids SummaryDocument4 pagesNucleic Acids SummaryIvan MiglioriniNo ratings yet
- Nucleic acidsLECTUREDocument116 pagesNucleic acidsLECTUREKesha Marie TalloNo ratings yet
- CI Casting Failre AnalysisDocument4 pagesCI Casting Failre Analysisdelta lab sangliNo ratings yet
- Hard Work Is The Key To Success: (2) How To Encourage Our Local ProductsDocument40 pagesHard Work Is The Key To Success: (2) How To Encourage Our Local ProductsMr-Ibrahem Mahmoud MorsyNo ratings yet
- How To Make DIY Activated Charcoal For Prepping and SurvivalDocument35 pagesHow To Make DIY Activated Charcoal For Prepping and SurvivalIsrael SalubiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 02 Eco-DesignDocument88 pagesLesson 02 Eco-DesignMariaNo ratings yet
- MSDS Colatrope 727Document3 pagesMSDS Colatrope 727mndmattNo ratings yet
- Vedic BrochureDocument32 pagesVedic BrochureFREAKEAT FOODSNo ratings yet
- Wilhelmsen Ships Service - Unitor Welding Handbook PDFDocument561 pagesWilhelmsen Ships Service - Unitor Welding Handbook PDFRubén MamaniNo ratings yet
- Astm F2619-F2619M-13Document13 pagesAstm F2619-F2619M-13OussamaNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Data Analysis Applied in Alkali-Based Pretreatment of Corn StoverDocument12 pagesMultivariate Data Analysis Applied in Alkali-Based Pretreatment of Corn StoverAldrienNo ratings yet
- Chakraborty Et Al - 2019 - Magnesium Implants - Prospects and ChallengesDocument21 pagesChakraborty Et Al - 2019 - Magnesium Implants - Prospects and Challengesfrankypanky123No ratings yet
- Kiyavash Sefidvash - Science Fair Research Paper 3Document5 pagesKiyavash Sefidvash - Science Fair Research Paper 3api-535481407No ratings yet
- Pharmacognosy 2 2021 Solution For Most Important QuestionsDocument21 pagesPharmacognosy 2 2021 Solution For Most Important Questionspapov95193No ratings yet
- Matriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 1Document24 pagesMatriculation Chemistry (Introduction To Organic Compound) Part 1ridwan71% (7)
- E2 Knockout Drum PDFDocument2 pagesE2 Knockout Drum PDFKyaw Kyaw AungNo ratings yet
- R-410a Freon GasDocument1 pageR-410a Freon GasMalayalam musical CollectionNo ratings yet
- 2015 Nylon Cable TiesDocument4 pages2015 Nylon Cable Tiesquality fluconNo ratings yet
- KAM SU 8 3000 Datasheet 7.10 FinalDocument6 pagesKAM SU 8 3000 Datasheet 7.10 Finalf20213161No ratings yet
- Program of NEWCA Workshop (V27-04)Document2 pagesProgram of NEWCA Workshop (V27-04)Queiroz PortorrealNo ratings yet
- Asset Intelligence Report - A Primer On High Temperature Hydrogen AttackDocument9 pagesAsset Intelligence Report - A Primer On High Temperature Hydrogen AttackVajid MadathilNo ratings yet
- Tremproof® 260: Single-Component Asphalt Emulsion Waterproofing MembraneDocument2 pagesTremproof® 260: Single-Component Asphalt Emulsion Waterproofing MembraneSky MoonNo ratings yet
- Mutual Occurrence and Dietary Exposure To Total Aflatoxin and Fumonisins in Bread: A Major Breakfast Bakery Product in NigeriaDocument7 pagesMutual Occurrence and Dietary Exposure To Total Aflatoxin and Fumonisins in Bread: A Major Breakfast Bakery Product in NigeriaFaiza NoorNo ratings yet
- Some Mechanical Properties of Cement Stabilized Malaysian Soft ClayDocument8 pagesSome Mechanical Properties of Cement Stabilized Malaysian Soft ClayHawaiiChongNo ratings yet
- Reactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 6Document37 pagesReactions of Alcohols: Organic Chemistry, 6fsalgado7No ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and Compounds HADocument4 pagesAtoms, Elements and Compounds HAHendry RaoNo ratings yet
- GB Assessment Test (Gbat) : #Covid-19. Stay Safe, Stay EducatedDocument9 pagesGB Assessment Test (Gbat) : #Covid-19. Stay Safe, Stay EducatedJASONNo ratings yet