Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MM Flow in Sap
Uploaded by
sankara28Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MM Flow in Sap
Uploaded by
sankara28Copyright:
Available Formats
MM FLOW IN SAP
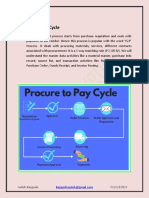
MM Process Flow
PR >Release the PR>RFQ>Quotation>Quotation Comparison>PO>Release the PO>GR>Invoice
Verification
The typical procurement cycle for a service or material consists of the following phases:
1. Determination of Requirements
Materials requirements are identified either in the user departments or via materials planning and
control. (This can cover both MRP proper and the demand-based approach to inventory control.
The regular checking of stock levels of materials defined by master records, use of the order-
point method, and forecasting on the basis of past usage are important aspects of the latter.) You
can enter purchase requisitions yourself, or they can be generated automatically by the materials
planning and control system.
Purchase Requisition
ME51N – Create ME52N – Change ME53N - Display
2. Source Determination
The Purchasing component helps you identify potential sources of supply based on past orders
and existing longer-term purchase agreements. This speeds the process of creating requests for
quotation (RFQs), which can be sent to vendors electronically via SAP EDI, if desired.
Request for Quotation (RFQ)
ME41 – Create ME42 – Change ME43 – Display ME44 – Maintain Supplement ME45 –
Release
Quotation
ME47 – Maintain ME48 – Display ME49 – Price Comparison
3. Vendor Selection and Comparison of Quotations
The system is capable of simulating pricing scenarios, allowing you to compare a number of
different quotations. Rejection letters can be sent automatically.
4. Purchase Order Processing
The Purchasing system adopts information from the requisition and the quotation to help you
create a purchase order. As with purchase requisitions, you can generate Pos yourself or have the
system generate them automatically. Vendor scheduling agreements and contracts (in the SAP
System, types of longer-term purchase agreement) are also supported.
Purchase Order
ME21N – Create ME22N – Change ME23N – Display
5. Purchase Order Follow-Up
The system checks the reminder periods you have specified and - if necessary - automatically
prints reminders or expediters at the predefined intervals. It also provides you with an up-to-date
status of all purchase requisitions, quotations, and purchase orders.
6. Goods Receiving and Inventory Management
Goods Receiving personnel can confirm the receipt of goods simply by entering the Po number.
By specifying permissible tolerances, buyers can limit over- and underdeliveries of ordered
goods.
Goods Movement – MIGO
7. Invoice Verification
The system supports the checking and matching of invoices. The accounts payable clerk is
notified of quantity and price variances because the system has access to PO and goods receipt
data. This speeds the process of auditing and clearing invoices for payment.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-
Integration Points for SD (Sales) and MM
1. During the creation of Sales Order Availability check is carried out which is integrated with
Inventory management
2. During the Delivery Creation the Stock is removed from the Inventory (Once u do Delivery a
material document is created triggering the Movement of material)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
-------
Display Document Flow & Status Overview are the two buttons on the right side of application
tool bar to click (See VA03 Display Sales order: Initial screen)
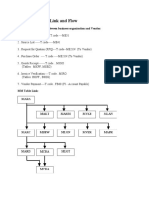
MM Cycle:
Purchase Requisition-> Staff in an organization places Purchase requisition for want of some
goods/products - ME51
Request for Quotation(RFQ)-> The Purchase dept in the organization calls/requests for the
quotation for the products against which PR was raised. - ME41
Vendor Evaluation->after receiving the RFQ's, after comparison a Vendor is finalized based on
the terms and conditions.
Purchase Order (PO) -> Purchase order was issued to that vendor asking him to supply the
goods/products -ME21N
Goods Receipt Note (GRN) ->Vendor supplies the material/Products to the organization
MB01
Goods Issue (GI) -> People receives their respective items for which they have placed the
Requisitions
Invoice Verification-> Along with the Material Vendor submits a Invoice for which the
Company Pays the amount - MIRO
Data to FI -> data will be posted to FI as per the vendor invoices
RFQ to Vendor - ME41
Raising Quotation - ME47
Comparison of Price - ME49
Creation of PO - ME21N
Goods Receipt - MIGO
Invoice (Bill Passing) - MIRO
Goods Issue - MB1A
Physical Inventory - MI01( Create doc)
MI04 (Enter Count)
MI07 (Post)
Common Tables used by SAP MM:
Below are few important Common Tables used in Materials Management Modules:
EINA Purchasing Info Record- General Data
EINE Purchasing Info Record- Purchasing Organization Data
MAKT Material Descriptions
MARA General Material Data
MARC Plant Data for Material
MARD Storage Location Data for Material
MAST Material to BOM Link
MBEW Material Valuation
MKPF Header- Material Document
MSEG Document Segment- Material
MVER Material Consumption
MVKE Sales Data for materials
RKPF Document Header- Reservation
T023 Mat. groups
T024 Purchasing Groups
T156 Movement Type
T157H Help Texts for Movement Types
MOFF Lists what views have not been created
A501 Plant/Material
EBAN Purchase Requisition
EBKN Purchase Requisition Account Assignment
EKAB Release Documentation
EKBE History per Purchasing Document
EKET Scheduling Agreement Schedule Lines
EKKN Account Assignment in Purchasing Document
EKKO Purchasing Document Header
EKPO Purchasing Document Item
IKPF Header- Physical Inventory Document
ISEG Physical Inventory Document Items
LFA1 Vendor Master (General section)
LFB1 Vendor Master (Company Code)
NRIV Number range intervals
RESB Reservation/dependent requirements
T161T Texts for Purchasing Document Types
You might also like
- SAP Purchasing: Prepared by Lavanya .MDocument28 pagesSAP Purchasing: Prepared by Lavanya .MZafar KhanNo ratings yet
- 22-SD and MM Flows in SAPDocument6 pages22-SD and MM Flows in SAPKIRANNo ratings yet
- Motion For Preliminary Injunction Against Temecula Valley Unified School DistrictDocument51 pagesMotion For Preliminary Injunction Against Temecula Valley Unified School DistrictThe Press-Enterprise / pressenterprise.comNo ratings yet
- Quality Assurance / Quality Control Program: Elevator and EscalatorDocument13 pagesQuality Assurance / Quality Control Program: Elevator and EscalatorPio RodolfoNo ratings yet
- Purchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsFrom EverandPurchasing, Inventory, and Cash Disbursements: Common Frauds and Internal ControlsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Wiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 1, Financial Reporting, Planning, Performance, and Control (1-year access)From EverandWiley CMAexcel Learning System Exam Review 2017: Part 1, Financial Reporting, Planning, Performance, and Control (1-year access)No ratings yet
- SAP Procure To Pay ProcessDocument61 pagesSAP Procure To Pay ProcessGaphur shaikNo ratings yet
- The Economist (Thu, 25 Oct 2018) - CalibreDocument222 pagesThe Economist (Thu, 25 Oct 2018) - CalibreOscar JimenezNo ratings yet
- Sales Order ProcessDocument30 pagesSales Order ProcessSivakoti KesaniNo ratings yet
- SAP Procure To Pay ScenariosDocument90 pagesSAP Procure To Pay Scenariosislamelshahat100% (1)
- Sarmasoftwareservices-Hyderabad. Mobile:9949210713. MM Process FlowDocument4 pagesSarmasoftwareservices-Hyderabad. Mobile:9949210713. MM Process FlowSARMANo ratings yet
- Procurement Process Cycle Procure To Pay Process P2PDocument3 pagesProcurement Process Cycle Procure To Pay Process P2PSdev123No ratings yet
- Krishna Menon - DisarmamentDocument139 pagesKrishna Menon - DisarmamentEnuga S. Reddy100% (2)
- AUTOMATIZAÇÃO - ThinkSmart-White-Paper-on-Legal-Workflow-AutomationDocument11 pagesAUTOMATIZAÇÃO - ThinkSmart-White-Paper-on-Legal-Workflow-AutomationAdriana MendonçaNo ratings yet
- SAP MM Interview Questions: Contact:-+91 6360959192Document50 pagesSAP MM Interview Questions: Contact:-+91 6360959192Tushar ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Interview Questions For SAP MMDocument36 pagesInterview Questions For SAP MMnareshraopendyalaNo ratings yet
- SAP MM Interview Q&ADocument4 pagesSAP MM Interview Q&AUttamNo ratings yet
- Procure To Pay (P2P) Process of SAP MMDocument5 pagesProcure To Pay (P2P) Process of SAP MMSwapnil KambleNo ratings yet
- Top 21 SAP MM Interview QuestionsDocument9 pagesTop 21 SAP MM Interview QuestionsVishnu Kumar SNo ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource PlanningDocument9 pagesEnterprise Resource PlanningRobbin HaidenNo ratings yet
- Procurement Process Consists The Following ProcessesDocument3 pagesProcurement Process Consists The Following ProcessesNaresh BabuNo ratings yet
- MM Master Data PRDocument40 pagesMM Master Data PRexcelhelplineNo ratings yet
- Basic of Sap MMDocument12 pagesBasic of Sap MMRooplata NayakNo ratings yet
- Procure To PayDocument14 pagesProcure To PaymeegunNo ratings yet
- 372 Autocracy Part 3 6 PDFDocument441 pages372 Autocracy Part 3 6 PDFandrijarakoNo ratings yet
- Top 22 SAP MM Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesTop 22 SAP MM Interview QuestionsTrishul SampathNo ratings yet
- B.6 LRTA v. Quezon CityDocument16 pagesB.6 LRTA v. Quezon CityCzarianne GollaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Ramos vs. Court of Appeals 321 SCRA 584Document60 pages2 - Ramos vs. Court of Appeals 321 SCRA 584BryanNo ratings yet
- List of Documents For SEDEX PDFDocument3 pagesList of Documents For SEDEX PDFSunilNo ratings yet
- Concept of ERS in SAP MMDocument9 pagesConcept of ERS in SAP MMARABINDA CHAKRAVARTYNo ratings yet
- Info From:: Re: SD Flow and MM FlowDocument6 pagesInfo From:: Re: SD Flow and MM FlowPoulomibNo ratings yet
- MM FlowDocument2 pagesMM FlowAshok kumar kethineniNo ratings yet
- Material Management Flow: Purchasing RequisitionDocument3 pagesMaterial Management Flow: Purchasing RequisitionAnonymous qjtOiPdTNNo ratings yet
- Sap MMDocument8 pagesSap MMcnewaskarNo ratings yet
- Important Transactions in MMDocument2 pagesImportant Transactions in MMJonnalagadda LakshmanNo ratings yet
- Sap MM Training: Purchase OrderDocument61 pagesSap MM Training: Purchase OrderGhassen BLNo ratings yet
- SD FlowDocument15 pagesSD FlowPatan KhanNo ratings yet
- MM Process FlowDocument2 pagesMM Process FlowAbhijit PrinceNo ratings yet
- 22-SD and MM Flows in SAPDocument6 pages22-SD and MM Flows in SAPKIRANNo ratings yet
- P2P PPT (Siddharth Kumar)Document12 pagesP2P PPT (Siddharth Kumar)siddharth.kumarshinNo ratings yet
- KK Sad Pricing Leccion LunesdocxDocument8 pagesKK Sad Pricing Leccion LunesdocxSmith F. JohnNo ratings yet
- What Is The DataFlow of MMDocument2 pagesWhat Is The DataFlow of MMexuser01No ratings yet
- Procurement Cycle in Sap MMDocument4 pagesProcurement Cycle in Sap MMtanusreeghoshNo ratings yet
- SAP Purchasing: Prepared by Lavanya .MDocument28 pagesSAP Purchasing: Prepared by Lavanya .MBaalu KathirveluNo ratings yet
- SAP Purchasing: Prepared by Lavanya .MDocument28 pagesSAP Purchasing: Prepared by Lavanya .MpavankalluriNo ratings yet
- MM Certification PreparationDocument3 pagesMM Certification PreparationSivaram KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Script COMACDocument3 pagesScript COMACRany Meldrenz FloresNo ratings yet
- Requisition To Check Training: Course ObjectivesDocument30 pagesRequisition To Check Training: Course ObjectivesgirishganalNo ratings yet
- Sap Flow MMDocument1 pageSap Flow MMDoreen Quatre BornesNo ratings yet
- Unit 5: The Expenditure CycleDocument20 pagesUnit 5: The Expenditure Cycleyadelew likinaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Generation of Purchase OrderDocument13 pagesAutomatic Generation of Purchase OrderShrey KanherkarNo ratings yet
- 1) Explain What Is SAP MM?Document5 pages1) Explain What Is SAP MM?dudhmogre23No ratings yet
- Sap ProcurementDocument1 pageSap ProcurementKalyan ChakravarthyNo ratings yet
- Procurement in Materials Management: PurposeDocument1 pageProcurement in Materials Management: PurposekurrysuchitNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management - Parts 2-3-4Document61 pagesSupply Chain Management - Parts 2-3-4Marjorie PamelaNo ratings yet
- Procurement Types:: MM FlowDocument11 pagesProcurement Types:: MM FlowKote RaviNo ratings yet
- SAP Purchasing User Training ManualDocument28 pagesSAP Purchasing User Training Manualamit huidrom100% (2)
- ERS - Evaluated Receipt SettlementDocument10 pagesERS - Evaluated Receipt SettlementAntonio Addeo MongellaNo ratings yet
- Sap QDocument14 pagesSap QPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- SCM - Proses PemesananDocument44 pagesSCM - Proses PemesananArief HidayatNo ratings yet
- Script AISDocument4 pagesScript AISbrennaNo ratings yet
- Procurement ProcessDocument1 pageProcurement Processram9199No ratings yet
- Oper8030 Business Process Integration Midterm Exam AssignmentDocument4 pagesOper8030 Business Process Integration Midterm Exam AssignmentYashasvi VermaNo ratings yet
- Evaluated Receipt SettlementDocument9 pagesEvaluated Receipt SettlementDISHIMUKH YADAVNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 SummaryDocument12 pagesChapter 10 SummaryWendelyn TutorNo ratings yet
- MM&SD Flow2Document13 pagesMM&SD Flow2paulusnipponboyNo ratings yet
- P2P Cycle Shirazul SAP ConsultantDocument2 pagesP2P Cycle Shirazul SAP ConsultantMithun Kumar ENo ratings yet
- Summary Unit 4 - SAP01 FundamentalsDocument2 pagesSummary Unit 4 - SAP01 FundamentalsMia AdzkiaNo ratings yet
- Parayno Vs JovellanosDocument3 pagesParayno Vs JovellanosMiguel Lorenzo AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Part C. Customs DutyDocument2 pagesPart C. Customs DutyThu Phương NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Autotuner BETA NDADocument1 pageAutotuner BETA NDAIBNproductionNo ratings yet
- DILG Memorandum Circular 2018-36Document49 pagesDILG Memorandum Circular 2018-36Janine Kae UrsulumNo ratings yet
- WIND Madhya PradeshDocument1 pageWIND Madhya PradeshEPTCL Hazira control roomNo ratings yet
- Arbitration and Exchange Control Laws of IndiaDocument12 pagesArbitration and Exchange Control Laws of IndiaCcapealNo ratings yet
- NHL Playoff Scoring Leaders 2023Document1 pageNHL Playoff Scoring Leaders 2023russettNo ratings yet
- Contrato de Representación ExclusivaDocument14 pagesContrato de Representación Exclusivaronald octavio lopez flores100% (1)
- Effective Date: 8th Aug'19: 'To Whom So Ever It May Concern'Document2 pagesEffective Date: 8th Aug'19: 'To Whom So Ever It May Concern'Anil kadamNo ratings yet
- Singer v. NordstrongDocument12 pagesSinger v. NordstrongJustin TetreaultNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Income Tax-1Document20 pagesIntroduction To Income Tax-1Mehtab MalikNo ratings yet
- Salient Features of Republic Act NoDocument7 pagesSalient Features of Republic Act NoSymone LapizNo ratings yet
- Dividend & Accounts of ComplanyDocument38 pagesDividend & Accounts of ComplanySrikant0% (1)
- GAY MARRIAGE (Same-Sex Couple) : Correct Awareness About The Benefit of Gay MarriedDocument3 pagesGAY MARRIAGE (Same-Sex Couple) : Correct Awareness About The Benefit of Gay MarriedNguyễn Trúc MyNo ratings yet
- The List of Official United States National SymbolsDocument3 pagesThe List of Official United States National SymbolsВікторія АтаманюкNo ratings yet
- Sentence Missing VerbsDocument2 pagesSentence Missing VerbsMurugananthan Ramadoss100% (3)
- Statement 6590792236 20220613 152348 8Document1 pageStatement 6590792236 20220613 152348 8mohamed arabathNo ratings yet
- 2 - Phys120 BS CE 1B - C2 Course Outline and Policy ContractDocument6 pages2 - Phys120 BS CE 1B - C2 Course Outline and Policy Contract中村カズハNo ratings yet
- De Lima v. Guerrero, G.R. No. 229781, 10 October 2017Document34 pagesDe Lima v. Guerrero, G.R. No. 229781, 10 October 2017Donnia MayeNo ratings yet
- Shooting An ElephantDocument2 pagesShooting An ElephantShilpaDasNo ratings yet
- SEM 6 - 10 - BCom - HONS - COMMERCE - DSE 61A - FINANCIAL REPORTING AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS - 10297Document5 pagesSEM 6 - 10 - BCom - HONS - COMMERCE - DSE 61A - FINANCIAL REPORTING AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT ANALYSIS - 10297Aaysha AgrawalNo ratings yet