Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 5 Mtap Notes
Uploaded by
appasual1648antOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Week 5 Mtap Notes
Uploaded by
appasual1648antCopyright:
Available Formats
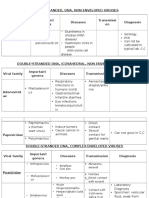
Nonenveloped (RNA) (CHP) • indicates the patient is in
convalescence or previously vaccinated
• Calicivirus
and has developed immunity.
• Hepevirus
• Picornaviruses
Envelope (DNA)
HSV-1 (KEP HCG)
• Hepadnaviruses • gingivostomatitis
• Herpesviruses • pharyngitis
Single-stranded, DNA virus. No envelope. • herpes labialis
• conjunctivitis
• Parvoviruses • keratitis
Double-stranded, RNA. No envelope • encephalitis (in adults)
HSV-1 and HSV-2
• Reoviruses/ Rotavirus • cause of: mucous membrane and skin
lesions and ocular, visceral, and CNS
disease
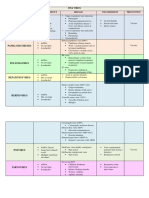
HEPATITIS B (HBV) CELL LINES:
Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) • Adenoviruses: A-549, HEp-2, and He-La
• most reliable marker for identifying cells. Grapelike cluster cytopathic effect
HBV infection. (CPE).
• It becomes evident in the patient’s • Herpes: A-549, MRC-5, or Vero cell -MAV
serum weeks before any biochemical lines. Rounding, refractile CPE.
evidence associated with liver damage • VZV:
(biochemical liver assays may show only ▪ In cell culture: CPE of small
minimal elevation). clusters of ovoid cells in fibroid
• It remains in the serum during the cells such as MRC-5, HF, and
acute and chronic stages of hepatitis B. A549
• The presence of HBsAg 6 months after ▪ Shell vial cultures: cytoplasmic,
acute infection indicates that the apple-green fluorescence
patient is a chronic carrier. • Coronaviruses: Vero-E6 cell line
HBeAg (hepatitis B e antigen) (CE) • CMV: human fibroblasts
• indicates high infectivity and a chronic • Influenza virus: Primary monkey kidney
carrier state. (PMK) cell lines. Fail to produce a CPE.
HBV DNA in the serum • Enterovirus: CPE of visible cell rounding
• The best indication of active viral and shrinking. Refractility and cell
replication and a high state of degeneration
infectivity • Rhinovirus: MRC-5. CPE large and small
IgM (anti-HBcAg) to hepatitis B core antigen round refractile cells in the fibroblast
(HBcAg) (AC)
• appears early in the course of disease,
during the acute infection. Coxsackie A
Anti-HBsAg (antibody to surface antigen) • Herpangina
• handfoot-mouth disease • Filoviridae
Coxsackie B • Flaviviridae
• pleurodynia • Orthomyxoviridae
• pericarditis • Paramyxoviridae
• myocarditis • Picornaviridae
Hepatitis A virus • Reoviridae
• only hepatitis group of viruses capable • Retroviridae
of growth in cell culture • Rhabdoviridae
• Togaviridae
• Other Infectious Agents
Winter months • Prions
• Rotavirus
• RSV
• Metapneumovirus negative sense RNA
• Influenza virus • Orthomyxoviruses
• SARS coronavirus
Urine
• adenovirus Hemorrhagic fever
• mumps virus • Ebola, Marburg, Lassa, yellow fever,
• enteroviruses (fecal contamination) dengue, and other viruses
• CMV
• Measles
• Rubella
• BK
DNA Viruses (AHH P^4)
• Adenoviridae
• Hepadnaviridae
• Herpesviridae
• Papillomaviridae
• Parvoviridae
• Polyomaviridae
• Poxviridae
RNA Viruses (mostly enveloped)
• Arenaviridae
• Astroviridae
• Bunyaviridae
• Caliciviridae
• Coronaviridae
You might also like
- DNA VirusesDocument154 pagesDNA VirusesRod Pasion0% (1)
- VirusesDocument2 pagesVirusesgregoryvo100% (4)
- 13 11 21 Antiviral AgentsDocument49 pages13 11 21 Antiviral AgentsRahul LakhaniNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis (Virus Hepatitis)Document75 pagesViral Hepatitis (Virus Hepatitis)Ilmiah Bagus100% (1)
- Herpes Simplex Varicella and Zoster: Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentFrom EverandHerpes Simplex Varicella and Zoster: Clinical Manifestations and TreatmentRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (19)
- Medically Important VirusesDocument3 pagesMedically Important Virusesgiannpee100% (1)
- Virology: Yvonne E. Pama RMT - MDDocument23 pagesVirology: Yvonne E. Pama RMT - MDValdez Francis ZaccheauNo ratings yet
- Virology TableDocument10 pagesVirology TablekevinNo ratings yet
- Isolation and Identification of Microorganisms From Mobile Phones in College EnvironmentDocument23 pagesIsolation and Identification of Microorganisms From Mobile Phones in College EnvironmentINTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENCE SCHOLARS100% (1)
- Part 2 of Medical VirologyDocument113 pagesPart 2 of Medical Virologygatete samNo ratings yet
- Virus ClassificationDocument5 pagesVirus ClassificationNUR AIN NADHIRAH SHAMSUL BADRINo ratings yet
- Infeksi Virus Pada Rongga MulutDocument41 pagesInfeksi Virus Pada Rongga MulutFaris MahdaniNo ratings yet
- CSMLS C2 QuestionsDocument49 pagesCSMLS C2 QuestionsApollo Ochieng100% (1)
- VirologyDocument55 pagesVirologySelvenThirumalai100% (4)
- Pathophysiology: HIV Infection and AIDSDocument7 pagesPathophysiology: HIV Infection and AIDSmeylin SNo ratings yet
- Blood TransfusionDocument25 pagesBlood Transfusionpriya9balan-863873No ratings yet
- VirologyDocument24 pagesVirologyRohama Qubra 279No ratings yet
- Case Conference Maternal HIV C Maternal Amphetamine Use PDFDocument44 pagesCase Conference Maternal HIV C Maternal Amphetamine Use PDFPloyz NattidaNo ratings yet
- VirologyDocument40 pagesVirologyKutub SikderNo ratings yet
- Oxygen 2222Document75 pagesOxygen 2222Salim AlmetewtyNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis VirusDocument83 pagesHepatitis VirusRudresh Shoorashetty ManoharNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Asaad Maidin Departement Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin University, MakassarDocument54 pagesMuhammad Asaad Maidin Departement Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Hasanuddin University, MakassarPratiwi PurnamaNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis VirusesDocument19 pagesHepatitis VirusesFort SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Viruses KMCDocument29 pagesHepatitis Viruses KMCmaregnrodiNo ratings yet
- Addtl Info ViroDocument6 pagesAddtl Info ViroAlondra SagarioNo ratings yet
- 15 HepatitisDocument48 pages15 HepatitisAlvin LaurenceNo ratings yet
- Purnomo Hadi: FK UNDIP - SemarangDocument36 pagesPurnomo Hadi: FK UNDIP - SemarangandreasNo ratings yet
- Virus Properties Unit-I-1Document15 pagesVirus Properties Unit-I-1Urdu KahaniNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lecture - 20 Enterovirus & HepatitisDocument64 pagesMicrobiology Lecture - 20 Enterovirus & HepatitisChris Queiklin100% (1)
- DNA Viruses 2Document28 pagesDNA Viruses 2sairahhannahNo ratings yet
- Organism. - 20-300 NM in Diameter. - Core of Nucleic Acids Either DNA or RNA - Capsid Composed of Protein - Envelope - Matrix ProteinDocument7 pagesOrganism. - 20-300 NM in Diameter. - Core of Nucleic Acids Either DNA or RNA - Capsid Composed of Protein - Envelope - Matrix ProteinShihab Sarar UdoyNo ratings yet
- RNA and DNA VirusesDocument62 pagesRNA and DNA Viruseseren16jaegerNo ratings yet
- Viral InfectionsDocument69 pagesViral InfectionsJonnie Rose Louise WeeNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis A GDocument23 pagesHepatitis A Gapi-3712326No ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted VirusesDocument25 pagesSexually Transmitted VirusesAliah Anne MagnoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Virology: Scott M. Hammer, M.DDocument46 pagesIntroduction To Virology: Scott M. Hammer, M.DAkmal Faiz100% (1)
- HepatitisDocument33 pagesHepatitisThomas UtomoNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis Training Manual: Federal Ministry of Health National Hepatitis Control Program 2017Document44 pagesViral Hepatitis Training Manual: Federal Ministry of Health National Hepatitis Control Program 2017Eleni HagosNo ratings yet
- Class 10 - Hepatitis Viruses: Ann Machablishvili, MD, PHDDocument23 pagesClass 10 - Hepatitis Viruses: Ann Machablishvili, MD, PHDqbcv4shshxNo ratings yet
- Viral InfectionsDocument59 pagesViral Infectionsrenato renatoNo ratings yet
- Viral HepatitisDocument58 pagesViral HepatitisKathrine SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis B & DDocument40 pagesHepatitis B & DMeena CtNo ratings yet
- MYCO VIRO 1-MergedDocument29 pagesMYCO VIRO 1-MergedGennelyn Ross Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- نسخة Virology Pictures for SpotsDocument25 pagesنسخة Virology Pictures for Spotsعبدالله العثمانNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 VirologyDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Virologyairareotutar16No ratings yet
- HepatitisDocument16 pagesHepatitisSaipulla SaibuNo ratings yet
- Virus Hepatitis RevDocument83 pagesVirus Hepatitis RevSukma WinahyuNo ratings yet
- 1010 M Balm - Viral HepatitisDocument17 pages1010 M Balm - Viral HepatitisSaad KhanNo ratings yet
- Virology 1 - FileDocument39 pagesVirology 1 - Fileali.tariq26No ratings yet
- VirusStructure 1Document21 pagesVirusStructure 1denisse moraNo ratings yet
- Emerging and Miscellaneous VirusesDocument25 pagesEmerging and Miscellaneous VirusesAliah Anne MagnoNo ratings yet
- Emerging and Miscellaneous VirusesDocument24 pagesEmerging and Miscellaneous VirusesMoon YoungheeNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis Virus: Bagian Mikrobiologi FK UnissulaDocument36 pagesHepatitis Virus: Bagian Mikrobiologi FK UnissulaKarina Mega WNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis MBBS 2Document41 pagesViral Hepatitis MBBS 2Sohail ShahNo ratings yet
- Hepatitis FK 2008Document42 pagesHepatitis FK 2008Dokter KarisNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 Intro VirusesDocument26 pagesLec 2 Intro Viruses007ginniNo ratings yet
- ViralDocument38 pagesViralJessica GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Viruses: Classification, General Characteristics, ReplicationDocument40 pagesViruses: Classification, General Characteristics, ReplicationLove AzaliaNo ratings yet
- DNA VirusesDocument99 pagesDNA VirusesCourtny Lenz Maygay GapaNo ratings yet
- Infeksi Virus Pada Sistem Pencernaan Bawah: Hepatitis: Ety AprilianaDocument27 pagesInfeksi Virus Pada Sistem Pencernaan Bawah: Hepatitis: Ety AprilianaAsmorowatiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - SCI 8007SEF Medical Microbiology & Virology-Virology II - 2023Document76 pagesLecture 8 - SCI 8007SEF Medical Microbiology & Virology-Virology II - 2023YY CheungNo ratings yet
- RETROVIRIDAEDocument1 pageRETROVIRIDAEjcpacate1178qcNo ratings yet
- Viral Hepatitis PC II 2023Document76 pagesViral Hepatitis PC II 2023Suhayb CumarNo ratings yet
- Paramyxovirus LecDocument25 pagesParamyxovirus Lecapi-19969058No ratings yet
- Virus Zoster VaricelaDocument204 pagesVirus Zoster VaricelaJosǝ Luiis BrjsNo ratings yet
- Human Endogenous Retroviruses and AIDS Research: Confusion, Consensus, or Science?Document6 pagesHuman Endogenous Retroviruses and AIDS Research: Confusion, Consensus, or Science?DisicienciaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Characterization of The Isolated Strains of Bovine Viral Diarrhea VirusDocument7 pagesMolecular Characterization of The Isolated Strains of Bovine Viral Diarrhea VirusGhada AfifiNo ratings yet
- Viruses 15 01622 v2Document71 pagesViruses 15 01622 v2Hanif Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Omipon M4pretDocument3 pagesOmipon M4pretPaolo Andrei OmiponNo ratings yet
- How To Collect A Stool Sample For Your Lab TestDocument2 pagesHow To Collect A Stool Sample For Your Lab TestcgermaineeNo ratings yet
- Communicable Disease Epidemiology-1Document84 pagesCommunicable Disease Epidemiology-1Solomon Nageso LaaftooNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Report - Mr. Ashish Gudka, Executive Assistant To MD & Group CEODocument2 pagesCOVID-19 Report - Mr. Ashish Gudka, Executive Assistant To MD & Group CEODeepak UpadhayayNo ratings yet
- Frcpath Part 1 in Infection / Combined Infection Certificate Examination Sample McqsDocument8 pagesFrcpath Part 1 in Infection / Combined Infection Certificate Examination Sample McqsdrNo ratings yet
- Microorganism Friend and FoeDocument7 pagesMicroorganism Friend and FoeNEIL GAROONo ratings yet
- Worksheet #8Document2 pagesWorksheet #8Anjela AprilNo ratings yet
- Microbial Resistance To DisinfectantsDocument7 pagesMicrobial Resistance To DisinfectantssyarifuddinNo ratings yet
- Effect of Disinfectants On Highly Pathogenic Avian in Uenza Virus (H5N1) in Lab and Poultry FarmsDocument7 pagesEffect of Disinfectants On Highly Pathogenic Avian in Uenza Virus (H5N1) in Lab and Poultry FarmsBalvant SinghNo ratings yet
- PRINT - 2020 ZCGs PDFDocument153 pagesPRINT - 2020 ZCGs PDFChalwe HowardNo ratings yet
- Fig. 4. X-Ray Diffraction Pattern of Bio-SynthesizedDocument3 pagesFig. 4. X-Ray Diffraction Pattern of Bio-SynthesizedAfrah MNo ratings yet
- Sterilization by HeatDocument8 pagesSterilization by HeatEjaj SumitNo ratings yet
- Cedar Point Welcoming You Back GuideDocument7 pagesCedar Point Welcoming You Back GuideWKYC.comNo ratings yet
- HIV Infection and AIDSDocument71 pagesHIV Infection and AIDShaechannie leeNo ratings yet
- CURS MG COVIT B) - + Fumatul PDFDocument68 pagesCURS MG COVIT B) - + Fumatul PDFOlariuSiminaOtiliaNo ratings yet
- Vesicular Exanthema of Swine Virus VESVDocument9 pagesVesicular Exanthema of Swine Virus VESVAngelie OngNo ratings yet
- Balanopostitis and Penyle Edema Atypical Manifestation of Primary SipilisDocument2 pagesBalanopostitis and Penyle Edema Atypical Manifestation of Primary SipilisTeja LaksanaNo ratings yet
- 2022 - Microbiology - Medically Important Bacteria II (Part 2)Document80 pages2022 - Microbiology - Medically Important Bacteria II (Part 2)Vaenusha MuruganNo ratings yet
- 2006 Identification of Plasmodium Falciparum Var1CSA and Var2CSA Domains That Bind IgM Natural AntibodiesDocument6 pages2006 Identification of Plasmodium Falciparum Var1CSA and Var2CSA Domains That Bind IgM Natural AntibodiesSethawud ChaikitgosiyakulNo ratings yet
- 2021 - Evaluation of Liver Histopathological Findings of COVID-19 by Minimally Invasive AutopsiesDocument24 pages2021 - Evaluation of Liver Histopathological Findings of COVID-19 by Minimally Invasive AutopsiesMario Martínez TorijaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - TransDocument8 pagesModule 1 - TransJohanna Kate DiestroNo ratings yet