Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2
Chapter 2
Uploaded by
elaco560 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesOriginal Title
Chapter-2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views5 pagesChapter 2
Chapter 2
Uploaded by
elaco56Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
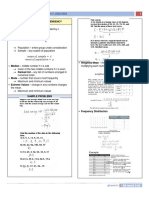
Graphical Presentation of Qualitative Data Frequency Distributions
-A graph made of bars whose -A frequency distribution for
heights represent the frequencies of quantitative data lists all the classes and
respective categories is called a bar graph. the number of values that belong to each
class. Data presented in the form of a
frequency distribution are called grouped
data.
Class Boundary
-is given by the midpoint of the
upper limit of one class and the lower limit
of the next class.
Finding Class Width
Class width = Upper boundary – Lower boundary
-A circle divided into portions that Calculating Class Midpoint or Mark
𝐿𝑜𝑤𝑒𝑟 𝑙𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑡+𝑈𝑝𝑝𝑒𝑟 𝑙𝑖𝑚𝑖𝑡
represent the relative frequencies or Class Midpoint or Mark =
2
percentages of a population or a sample Calculation of Class Width
𝐿𝑎𝑟𝑔𝑒𝑠𝑡 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒−𝑆𝑚𝑎𝑙𝑙𝑒𝑠𝑡 𝑉𝑎𝑙𝑢𝑒
belonging to different categories is called a Approximate class width=
𝑁𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑐𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠𝑒𝑠
pie chart.
Relative Frequency and Percentage
Distributions
𝑓𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
Relative frequency of a class=
𝑓𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦
Percentage = 𝑅𝑒𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑓𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦 × 100
Histogram Shapes of Histograms
-is a graph in which classes are ‣ Symmetric
marked on the horizontal axis and the
frequencies, relative frequencies, or
percentages are marked on the vertical
axis.
-The frequencies, relative ‣ Skewed
frequencies, or percentages are
represented by the heights of the bars.
-In a histogram, the bars are drawn
adjacent to each other.
‣ Uniform or Rectangular
A cumulative frequency distribution gives the
Polygon total number of values that fall below the
-A graph formed by joining the upper boundary of each class.
midpoints of the tops of successive bars in
a histogram with straight lines.
Calculating Cumulative Relative Frequency
and Cumulative Percentage Stem and leaf Display
Cumulative Relative Frequency -In a stem-and-leaf display of
𝐶𝑜𝑚𝑚𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑓𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦 𝑜𝑓 𝐶𝑙𝑎𝑠𝑠
=
𝑇𝑜𝑡𝑎𝑙 𝑂𝑏𝑠𝑒𝑟𝑐𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛𝑠 𝑖𝑛 𝑡ℎ𝑒 𝑑𝑎𝑡𝑎 𝑠𝑒𝑡
quantitative data, each value is divided into
Commulative Percentage two portions – a stem and a leaf. The leaves
= 𝐶𝑜𝑚𝑚𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝑅𝑒𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑣𝑒 𝐹𝑟𝑒𝑞𝑢𝑒𝑛𝑐𝑦 × 100 for each stem are shown separately in a
display.
An ogive is a curve drawn for the cumulative
frequency distribution by joining with straight
lines the dots marked above the upper
boundaries of classes at heights equal to the
cumulative frequencies of respective classes.
You might also like
- Lesson 4 - EDADocument8 pagesLesson 4 - EDANicko CortoNo ratings yet
- Stat Review 2020Document5 pagesStat Review 2020Ruby Ann BaniquedNo ratings yet
- Biostats 1Document2 pagesBiostats 1bryan.zabala.mnlNo ratings yet
- Describing Data:: Frequency Tables, Frequency Distributions, and Graphic PresentationDocument14 pagesDescribing Data:: Frequency Tables, Frequency Distributions, and Graphic PresentationARKONo ratings yet
- A Relative Frequency Histogram Uses The SameDocument1 pageA Relative Frequency Histogram Uses The SameDyna BalloconNo ratings yet
- Statistic 1Document2 pagesStatistic 1api-26281458No ratings yet
- StatisticsDocument2 pagesStatisticsShera ShahNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability DictionaryDocument6 pagesStatistics and Probability DictionaryJanna PiqueroNo ratings yet
- Presentation of DataDocument2 pagesPresentation of DataAlishba NadeemNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document3 pagesChapter 2Cruzzy KaitNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document16 pagesPresentation 1geo raganasNo ratings yet
- Data Presentation-PrintDocument4 pagesData Presentation-PrintFevee Joy BalberonaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics: Descriptive Statistics Are Used by Researchers To Report On Populations and SamplesDocument41 pagesDescriptive Statistics: Descriptive Statistics Are Used by Researchers To Report On Populations and SamplesMuhammed FuadNo ratings yet
- Presentation of Data 1Document33 pagesPresentation of Data 1Kamran HanifNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 2 Descriptive StatisticsDocument5 pagesCHAPTER 2 Descriptive StatisticsPark MinaNo ratings yet
- 002 Frequency Distribution PSY102Document59 pages002 Frequency Distribution PSY102Angelica NavarreteNo ratings yet
- Frequency Tables, Frequency Distributions and Graphic PresentationDocument22 pagesFrequency Tables, Frequency Distributions and Graphic PresentationZaid Bin NisarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Frequency DistributionsDocument30 pagesChapter 2: Frequency DistributionssaraNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Statistics: Tabular and Graphical Methods: Summarizing Qualitative Data Summarizing Quantitative DataDocument32 pagesDescriptive Statistics: Tabular and Graphical Methods: Summarizing Qualitative Data Summarizing Quantitative DataNivar selevanayNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Intro Stats Freq DistDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 Intro Stats Freq DistHaris HasanNo ratings yet
- SASADocument5 pagesSASAMichaella MaderableNo ratings yet
- Frequency Distribution:: Tabular Presentation For Qualitative DataDocument4 pagesFrequency Distribution:: Tabular Presentation For Qualitative Datamasrawy eduNo ratings yet
- Catatan Statisktik FIXDocument59 pagesCatatan Statisktik FIXAndrian WicaksonoNo ratings yet
- MMW - Midterm Notes (FINAL) PDFDocument8 pagesMMW - Midterm Notes (FINAL) PDFDhon Aldrin CastroNo ratings yet
- Calculating Standard Deviation Step by StepDocument21 pagesCalculating Standard Deviation Step by StepBayissa BekeleNo ratings yet
- 002 Data Presentation (Modified)Document31 pages002 Data Presentation (Modified)JM MaguigadNo ratings yet
- 02 Data and Preliminary Data Analysis - PrintDocument20 pages02 Data and Preliminary Data Analysis - PrintCahyo Agung SaputraNo ratings yet
- Frequency and Distribution Graphical and TextualDocument21 pagesFrequency and Distribution Graphical and Textualgreatchelle sumayangNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Frequency Distribution: HistogramDocument13 pagesGraphs of Frequency Distribution: HistogramRajNo ratings yet
- Basic Statistics Terms DefinedDocument5 pagesBasic Statistics Terms DefinedHarvey PedrosaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document22 pagesChapter 2t524qjc9bvNo ratings yet
- Organizing and Graphing Data - Francheska G. AlvizDocument13 pagesOrganizing and Graphing Data - Francheska G. AlvizFrancheska AlvizNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 MAS202Document43 pagesChapter2 MAS202Quỳnh VânNo ratings yet
- Case VariableDocument4 pagesCase VariableneethiNo ratings yet
- Graphical PresentationDocument27 pagesGraphical PresentationEj VillarosaNo ratings yet
- Class - 2tabulation 0Document14 pagesClass - 2tabulation 0Fady FakhryNo ratings yet
- Class - 2tabulation 0Document14 pagesClass - 2tabulation 0rijahNo ratings yet
- SLIDES Statistics-Chapter 2Document31 pagesSLIDES Statistics-Chapter 2nganda234082eNo ratings yet
- When Working With Statistical Diagrams, Make Sure You Look at The Scale CarefullyDocument8 pagesWhen Working With Statistical Diagrams, Make Sure You Look at The Scale CarefullyHannah YeungNo ratings yet
- Finals in Edu 533Document11 pagesFinals in Edu 533ISSUE TVNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document16 pagesPresentation 1geo raganasNo ratings yet
- 1 CH 1-2Document80 pages1 CH 1-2Ahmed AlarashiNo ratings yet
- Organizing and Graphing Quantitative Data: Sections 2.3 - 2.4Document15 pagesOrganizing and Graphing Quantitative Data: Sections 2.3 - 2.4obadfaisal24No ratings yet
- Document 1Document7 pagesDocument 1Tanveer KhuranaNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet g10mt06 FinalDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet g10mt06 FinalLobi RybgNo ratings yet
- Basic Terminologies in StatisticsDocument4 pagesBasic Terminologies in StatisticsMARCOS GUADALOPENo ratings yet
- Craphing Statistical DataDocument3 pagesCraphing Statistical Datakevin funtallesNo ratings yet
- 1.2. Graphical Representation - ReviewDocument4 pages1.2. Graphical Representation - ReviewJuditNo ratings yet
- Statistic RefresherDocument3 pagesStatistic RefresherjesperlaheyNo ratings yet
- STATISTICS. DSPDocument16 pagesSTATISTICS. DSPHam HereNo ratings yet
- Describing Data:: Frequency Tables, Frequency Distributions, and Graphic PresentationDocument31 pagesDescribing Data:: Frequency Tables, Frequency Distributions, and Graphic PresentationElwin Michaelraj VictorNo ratings yet
- Collection of Data Part 2 Edited MLISDocument45 pagesCollection of Data Part 2 Edited MLISWhieslyn ColeNo ratings yet
- Measures of DispersionDocument10 pagesMeasures of DispersionTasbir HasanNo ratings yet
- BraseUStat10 02 01Document42 pagesBraseUStat10 02 01billups400No ratings yet
- Frequency Distributions: Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral SciencesDocument40 pagesFrequency Distributions: Essentials of Statistics For The Behavioral SciencesMarsa K FNo ratings yet
- Unit II Question Bank With Hints and AnswersDocument16 pagesUnit II Question Bank With Hints and Answersakshaya vijayNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument12 pagesDescriptive StatisticsAndrew MwingaNo ratings yet
- What Is Frequency Distribution?Document3 pagesWhat Is Frequency Distribution?ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Stats (Descriptive) Study GuideDocument15 pagesStats (Descriptive) Study GuidePatrick Joshua GlimadaNo ratings yet
- Community Needs Assessment QuestionnaireDocument4 pagesCommunity Needs Assessment Questionnaireelaco56No ratings yet
- Group 2-System MapDocument2 pagesGroup 2-System Mapelaco56No ratings yet
- CE 13 ReviewerDocument34 pagesCE 13 Reviewerelaco56No ratings yet
- Esc 23.1Document4 pagesEsc 23.1elaco56No ratings yet
- Annuity Quiz KeyDocument1 pageAnnuity Quiz Keyelaco56No ratings yet
- Mathematics7 Q4 Mod3 PresentationofData-v3Document29 pagesMathematics7 Q4 Mod3 PresentationofData-v3charitocalangan605No ratings yet
- Exp19 Excel Ch08 HOEAssessment Robert's Flooring InstructionsDocument1 pageExp19 Excel Ch08 HOEAssessment Robert's Flooring InstructionsMuhammad ArslanNo ratings yet
- 2d Density ChartDocument9 pages2d Density ChartTomas Barrientos BrunaNo ratings yet
- Unit 01 DWDMDocument105 pagesUnit 01 DWDMVS creationsNo ratings yet
- Business Stat Week 3-4Document12 pagesBusiness Stat Week 3-4Axv ErnestoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 Attempt ReviewDocument5 pagesQuiz 3 Attempt ReviewAnrudh kumarNo ratings yet
- Minitab Meet15 - EngDocument140 pagesMinitab Meet15 - EngAsachan rujeephisitNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document2 pagesHW 1Luis Fernando Vergaray AstupiñaNo ratings yet
- Universidad de Las Fuerzas Armadas "Espe": Departamento de Ciencias de La Energia Y Mecanica Diseño MecatronicoDocument10 pagesUniversidad de Las Fuerzas Armadas "Espe": Departamento de Ciencias de La Energia Y Mecanica Diseño MecatronicoCesar QuilumbaquinNo ratings yet
- SFB Module I 2019Document37 pagesSFB Module I 2019Ashwani SharmaNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Managers Using Microsoft Excel: Chapter 1 (Textbook Ch1-Ch2)Document36 pagesStatistics For Managers Using Microsoft Excel: Chapter 1 (Textbook Ch1-Ch2)Tsoi Yun PuiNo ratings yet
- Misconceptions in Descriptive Statistics Among Postgraduates in Social SciencesDocument6 pagesMisconceptions in Descriptive Statistics Among Postgraduates in Social SciencesallenNo ratings yet
- Presentation of DataDocument9 pagesPresentation of DataFaizan KhanNo ratings yet
- Using Your TI-83/84 Calculator: Binomial Probability DistributionsDocument3 pagesUsing Your TI-83/84 Calculator: Binomial Probability DistributionseugenezainNo ratings yet
- Charmy G. Estoquia BSBA FM3 - A: Performance Task - Cbmec2Document7 pagesCharmy G. Estoquia BSBA FM3 - A: Performance Task - Cbmec2Trexy NaNo ratings yet
- Titanic Dataset 1677256844Document27 pagesTitanic Dataset 1677256844Mariappan RNo ratings yet
- CH 5Document4 pagesCH 5Maulik ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document84 pagesChapter 03khanhnguyenfgoNo ratings yet
- IQM - Lecture GuideDocument12 pagesIQM - Lecture GuideKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Review of Preventive and Social MedicineDocument7 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Review of Preventive and Social MedicineDr-Sanjay SinghaniaNo ratings yet
- Biostatistic د- داليا احمدDocument12 pagesBiostatistic د- داليا احمدMostafa FayadNo ratings yet
- 7 QC TOOLS PPT Everest Industries LimitedDocument70 pages7 QC TOOLS PPT Everest Industries LimitedDeepakvanguri100% (2)
- Tabulation Coding and EditingDocument16 pagesTabulation Coding and EditingKritika Jaiswal100% (2)
- 08 Maths Key Notes CH 05 Data HandlingDocument2 pages08 Maths Key Notes CH 05 Data HandlingAryan DamodharNo ratings yet
- Econometrics I 1Document40 pagesEconometrics I 1Mimansa BairathiNo ratings yet
- The Process Capability AnalysisDocument18 pagesThe Process Capability AnalysisMohamed HamdyNo ratings yet
- MMW Chap 4 Data Management Part 1Document58 pagesMMW Chap 4 Data Management Part 1Carl GilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 & 3 pt.3Document31 pagesChapter 2 & 3 pt.3Joseph Raafat Keddis Tawfik YessaNo ratings yet
- Statistics SPM QuestionsDocument4 pagesStatistics SPM QuestionsRita LauNo ratings yet
- Statistics CombineDocument65 pagesStatistics CombineMustansar saeedNo ratings yet