Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sheet 2
Sheet 2
Uploaded by
es.ahmed.esmail2023Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sheet 2
Sheet 2
Uploaded by
es.ahmed.esmail2023Copyright:
Available Formats
Nuclear Reactor Kinetics
Sheet 2: Control Rods and Chemical Shim
1. An experimental reactor facility is a bare square cylinder 100 cm high, composed of small beryllium
blocks with thin foils of 235U placed in between, so that the system can be considered a homogeneous
mixture of Be and 235U. The reactor is to be controlled with a single black control rod 2.5 cm in radius
and located along the axis of the system. (a) If the reactor is critical with the rod fully withdrawn, how
much negative reactivity is introduced into the system when the rod is fully inserted? (b) Assuming
that the rod moves into the reactor instantaneously, on what period does the reactor go?
[Σt = 0.760037 cm-1, D = 0.50 cm, ηT = 2.065, LTM = 21 cm, τT = 102 cm2]
2. A small bare reactor is a square cylinder of extrapolated height 70 cm. The reactor consists of a mixture
of ordinary water and 235U at room temperature. Suppose it is desired to control the reactor with one
central rod having a worth of 10%. How big should the rod be?
[Σt = 3.443 cm-1, D = 0.16 cm, ηT = 2.065, LTM2 = 8.1 cm2, τT = 27 cm2]
3. A certain pressurized-water reactor is to be controlled by 61 cluster control assemblies, each assembly
containing 20 black rods 1.15 cm in diameter. The reactor core is a cylinder 320 cm in diameter. The
average thermal diffusion length in the core is 1.38 cm, D = 0.21 cm, and ΣT in the core material is
approximately 2.6 cm-1. Calculate the total worth of the rods.
4. Cruciform rods used for the control of a certain boiling-water reactor consist of blades 24.8 cm wide
and 0.792 cm thick. The parameters of the core material are LT = 1.2 cm and Σa = 0.20 cm-1. The rods
are black to thermal neutrons. How far apart should these rods be placed to provide a total worth
0.0917.
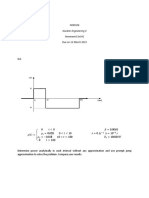
5. A control rod 100 cm long is worth 50 cents when totally inserted. (a) How much reactivity is
introduced into the reactor when the rod is pulled one-quarter of the way out? (b) At what rate is
reactivity introduced at this point per cm motion of the rod?
6. Suppose that, at some time during its operating history, the reactor described in problem 2 is critical
with the rod withdrawn one-half of its full length. If the rod is now suddenly withdrawn another 10
cm, (a) how much reactivity is introduced? (b) On what period does the reactor power rise?
7. What concentration of boron in ppm will give worth of 0.13?
8. An infinite 235U-fueled, water-moderated reactor contains 20% more 235U than required to become
critical. What concentration of (a) boron in ppm or (b) boric acid in g/liter is required to hold down the
excess reactivity of the system?
You might also like
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Final - Report Hydroelectric Power PlantDocument39 pagesFinal - Report Hydroelectric Power PlantnisarNo ratings yet
- Hydroelectric Power PlantDocument40 pagesHydroelectric Power Planttamilvananirtt100% (2)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Modeling, Simulation and Control of A Drum BoilerDocument55 pagesModeling, Simulation and Control of A Drum BoilerDipankar Kalita75% (4)
- Final - Report Hydroelectric Power PlantDocument39 pagesFinal - Report Hydroelectric Power Plantfasihazam100% (4)
- Elecon Gear CouplingDocument7 pagesElecon Gear CouplingVipul Chaudhari100% (4)
- BNP-B2207 (Maintainance Manual)Document45 pagesBNP-B2207 (Maintainance Manual)James WinsorNo ratings yet
- CSTR in SeriesDocument12 pagesCSTR in Seriesmnizamarzuki0% (2)
- Final - Report Hydroelectric Power PlantDocument39 pagesFinal - Report Hydroelectric Power PlantniteshmchopraNo ratings yet
- Wastewater QuestionDocument18 pagesWastewater Questionth3mannnNo ratings yet
- Raw Board Battle Round 1Document13 pagesRaw Board Battle Round 1Maridil Joy IsidroNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetFrom EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetNo ratings yet
- Tubular ReactorDocument20 pagesTubular ReactorMuhamad Hafifi AjwadNo ratings yet
- Tubular Flow Reactor ReportDocument19 pagesTubular Flow Reactor ReportN Afiqah Razak100% (1)
- Annex 31 Tool Design Extended AerationDocument5 pagesAnnex 31 Tool Design Extended AerationJong Dollente Jr.100% (1)
- Stirred Tank in Series ReportDocument20 pagesStirred Tank in Series ReportEmonbeifo EfosasereNo ratings yet
- Saint Louis University: Chemical Engineering PrinciplesDocument6 pagesSaint Louis University: Chemical Engineering PrinciplesAileen MayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document4 pagesChapter 7Jerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- NEM326 HW 1 PDFDocument2 pagesNEM326 HW 1 PDFyaprak dönerNo ratings yet
- FMA3601 Assignment 2 MemoDocument6 pagesFMA3601 Assignment 2 MemoDaniel MabengoNo ratings yet
- CT1 21'Document2 pagesCT1 21'KAMAL HAASANNo ratings yet
- Numerical For Practice MidtermDocument3 pagesNumerical For Practice MidtermSiddhant SinhaNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentDocument17 pagesTable of ContentOh DausNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Reactor InstrumentationDocument12 pagesNuclear Reactor InstrumentationRachit KanchanNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryDocument8 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryDhanush RagavNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument12 pagesLab ReportkaimanwatsoNNo ratings yet
- CH3080 Problem Set1to3 2014Document7 pagesCH3080 Problem Set1to3 2014iifNo ratings yet
- Lab CSTR in SeriesDocument13 pagesLab CSTR in SeriesKhairul Zakirin78% (9)
- Nem325 2019 HW7Document2 pagesNem325 2019 HW7MUSTAFA DOĞUKANNo ratings yet
- HW8 2nd2021Document1 pageHW8 2nd2021Natchapongchai KHANCHANNo ratings yet
- CCB 3062 Unit Operation Lab Ii Experiment 5: CSTR: TH RDDocument14 pagesCCB 3062 Unit Operation Lab Ii Experiment 5: CSTR: TH RDBhinitha ChandrasagaranNo ratings yet
- Design The Temperature Controller Application For Heat Transfer System in The LaboratoryDocument5 pagesDesign The Temperature Controller Application For Heat Transfer System in The LaboratoryDuy KhánhNo ratings yet
- TFR ExperimentDocument25 pagesTFR ExperimentSiti Norbaya100% (1)
- Chemical Reactors: DC DT RDocument8 pagesChemical Reactors: DC DT ROsas Jessica UwoghirenNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Document7 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)29viswa12No ratings yet
- Dynamic ProblemDocument3 pagesDynamic ProblemKavish RanaNo ratings yet
- Water Heater CalculationsDocument5 pagesWater Heater CalculationsNelson VargasNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems (Pumps Agitation)Document1 pagePractice Problems (Pumps Agitation)Lin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- CSTR in SeriesDocument17 pagesCSTR in SeriesDhiyyah MardhiyyahNo ratings yet
- Stirred Tank in Series ReportDocument20 pagesStirred Tank in Series ReportEmonbeifo EfosasereNo ratings yet
- All Problem Sets For The Second QuarterDocument5 pagesAll Problem Sets For The Second QuarterAlex GaskarthNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.0 TCE 5202 FB Control System With Large Dead Time 1Document28 pagesTopic 1.0 TCE 5202 FB Control System With Large Dead Time 1Prince EugoNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: InstructionsBhakti MahbubaniNo ratings yet
- TubularDocument15 pagesTubularSharing CaringNo ratings yet
- FM &HM Old PapersDocument4 pagesFM &HM Old Paperssai leenaNo ratings yet
- 9A23303 Fluid Flow in BioprocessesDocument4 pages9A23303 Fluid Flow in BioprocessessivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Michell Banki Turbine PDFDocument6 pagesMichell Banki Turbine PDFAnonymous Hy5Ir9QXNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.0 TCE 5202 FB Control System With Large Dead Time 1Document28 pagesTopic 1.0 TCE 5202 FB Control System With Large Dead Time 1Caleb HungweNo ratings yet
- Exp5 Teo ResultsanddiscussionDocument21 pagesExp5 Teo ResultsanddiscussionGökhan CesurNo ratings yet
- TFRDocument19 pagesTFRsueeumuraNo ratings yet
- 2 Marks Power Plant InstrumentationDocument18 pages2 Marks Power Plant InstrumentationVaishnavi SureshNo ratings yet
- Tubular Flow ReactorDocument21 pagesTubular Flow ReactorSabrinaNo ratings yet
- Lect 2 (Design Features)Document60 pagesLect 2 (Design Features)Ainun MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Effect of Residence Time On TDocument26 pagesLab Report Effect of Residence Time On TMuhammad IqmalNo ratings yet
- Rr212201 Prime Movers and Mechanical MeasurementsDocument8 pagesRr212201 Prime Movers and Mechanical MeasurementsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- ME Con-1 Mock-1Document15 pagesME Con-1 Mock-1vidya chakitwarNo ratings yet
- Fuel Rod - EfficiencyDocument5 pagesFuel Rod - EfficiencykabisekNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document1 pageAssignment 2ArkadebSenguptaNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document44 pagesCH 08kentalNo ratings yet
- Design SpecificationsDocument3 pagesDesign SpecificationsAfnan MazNo ratings yet
- Plug Flow ReactorDocument16 pagesPlug Flow ReactorN Afiqah RazakNo ratings yet
- Product Catalogue 1501743701030817Document1 pageProduct Catalogue 1501743701030817erode els erodeNo ratings yet
- Graduation ProjectDocument8 pagesGraduation ProjectAhmed AllamNo ratings yet
- ICTDBS502: Design A DatabaseDocument41 pagesICTDBS502: Design A DatabaseaarushNo ratings yet
- MCRP 3-32D.1 (Formerly MCWP 3-40.5) EW电子战 (2015 - 74页)Document74 pagesMCRP 3-32D.1 (Formerly MCWP 3-40.5) EW电子战 (2015 - 74页)wanjunNo ratings yet
- Eager Xperience 2014Document252 pagesEager Xperience 2014Fatma AhmedNo ratings yet
- 140037-PM Unit 3Document18 pages140037-PM Unit 3selvalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Unit 10Document11 pagesUnit 10Nguyễn Thị Thùy DươngNo ratings yet
- External Manager Selection and MonitoringDocument14 pagesExternal Manager Selection and MonitoringHadyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5: Flow Measurement Using Venturi Meter (Flow Through A Venturi Meter)Document6 pagesExperiment 5: Flow Measurement Using Venturi Meter (Flow Through A Venturi Meter)Cece SesNo ratings yet
- Xi'an Yuanqi Elevator Parts Co.,Ltd: Packing ListDocument1 pageXi'an Yuanqi Elevator Parts Co.,Ltd: Packing ListMesNo ratings yet
- Internal Secondary Data & AnalyticsDocument11 pagesInternal Secondary Data & AnalyticsRirip PiririNo ratings yet
- Electric Power's Seasons: Mihai Octavian POPESCU, Claudia Laurenta POPESCU, Catalina Alexandra SIMADocument6 pagesElectric Power's Seasons: Mihai Octavian POPESCU, Claudia Laurenta POPESCU, Catalina Alexandra SIMAFlorian NarcisNo ratings yet
- Pneumatic Developer ApkDocument5 pagesPneumatic Developer ApkSilvio ZelayaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Microsoft Intune Suite vs. Endpoint ManagerDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Microsoft Intune Suite vs. Endpoint ManagerRusty LironNo ratings yet
- Ap State Fibernet LimitedDocument17 pagesAp State Fibernet LimitedSai VenkyNo ratings yet
- Theory and Application of Trapdoor FunctionsDocument12 pagesTheory and Application of Trapdoor FunctionsPeilin XinNo ratings yet
- Algospeak Academic EssayDocument9 pagesAlgospeak Academic EssayJulieta RagnoNo ratings yet
- Improving Railway Switch System Reliability With Innovative Condition Monitoring AlgorithmsDocument10 pagesImproving Railway Switch System Reliability With Innovative Condition Monitoring AlgorithmsGenuslee MapedzeNo ratings yet
- ERP Evaluation ChecklistDocument4 pagesERP Evaluation ChecklistAmish DebNo ratings yet
- Trailerland: Price List April 2014Document4 pagesTrailerland: Price List April 2014nicehornetNo ratings yet
- FCCDocument9 pagesFCCWFTVNo ratings yet
- Business Opportunities For Women in A Changing Energy Value ChainDocument51 pagesBusiness Opportunities For Women in A Changing Energy Value ChainAtieNo ratings yet
- Ankit Patel ResumeDocument1 pageAnkit Patel ResumeAnkitkumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Ebook Mastering Stm32 A Step by Step Guide To The Most Complete Arm Cortex M Platform Using The Official Stm32Cube Development Environment 2Nd Edition Carmine Noviello Online PDF All ChapterDocument63 pagesEbook Mastering Stm32 A Step by Step Guide To The Most Complete Arm Cortex M Platform Using The Official Stm32Cube Development Environment 2Nd Edition Carmine Noviello Online PDF All Chaptervictoria.clinch124100% (2)
- SamplesDocument4 pagesSamplesMadhuKumarNo ratings yet
- Netscaler: The World'S Most Advanced Cloud Network PlatformDocument24 pagesNetscaler: The World'S Most Advanced Cloud Network PlatformMujahid PashaNo ratings yet
- Decorative Handles ReferenceDocument32 pagesDecorative Handles ReferenceMarnie B. GutibNo ratings yet
- Ebook Engineering Mathematics For Semesters Iii and Iv PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Engineering Mathematics For Semesters Iii and Iv PDF Full Chapter PDFmichael.dye870100% (30)