Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Elective Reviewer
Uploaded by
tiukristiannicolasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Elective Reviewer
Uploaded by
tiukristiannicolasCopyright:
Available Formats
ELECTIVE 1 ELECTIVE
1
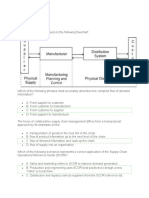
What are the functions of
‘supply chain’ as illustrated in
the presentation?
Why shipping is very important
in world economy, trade, and
Demand and supply
transport?
planning
Transportation and
- Shipping is crucial
Distribution
because it moves goods
Costumer and order
around the world
management
efficiency and making
Manufacturing and
global trade possible.
operations
Sourcing and supplier
management
MP & L is an important part of
international trade.
What is port management and
Logistics?
Port’s efficiency is measured in
- It is the process of
terms of: TIME, SAFETY, and
managing the movement
VALUE FOR MONEY.
of goods and services
from one place to
another.
Port’s efficiency is crucial to
ensure the Safe, Secure,
Productive, and Ecofriendly
MP & involves the planning,
practices of marine operations.
implementation, and control of
the flow of goods and services
from the point of origin to the point
of consumption.
GABLINO, RYAN B. BSMT ll-DELTA GABLINORAY
ELECTIVE 1 ELECTIVE
1
How much (in percentage) of
world trade being
transported by ships?
Name the major channels that - 90%
are very important in world
Economy, Trade, Carriage, &
Transport. Why these channels
were important? What is Port?
- Facilities that are used
- PANAMA CANAL and for loading and unloading
SUEZ CANAL are both ships by taking into
vital because they account that involve
provide shorter routes for financial and resources
ships, saving time and conditions.
money. They connect
oceans, facilitating global
trade. Port Managers?
- Port managers are
responsible for ensuring
Name the type of terminals that ports are operating
shown in the slide. What type efficiently and effectively,
of cargo/goods/materials each and that they are meeting
of them were dedicated to the needs of their
receive? customers.
Container Port Logistics
- Container - Involves the
management of the flow
Bulk of goods and services
- Coals from one place to
another.
Oil Port
- LNG and LPG
Supply chain
GABLINO, RYAN B. BSMT ll-DELTA GABLINORAY
ELECTIVE 1 ELECTIVE
1
- All the functions - Port operations refer to a
within/outside the series of maritime procedures
company that enable the aimed to ensure the smooth
value chain to make transition of vessels and their
products. containers from one terminal to
another. Sea travel can be
undertaken through many different
means, with each type of vessel
having its own specifications.
Who carries out port
operations?
- There are two groups of
participants that control and carry
out the main port operations:
A port authority
- is an entity that can
make policy at a port
on behalf of the
government or local
public agencies.
What Are Port Operations?
GABLINO, RYAN B. BSMT ll-DELTA GABLINORAY
ELECTIVE 1 ELECTIVE
1
• Packaging
• Monitoring
1. Order Placing
- A logistics company must
complete order
processing. Order
processing is the first
step in logistics. This may
fall under the purview of
the company’s
commercial department.
2. Materials Handling
- Material handling is the
act or process of moving
goods around a
warehouse. This involves
managing inventory so
that orders can be
fulfilled quickly and
accurately.
Seven elements of logistics are:
• Order Placing
• Materials Handling
3. Warehousing
• Warehousing
- Take LG and Samsung as an
• Inventory Management example. These are long-lasting
consumer companies with a
• Transport
worldwide presence. Although their
GABLINO, RYAN B. BSMT ll-DELTA GABLINORAY
ELECTIVE 1 ELECTIVE
1
products are located in one place, - The packaging found in
their distribution is worldwide. supermarkets and hypermarkets is
divided into two types. One is the
Warehousing is an important
one customer see on the shelf. It
Logistics activity that has a
appeals to them and makes them
significant impact. The warehouse
want to buy the package. The
must be located near the distributor
second type is transport packaging.
or retailer to deliver goods quickly. A
branded product may take longer to
arrive than a product with a similar
name. 7. Monitoring
- Logistics companies must
keep track of inventory management,
4. Inventory Management transportation, warehousing, and
other information.
- One of the most important
functions of a logistics business is
inventory management. It is about
managing sufficient inventory to
satisfy client demand while keeping
the cost of carrying goods minimum.
5. Transport
- The logistics company’s
most important activity is
transportation. It is also one of the
most resource-intensive and
revenue-generating logistics
segments. One reason transportation
is so expensive is fuel.
6. Packaging
GABLINO, RYAN B. BSMT ll-DELTA GABLINORAY
ELECTIVE 1 ELECTIVE
1
Different Types of Logistics outsourcing of logistics
Management: management activities.
Third-party logistics
management
Inbound Logistics - can involve outsourcing
Management inbound or outbound logistic
- Inbound logistics activities. Supply Management
management refers to the Logistics Management This involves
logistics activities that are the planning, procuring and
necessary to transport materials, coordinating materials that are
equipment and machinery from needed at a certain time at a
a supplier to a production particular place for the production of
facility. a task.
Production Logistics and
Management Distribution Logistics
- Production logistics Management
management manages the
transportation of goods during - This takes stored materials
the production process. This and transports them to where they
involves the staging of materials need to go. The issues in this
from production warehouses to involve moving materials;
the production line at the right including loading, unloading and
time to streamline the production transportation, as well as keeping
process. track of the stock and how it’s
used.
Outbound Logistics
Management Customer Service Logistics
- Outbound logistics Management
management is the opposite of
inbound logistics. It involves the - Customer service logistics
transportation of goods from the management consists of
production or distribution center ensuring products are delivered
to the final customer. Third- on time and damage-free to
Party Logistics Management ensure customer satisfaction.
Third-party logistics
management refers to the
GABLINO, RYAN B. BSMT ll-DELTA GABLINORAY
ELECTIVE 1 ELECTIVE
1
Reverse Logistics
Management
- This is about the management
of reclaiming materials and supplies
from the customer back to
production.
GABLINO, RYAN B. BSMT ll-DELTA GABLINORAY
ELECTIVE 1 ELECTIVE
1
Port Operations and
Services: This includes the
management of port facilities,
cargo handling, and vessel
traffic. It also involves the
provision of services such as
pilotage, towage, and mooring.
Port Planning and
Development: This involves
the planning and development
of port facilities to meet the
needs of the shipping industry.
It includes the design of port
infrastructure, the development
of port policies, and the
management of environmental
issues.
Supply Chain
Management: This involves
the management of the supply
chain from raw materials to
finished products. It includes
the management of
procurement, production,
transportation, and distribution.
Elements of Port Management:
GABLINO, RYAN B. BSMT ll-DELTA GABLINORAY
ELECTIVE 1 ELECTIVE
1
Logistics and Distribution
Management: This involves Port Economics and
the management of logistics
Finance: This involves the
operations, including inventory
management of financial
management, warehousing,
resources, including budgeting,
transportation planning, and
accounting, and financial
distribution.
analysis. It also includes the
management of economic
issues such as pricing, tariffs,
and competition.
Intermodal Transportation:
This involves the management
of transportation systems that Maritime Law and
use multiple modes of Regulations: This involves
transportation. It includes the the management of legal
management of rail, road, air, issues related to shipping and
and sea transportation port operations. It includes the
systems. management of international
maritime law, national maritime
law, and local regulations.
Environmental Issues in
Port Management: This
involves the management of
environmental issues related to
Shipping and Freight
port operations. It includes the
management of air pollution, Forwarding: This involves
water pollution, waste disposal, the management of shipping
and environmental regulations. operations, including cargo
transportation, freight
forwarding, and logistics.
GABLINO, RYAN B. BSMT ll-DELTA GABLINORAY
ELECTIVE 1 ELECTIVE
1
GABLINO, RYAN B. BSMT ll-DELTA GABLINORAY
You might also like
- Integrated Logistics Support Handbook Mcgraw Hill Logistics Series Ebook PDF VersionDocument62 pagesIntegrated Logistics Support Handbook Mcgraw Hill Logistics Series Ebook PDF Versionteresa.vanhorn90798% (45)
- Logistics Process of Coca ColaDocument4 pagesLogistics Process of Coca ColaMajoy Mendoza67% (18)
- Analysis of Marketing Mix of FedEx CorpoDocument11 pagesAnalysis of Marketing Mix of FedEx CorpoLorik H GashiNo ratings yet
- Shipchain WhitepaperDocument29 pagesShipchain Whitepapera11914212No ratings yet
- Chap 1. Characteristics of Transport OperationsDocument59 pagesChap 1. Characteristics of Transport OperationsAina GhafarNo ratings yet
- CBBC Digital China Webinar With DP World - Digital Technology Impact On The Supply Chain Industry - Thursday 28 May 2020Document23 pagesCBBC Digital China Webinar With DP World - Digital Technology Impact On The Supply Chain Industry - Thursday 28 May 2020VaqenNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Resume - Dewa Gede Sidan Magna Dinata - 04211840000011Document17 pagesAsynchronous Resume - Dewa Gede Sidan Magna Dinata - 04211840000011Sidan MagnaNo ratings yet
- Port Competition Revisited: Hilde Meersman, Eddy Van de Voorde & Thierry VanelslanderDocument23 pagesPort Competition Revisited: Hilde Meersman, Eddy Van de Voorde & Thierry VanelslanderPhileas FoggNo ratings yet
- UNCTAD 1995 Strategi Port PricingDocument26 pagesUNCTAD 1995 Strategi Port PricingJon NomadenNo ratings yet
- Green Shipping Corridor GSC Presentation V23 082123 ENG CompressedDocument21 pagesGreen Shipping Corridor GSC Presentation V23 082123 ENG CompressedQian XinzhouNo ratings yet
- Ship Project Autonomous ShipsDocument23 pagesShip Project Autonomous ShipsMohammed EhabNo ratings yet
- Contemporary PortsDocument24 pagesContemporary PortsknowsieybearNo ratings yet
- Role of Ports in The 21st CenturyDocument47 pagesRole of Ports in The 21st CenturyknowsieybearNo ratings yet
- 1 Logistics IntroductionDocument14 pages1 Logistics IntroductionMinivensNo ratings yet
- VAT Guideline Sea Land AirDocument24 pagesVAT Guideline Sea Land AiraliNo ratings yet
- Optimising The Operational Front LineDocument18 pagesOptimising The Operational Front LineJose Mendelle Murry TombadoNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - Ports Carrier - Final To SV by PLDungDocument28 pagesTopic 3 - Ports Carrier - Final To SV by PLDungPhạm Phương ThảoNo ratings yet
- C1mem42019 10 Williams-RichardsDocument26 pagesC1mem42019 10 Williams-RichardsKacper KonopaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.1 Introduction To Distribution ManagementDocument25 pagesChapter 1.1 Introduction To Distribution Management有川静寂No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Physical Flow of LogisticsDocument70 pagesChapter 2 Physical Flow of LogisticsEly GragasinNo ratings yet
- GLobal Trade Magazine June 2021Document14 pagesGLobal Trade Magazine June 2021AditNo ratings yet
- Daniel Alejandro Baena Piña Port Management Final Exam MAY-2020Document6 pagesDaniel Alejandro Baena Piña Port Management Final Exam MAY-2020Brayan Javier Castro CedeñoNo ratings yet
- 14 Chapter 7Document45 pages14 Chapter 7SanjayNo ratings yet
- BST Class 11 (Transportation)Document7 pagesBST Class 11 (Transportation)saleha100% (1)
- TestDocument4 pagesTestsalmanqurashiNo ratings yet
- Dual Degree Program: International Freight and InsuranceDocument5 pagesDual Degree Program: International Freight and InsuranceDiego Ninanya VelardeNo ratings yet
- Globallogistics 141230113412 Conversion Gate02 PDFDocument20 pagesGloballogistics 141230113412 Conversion Gate02 PDF邹冉No ratings yet
- Lloyds Port Operations Brochure LRDocument4 pagesLloyds Port Operations Brochure LRAna Angélica Netto BorgoNo ratings yet
- Freight Rates Mand Maritime TransprtDocument18 pagesFreight Rates Mand Maritime Transprtritxi88No ratings yet
- Lessons PracticesDocument12 pagesLessons PracticesyrperdanaNo ratings yet
- Role of Private Off Dock Terminals On Port EfficiencyDocument11 pagesRole of Private Off Dock Terminals On Port EfficiencyRyan MinaNo ratings yet
- The Role of Private Off Dock Terminals On Port Efficiency (A Study of Sifax Off Dock Nig, LTD.)Document11 pagesThe Role of Private Off Dock Terminals On Port Efficiency (A Study of Sifax Off Dock Nig, LTD.)IJEMR JournalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Port Management ModelDocument21 pagesChapter 4 Port Management ModelChíi KiệttNo ratings yet
- Measuring The Impact of Trde Facilitation Refom - WORLD BANK GROUP Methodologies and IndicatorsDocument23 pagesMeasuring The Impact of Trde Facilitation Refom - WORLD BANK GROUP Methodologies and IndicatorshanyimwdmNo ratings yet
- Unit-5 (Global Logisitcs) L&SCMDocument20 pagesUnit-5 (Global Logisitcs) L&SCMAalok GhoshNo ratings yet
- Temu 01 - Freight ShippingDocument34 pagesTemu 01 - Freight ShippingMelli NiaNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - L.M in Port TerminalsDocument80 pagesUnit 7 - L.M in Port TerminalsNyoka DunnNo ratings yet
- Aa19 Evi7 EnglishDocument4 pagesAa19 Evi7 EnglishJame PiñeresNo ratings yet
- Ia - UniAndes - Intro To FreightDocument10 pagesIa - UniAndes - Intro To FreightPaula BetancourtNo ratings yet
- Managing Maritime Infrastructure: Lessons From UAE and ChinaDocument18 pagesManaging Maritime Infrastructure: Lessons From UAE and ChinaKantaJupolaNo ratings yet
- Shipping Business and Loss PreventionDocument34 pagesShipping Business and Loss PreventionCalisto Moon100% (1)
- Aleksandra BartosiewiczDocument10 pagesAleksandra BartosiewiczRiza DwiNo ratings yet
- Ch7 - Port Centric ICT SystemDocument29 pagesCh7 - Port Centric ICT SystemPhương Linh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Manuchar Bangladesh Ltd.Document14 pagesManuchar Bangladesh Ltd.SagarNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Logistics 2015Document8 pagesA Brief Introduction To Logistics 2015Hui Sin PangNo ratings yet
- Factors Behind The Development of Transport SystemsDocument12 pagesFactors Behind The Development of Transport SystemsJindalNo ratings yet
- Sustainable and Resilient Maritime Supply Chains - Apr22 - ditc-ted-06042022-Oceans4-IssaDocument15 pagesSustainable and Resilient Maritime Supply Chains - Apr22 - ditc-ted-06042022-Oceans4-IssaLean ZechNo ratings yet
- Port Development 1Document12 pagesPort Development 1Risma Karindina Syafa100% (1)
- Session Two Function of Shipping - Port - ShipyardDocument19 pagesSession Two Function of Shipping - Port - ShipyardBagusPrambudiNo ratings yet
- Dr. Funda Yercan, Professor: Piri Reis University Dean, Maritime FacultyDocument16 pagesDr. Funda Yercan, Professor: Piri Reis University Dean, Maritime FacultyCagatay alpNo ratings yet
- Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and TechnologyDocument6 pagesJomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and TechnologyBruse OluochNo ratings yet
- Careers in Logistics: What Is Logistics About?Document8 pagesCareers in Logistics: What Is Logistics About?Cidália FonsecaNo ratings yet
- TransportationDocument38 pagesTransportationkkv_phani_varma5396100% (2)
- Poster 1Document2 pagesPoster 1Milan ShahNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Port Logistics and Global Logistics PerformanceDocument6 pagesThe Relationship Between Port Logistics and Global Logistics PerformanceMego PlamoniaNo ratings yet
- Imroving Performance in Port AuthoritiesDocument41 pagesImroving Performance in Port AuthoritiesmrccahmedNo ratings yet
- Cranes With Brains: Euromax - The Modern Automatic Container TerminalDocument4 pagesCranes With Brains: Euromax - The Modern Automatic Container TerminalElafanNo ratings yet
- 31 07 2019 14 34 36officer Marine OperationsDocument2 pages31 07 2019 14 34 36officer Marine Operationsashish kumar singhNo ratings yet
- Customs Broker Freight ForwarderDocument1 pageCustoms Broker Freight ForwarderMaden FranciscoNo ratings yet
- 3 - Role of Transportation in Supply ChainDocument33 pages3 - Role of Transportation in Supply ChainHassan MansoorNo ratings yet
- Efficiency Assessment of Off-Dock Container Terminals at Tema Port Using Data Envelopment Analysis (Dea)Document12 pagesEfficiency Assessment of Off-Dock Container Terminals at Tema Port Using Data Envelopment Analysis (Dea)Novelty JournalsNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT IN VRL LOGISTICS LTD VARURDocument90 pagesA Project Report On LOGISTICS MANAGEMENT IN VRL LOGISTICS LTD VARURSamraizTejaniNo ratings yet
- Effects of Modular Class To The Students of Brgy. Sagkahan Carigra, Leyte (PR Group-1)Document21 pagesEffects of Modular Class To The Students of Brgy. Sagkahan Carigra, Leyte (PR Group-1)tiukristiannicolasNo ratings yet
- Activity On Mental HealthDocument2 pagesActivity On Mental HealthtiukristiannicolasNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument1 pageLettertiukristiannicolasNo ratings yet
- SCRIPTDocument4 pagesSCRIPTtiukristiannicolasNo ratings yet
- Suez Canal Obstruction A Case Study About Ever Given IncidentDocument8 pagesSuez Canal Obstruction A Case Study About Ever Given IncidenttiukristiannicolasNo ratings yet
- KMTCNBO6582712F24Document1 pageKMTCNBO6582712F24ahakeem568No ratings yet
- Customer Service ConversationDocument1 pageCustomer Service ConversationAri IlyaszNo ratings yet
- Logistics Officer: Job DescriptionDocument3 pagesLogistics Officer: Job DescriptionAbdala Eda'oNo ratings yet
- Mindmap Supply Chain Network Redesign Chainalytics 2020Document1 pageMindmap Supply Chain Network Redesign Chainalytics 2020Ngoc PhamNo ratings yet
- Third Party Logistics Company in Delhi-NCRDocument3 pagesThird Party Logistics Company in Delhi-NCRGurjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- HANS WORLD LOGISTICS Company Profile (EN)Document29 pagesHANS WORLD LOGISTICS Company Profile (EN)AndrianoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Logistics Systems Management - (6.1 Introduction)Document8 pagesIntroduction To Logistics Systems Management - (6.1 Introduction)BSNo ratings yet
- Sample Assignment 1-1Document20 pagesSample Assignment 1-1Nir IslamNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Third Party Logistics PerformanceDocument24 pagesAnalysis of Third Party Logistics PerformanceYasmine MohamedNo ratings yet
- Key Performance Indicators in Humanitarian LogisticsDocument88 pagesKey Performance Indicators in Humanitarian LogisticsIntan Puspa WNo ratings yet
- ME 328 Manufacturing EngineeringDocument47 pagesME 328 Manufacturing EngineeringZeynep BoranNo ratings yet
- List of Forwarding AgentDocument9 pagesList of Forwarding AgentAris NurohmanNo ratings yet
- Background or History of 2GO and Asian TerminalsDocument2 pagesBackground or History of 2GO and Asian TerminalsAndrea Angelica Dumo GalvezNo ratings yet
- 20DM021 - Alvin Subash - SIP Report SafexpressDocument72 pages20DM021 - Alvin Subash - SIP Report Safexpresshyper squirrelNo ratings yet
- UK and International Services: Tariff GuideDocument27 pagesUK and International Services: Tariff GuideDani DaniNo ratings yet
- Maritime Logistics A Guide To Contemporary Shipping and Port Management (251-300)Document50 pagesMaritime Logistics A Guide To Contemporary Shipping and Port Management (251-300)ZaNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan 1 - SCM - SDL - Genap - 19 - 20 - Lec1Document22 pagesPertemuan 1 - SCM - SDL - Genap - 19 - 20 - Lec1DivaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain Management - SyllabusDocument5 pagesSupply Chain Management - SyllabusKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- SHAZ22662700 电放 PDFDocument2 pagesSHAZ22662700 电放 PDFJay Arnel FloresNo ratings yet
- Management Report On Pizzahut With Respect To TheirDocument14 pagesManagement Report On Pizzahut With Respect To TheirSakshi KapoorNo ratings yet
- Eucomed Guidance On Revised Good Distribution PracticeDocument17 pagesEucomed Guidance On Revised Good Distribution Practicediego calamanteNo ratings yet
- Arrastre and Stevedoer Difference and DistinctionDocument2 pagesArrastre and Stevedoer Difference and DistinctionMarkyHeroiaNo ratings yet
- Logistics and TransportionDocument22 pagesLogistics and TransportionLableh ArpyahNo ratings yet
- Afjrotc Ga-932 LogisticsDocument13 pagesAfjrotc Ga-932 Logisticsapi-619531708No ratings yet
- JBLDocument42 pagesJBLApparna BalajiNo ratings yet
- Câu Hỏi Trắc No Đi Thi ScraceDocument70 pagesCâu Hỏi Trắc No Đi Thi ScraceHoàng VũNo ratings yet
- Combined Transport Bill of Lading: Lady of Luck V.143NDocument1 pageCombined Transport Bill of Lading: Lady of Luck V.143NRaja GuntarNo ratings yet