Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Histogram
Histogram
Uploaded by
PRASAD SATAVCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Histogram
Histogram
Uploaded by
PRASAD SATAVCopyright:
Available Formats
Histogram
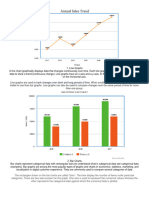
A histogram is used to summarize discrete or continuous data. In other words, it provides
a visual interpretation of numerical data by showing the number of data points that fall within
a specified range of values (called “bins”). It is similar to a vertical bar graph. However, a
histogram, unlike a vertical bar graph, shows no gaps between the bars.
Parts of a Histogram
1. The title: The title describes the information included in the histogram.
2. X-axis: The X-axis are intervals that show the scale of values which the measurements
fall under.
3. Y-axis: The Y-axis shows the number of times that the values occurred within the
intervals set by the X-axis.
4. The bars: The height of the bar shows the number of times that the values occurred
within the interval, while the width of the bar shows the interval that is covered. For a
histogram with equal bins, the width should be the same across all bars.
Importance of a Histogram
Creating a histogram provides a visual representation of data distribution. Histograms can
display a large amount of data and the frequency of the data values. The median and
distribution of the data can be determined by a histogram. In addition, it can show any outliers
or gaps in the data.
Distributions of a Histogram
A normal distribution: In a normal distribution, points on one side of the average are as
likely to occur as on the other side of the average.
A bimodal distribution: In a bimodal distribution, there are two peaks. In a bimodal
distribution, the data should be separated and analyzed as separate normal distributions.
A right-skewed distribution: A right-skewed distribution is also called a positively skewed
distribution. In a right-skewed distribution, a large number of data values occur on the left
side with a fewer number of data values on the right side. A right-skewed distribution usually
occurs when the data has a range boundary on the left-hand side of the histogram. For
example, a boundary of 0.
A left-skewed distribution: A left-skewed distribution is also called a negatively skewed
distribution. In a left-skewed distribution, a large number of data values occur on the right
side with a fewer number of data values on the left side. A right-skewed distribution usually
occurs when the data has a range boundary on the right-hand side of the histogram. For
example, a boundary such as 100.
A random distribution: A random distribution lacks an apparent pattern and has several
peaks. In a random distribution histogram, it can be the case that different data properties
were combined. Therefore, the data should be separated and analyzed separately.
You might also like
- HistogramDocument10 pagesHistogramSrikirupa V MuralyNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 2023Document31 pagesTopic 5 2023amerahmedkhanNo ratings yet
- Picturing Distributions With GraphsDocument21 pagesPicturing Distributions With GraphsFernan CaboteNo ratings yet
- Histogram CanvaDocument30 pagesHistogram CanvaMaureen AlmazarNo ratings yet
- Graphical PresentationDocument6 pagesGraphical PresentationHarsh ThakurNo ratings yet
- Types of GraphDocument3 pagesTypes of Graphpcjohn computershopNo ratings yet
- MAPC006Document12 pagesMAPC0068158Anshika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Kinds of Graphs: Frequency Tells You How Often Something Happened. The Frequency of An Observation TellsDocument5 pagesKinds of Graphs: Frequency Tells You How Often Something Happened. The Frequency of An Observation Tellsmickyist the greatNo ratings yet
- Bio StatisticsDocument7 pagesBio StatisticsBaloch Mubin tvNo ratings yet
- Histogram & Box PlotDocument6 pagesHistogram & Box PlotAre MeerNo ratings yet
- DM015SM P-IDocument15 pagesDM015SM P-IAnanya TyagiNo ratings yet
- How To Use Histograms ModifiedDocument4 pagesHow To Use Histograms ModifiedMunawar ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Displaying Quantitative DataDocument27 pagesChapter 4: Displaying Quantitative DatagagakakaNo ratings yet
- Written Report HistogramDocument9 pagesWritten Report HistogramMaureen AlmazarNo ratings yet
- Statistics (Part 1)Document15 pagesStatistics (Part 1)ABRIANNA HARRISNo ratings yet
- Engineering Data AnalysisDocument12 pagesEngineering Data AnalysisDeniell Kahlil Kyro GabonNo ratings yet
- 05 Handout 1Document13 pages05 Handout 1raulNo ratings yet
- Terms 2Document11 pagesTerms 2jlayambotNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Descriptive Statistics I: Sanju Rusara Seneviratne MbpssDocument35 pagesIntroduction To Descriptive Statistics I: Sanju Rusara Seneviratne MbpssVincent Raj KumarNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Mathematics Module 2 PDFDocument13 pagesQuantitative Mathematics Module 2 PDFyelzNo ratings yet
- 1 Collecting and Interpreting Data Edexcel PDFDocument3 pages1 Collecting and Interpreting Data Edexcel PDFRaunak PrasadNo ratings yet
- Graphical PresentationDocument6 pagesGraphical PresentationAtiqah RazifNo ratings yet
- Histograms: Construction, Analysis and Understanding: What Is A Histogram?Document3 pagesHistograms: Construction, Analysis and Understanding: What Is A Histogram?nixen99_gellaNo ratings yet
- Descriptive StatisticsDocument21 pagesDescriptive Statistics21010324029No ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Summarizing Data - Charts and TablesDocument33 pagesUnit 2 - Summarizing Data - Charts and Tablesjemima100% (1)
- HistogramDocument6 pagesHistogramlapNo ratings yet
- Data Visualization & Data Exploration - Unit IIDocument26 pagesData Visualization & Data Exploration - Unit IIpurusingh23No ratings yet
- HistogramDocument34 pagesHistogramመለክ ሓራNo ratings yet
- VisualizationDocument27 pagesVisualizationsbapoorvaa1No ratings yet
- Bar Charts NOTESDocument8 pagesBar Charts NOTESlastnotes84No ratings yet
- 09 HistogramDocument50 pages09 HistogramLikhith Kumar C MNo ratings yet
- Graphical Representation OF Statistical DataDocument21 pagesGraphical Representation OF Statistical Datarmconvidhya sri2015No ratings yet
- GraphDocument18 pagesGraphBahauddin BalochNo ratings yet
- Quantatitive Data AnalysisDocument37 pagesQuantatitive Data AnalysisAinurNo ratings yet
- Distribution of A Single VariableDocument14 pagesDistribution of A Single VariableAshish kumar ThapaNo ratings yet
- Image Histogram: Unveiling Visual Insights, Exploring the Depths of Image Histograms in Computer VisionFrom EverandImage Histogram: Unveiling Visual Insights, Exploring the Depths of Image Histograms in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- 1 What Do You Mean by Measures of Central Tendency? Explain The Measures of Central Tendency. ANSDocument5 pages1 What Do You Mean by Measures of Central Tendency? Explain The Measures of Central Tendency. ANSAnonymous DfZxg1NZudNo ratings yet
- I. About Graphs: What Is A Graph?Document29 pagesI. About Graphs: What Is A Graph?Mae DinDinNo ratings yet
- Skewness Kurtosis and HistogramDocument4 pagesSkewness Kurtosis and HistogramAdamu MadiNo ratings yet
- Bar ChartDocument4 pagesBar Chartamelia99No ratings yet
- Foundation Notes 2013Document25 pagesFoundation Notes 2013Anonymous wXV066fANo ratings yet
- Multivariate Analysis: Descriptive Statistics Is The Discipline of Quantitatively Describing The Main Features of ADocument5 pagesMultivariate Analysis: Descriptive Statistics Is The Discipline of Quantitatively Describing The Main Features of AMegumi FujiNo ratings yet
- Eda01 (Assgmt2)Document4 pagesEda01 (Assgmt2)aljonNo ratings yet
- DemographyDocument4 pagesDemographyHannah aswiniNo ratings yet
- Types of GraphsDocument29 pagesTypes of GraphsParamita KaranNo ratings yet
- Subhashree.SDocument2 pagesSubhashree.SSubhashree.S IT 2018No ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chapter 2 Notes - StatisticsDocument4 pagesUnit 2 Chapter 2 Notes - StatisticsVhuhwavhoNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument4 pagesMeasures of Central TendencydeepikaajhaNo ratings yet
- Case VariableDocument4 pagesCase VariableneethiNo ratings yet
- Question No. 01:: Definition of Graphs. 1. Line GraphDocument13 pagesQuestion No. 01:: Definition of Graphs. 1. Line GraphŚađia ÃbbašîNo ratings yet
- Types of Graphs Used in Math and StatisticsDocument14 pagesTypes of Graphs Used in Math and StatisticsElmalyn Bernarte0% (1)
- Please Download and Read The PDF Below.: 2. Explain The Various Data Presentation Techniques!Document3 pagesPlease Download and Read The PDF Below.: 2. Explain The Various Data Presentation Techniques!MASELIA ADINDA PUTRINo ratings yet
- DataDocument10 pagesDataAnindita GhoseNo ratings yet
- Cofactor StatisticsDocument27 pagesCofactor StatisticsAdam100% (1)
- Statistics - Docx Unit 1Document9 pagesStatistics - Docx Unit 1Muthukumar V P CS&CANo ratings yet
- Research Unit 5 BbaDocument17 pagesResearch Unit 5 Bbayash soniNo ratings yet
- 1 Descriptive Statistics - UnlockedDocument18 pages1 Descriptive Statistics - UnlockedNidaOkuyazTüregünNo ratings yet
- Shape of Data Skewness and KurtosisDocument6 pagesShape of Data Skewness and KurtosisGovind TrivediNo ratings yet
- Engdata Module 1Document4 pagesEngdata Module 1Crisalyn BacaniNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning - A Complete Exploration of Highly Advanced Machine Learning Concepts, Best Practices and Techniques: 4From EverandMachine Learning - A Complete Exploration of Highly Advanced Machine Learning Concepts, Best Practices and Techniques: 4No ratings yet
- Cybermind 3Document8 pagesCybermind 3Adam FredrikssonNo ratings yet
- Raising Succesfull Children: Pre-Listening ExerciseDocument5 pagesRaising Succesfull Children: Pre-Listening ExerciseAndrea SzigetfalviNo ratings yet
- Specifications YCL 15 To 50 Ton ChillersDocument4 pagesSpecifications YCL 15 To 50 Ton ChillersEdgar MoyaoNo ratings yet
- Dredgepack - Preparation.2022Document60 pagesDredgepack - Preparation.2022Juan Eduardo SchebelaNo ratings yet
- Ili RiverDocument4 pagesIli RiverRathiJyothiNo ratings yet
- Building Fonts For WriteScadDocument16 pagesBuilding Fonts For WriteScadKale SmithNo ratings yet
- GasTIPS Winter04 PDFDocument36 pagesGasTIPS Winter04 PDFmelvincabeNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestDocument20 pagesQualitative Tests For Carbohydrates: 1) Molisch TestFRANCEEN LEANNA KATIGBAKNo ratings yet
- Using Instrumentino v02Document10 pagesUsing Instrumentino v02Fernando CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Syahbudin - Complicated Perianal FistelDocument22 pagesDr. Syahbudin - Complicated Perianal FistelBlack DroneNo ratings yet
- 400 Bad Request 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.9Document16 pages400 Bad Request 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.9thepraetorionNo ratings yet
- Apricot Kernel Shell MSDSDocument3 pagesApricot Kernel Shell MSDSdesi AdelinaNo ratings yet
- Mobile Phone CloningDocument1 pageMobile Phone Cloningsaideep JadalaNo ratings yet
- Sciencedirect: Fabian Dillinger, Olivia Bernhard, Gunther Reinhart Fabian Dillinger, Olivia Bernhard, Gunther ReinhartDocument6 pagesSciencedirect: Fabian Dillinger, Olivia Bernhard, Gunther Reinhart Fabian Dillinger, Olivia Bernhard, Gunther ReinhartAnita SetyastutiNo ratings yet
- Practice Exercises CAEDocument2 pagesPractice Exercises CAENiya PreldjichNo ratings yet
- PDS-Mosalinker PC30 (V1.0) enDocument2 pagesPDS-Mosalinker PC30 (V1.0) enLIM YE HENGNo ratings yet
- Internal FlowDocument6 pagesInternal FlowdenisarissetiajiNo ratings yet
- The Act of Proclamation of The Independence of The Filipino PeopleDocument33 pagesThe Act of Proclamation of The Independence of The Filipino PeopleJULIANA RAE CONTRERASNo ratings yet
- Philosophy NotesDocument6 pagesPhilosophy NotesRishi Raj MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- OCD - Key Facts"Document3 pagesOCD - Key Facts"Santosh ParabNo ratings yet
- Albumin (Human) 20%, USPPlasbumin®-20Document8 pagesAlbumin (Human) 20%, USPPlasbumin®-20Marfu'ah Mar'ahNo ratings yet
- Science (Reproductive System) Grade 6Document4 pagesScience (Reproductive System) Grade 6Nurwulan Yuni HapsariNo ratings yet
- Septone Brake Dust Cleaner SDSDocument15 pagesSeptone Brake Dust Cleaner SDSMarkSomniumNo ratings yet
- 3D Multizone Scaling Method of An NC Program For Sole Mould ManufacturingDocument5 pages3D Multizone Scaling Method of An NC Program For Sole Mould ManufacturingrajrythmsNo ratings yet
- How Old Is The Man Who Wrote The Letter?Document4 pagesHow Old Is The Man Who Wrote The Letter?Solis GerardoNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument2 pagesSamplingMerleAngeliM.SantosNo ratings yet
- Gillvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv PDFDocument45 pagesGillvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv PDFIsraa EzzetNo ratings yet
- Á1111Ñ Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products: Acceptance Criteria For Pharmaceutical Preparations and Substances For Pharmaceutical UseDocument2 pagesÁ1111Ñ Microbiological Examination of Nonsterile Products: Acceptance Criteria For Pharmaceutical Preparations and Substances For Pharmaceutical UseDr usama El ShafeyNo ratings yet
- Smart Eco City PPT Presentations 1Document17 pagesSmart Eco City PPT Presentations 1welvye 1No ratings yet
- Supporting Decisions and ProcessesDocument32 pagesSupporting Decisions and ProcessestoysdreatNo ratings yet