Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Forensic Ballistics Chapter 6
Forensic Ballistics Chapter 6
Uploaded by
Gladys OconOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Forensic Ballistics Chapter 6
Forensic Ballistics Chapter 6
Uploaded by
Gladys OconCopyright:
Available Formats
69
FORENSIC BALLISTICS
Chapter 6
Cartridge Case
Definition
Cartridge Case - is the metallic or non-metallic tabular con-tainer usually
made of brass (70% copper and 30%zinc); it is de-signed to unite the bullet,
primer and the gunpowder into one unit.It is also known as a shell or casing:
Traditionally, a cartridge case is made of brass although there
are many present day cartridges that are made of plastic, var-nish
steel, zinc-coated or even chemically coated are t use.
Functions of the Cartridge Case
1. It properly locates the bullet relative to the bore of the fire-arm.
2. It is used to carry the means of igniuon.
3. It provides gas seals at the preech against an unwanted escape of
propellant gas upon firing.
4. Serves as the waterproof container for the propellant or powder
charge.
5. Acts as the insulator between the propellant and the hot walls of
the chamber in a rapid firing of firearms.
CHAPTER 6: CARTRIDGE CASE
70
FORENSIC BALLISTICS
Figure 44. Various Types of
Cartridge Cases
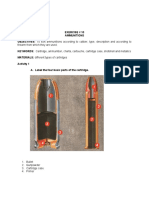
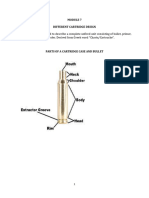
Parts of the Cartridge Case
1. Base -the bottom portion of the cartridge case which con-tains the
head stamp marking on the base of the shell con-taining the
caliber,manufacturer and in some cases includ-ing the date, trade name,
and batch number.
2. Rim - is that part of the cartridge case designed to limit the forward
movement of the cartridge to the chamber.
3. Extracting grooves - is the circular groove near the rim of the
shell designed for automatic withdrawal of the case from the
chamber.
4. Primer Pocket - is that part of the shell which provides the means for
the primer to be put in the central position.Its function is extended to: (a)
hold the primer in place; (b) to provide means to prevent the escape of
gas; (c) to provide solid support for primer anvil.
CHAPTER 6: CARTRIDGE CASE
71
FORENSIC BALLISTICS
5. Body - is the cylindrical part of the shell which houses the
gunpowder.
6. Shoulder -that part of the cartridge case which supports the neck of the
cartridge which is evident in a bottleneck type.
7. Cannelure -is the cylindrical groove in the outer surface of the
cartridge case designed to secure the shell to the cham-ber as well as
to prevent the bullet from being pushed down to the powder charge. In
some instance it is even being uti-lized for identification.
8. Neck - is that part of the shell which is actually occupied by the
bullet. This is obvious in a bottleneck type of shell but not with the
straight type.
9.Crimp-is the cylindrical groove on the mouth of the shell designed for
two purposes: One (1) is to hold the bullet and prevent it from being
pulled out from the shell and Two (2)to offer resistance to the bullet
out of the neck to ensure the burning of the gun powder.
10. Vent or Flash hole - is the hole at the bottom of the primer pocket
that serves as the passage way for the priming mix-ture to impart an
ignition to the propellant charge.
CHAPTER 6: CARTRIDGE CASE
72
FORENSIC BALLISTICS
Figure 45. Parts of the Cartridge Case
Types of Cartridge Case
1. Straight type = a type of a cartridge case or shell which has a straight shell
body usually found on cartridge usedin an automatic weapon.
2. Tapered type =a type of a cartridge case similar to a flow er base. It is found in
caliber.22 magnum-jet.
3. Botype of cartridge commonly found in am munitions for rifles.
CHAPTER 6: CARTRIDGE CASE
You might also like
- Zip Guns and Crude Coversions - Identifying Characteristics and PRDocument12 pagesZip Guns and Crude Coversions - Identifying Characteristics and PRMichael Turner67% (3)
- Wasteland NecessitiesDocument157 pagesWasteland NecessitiesPhil Hype100% (2)
- Military Glossary of AcronymsDocument7 pagesMilitary Glossary of Acronymsjual76No ratings yet
- Weight Estimation of Vessels AppsDocument39 pagesWeight Estimation of Vessels Appsmacwan23No ratings yet
- (RPG) Palladium - Rifts - Weapons & EquipmentDocument113 pages(RPG) Palladium - Rifts - Weapons & EquipmentKristin Molle80% (5)
- Proximity Fuzes Theory and TechniquesDocument59 pagesProximity Fuzes Theory and TechniquesMoltKee80% (5)
- How Shotguns WorkDocument6 pagesHow Shotguns WorkMurat SAVSA100% (4)
- Titanium Heat ExchangersDocument13 pagesTitanium Heat Exchangersxo123456789No ratings yet
- Zip Guns and Crude Coversions - Identifying Characteristics and ProblemsDocument12 pagesZip Guns and Crude Coversions - Identifying Characteristics and ProblemsNORDB100% (1)
- Hardware Hardware Hardware Hardware Catalogue Catalogue Catalogue CatalogueDocument80 pagesHardware Hardware Hardware Hardware Catalogue Catalogue Catalogue CatalogueLars PedersenNo ratings yet
- Bullet, Carthridge Case, FirearmsDocument15 pagesBullet, Carthridge Case, FirearmsWarlito D CabangNo ratings yet
- Ballistic ModuleDocument6 pagesBallistic ModuleJoseNo ratings yet
- Layson Asynchronous ActivityDocument13 pagesLayson Asynchronous ActivityKatleen Ann LaysonNo ratings yet
- A Glossary of Ammunition TermsDocument4 pagesA Glossary of Ammunition TermsUSFirearmsTraining83% (6)
- MOdule For AmmunitionDocument30 pagesMOdule For AmmunitiongracelynNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument94 pagesForensic BallisticsVergara BenjNo ratings yet
- Module 2 in Forensic BallisticsDocument9 pagesModule 2 in Forensic Ballisticscriminologyalliance100% (2)
- Field Artillery Journal - Dec 1943Document83 pagesField Artillery Journal - Dec 1943CAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- Pinecastle Jeep RangeDocument63 pagesPinecastle Jeep RangeCAP History LibraryNo ratings yet
- CAEF Roll Failures ManualDocument28 pagesCAEF Roll Failures ManualBirkan GökpınarNo ratings yet
- PALM SQUEEZERS and Other Unique HandgunsDocument10 pagesPALM SQUEEZERS and Other Unique Handgunsblowmeasshole1911No ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics - 4Document13 pagesForensic Ballistics - 4Catherine Acedo100% (1)
- Ammunitions and Cartridges: Presented By: Alex P. Sarmiento MS CrimDocument114 pagesAmmunitions and Cartridges: Presented By: Alex P. Sarmiento MS CrimSundae Angenette100% (1)
- BM-21 Grad PDFDocument37 pagesBM-21 Grad PDFLeko Mladenovski100% (1)
- For MidtermDocument30 pagesFor MidtermJaneth AsuncionNo ratings yet
- 2nd Edition Codex UpdatesDocument26 pages2nd Edition Codex Updatestoggleknot100% (5)
- Handbook of Enemy Ammunition, Pamphlet 2Document13 pagesHandbook of Enemy Ammunition, Pamphlet 2Marlin ZamoraNo ratings yet
- Glossary of Firearms TerminologyDocument14 pagesGlossary of Firearms Terminologyaaraujo_117636No ratings yet
- Fluted and Annular Grooved Barrel Chambers in FirearmsDocument11 pagesFluted and Annular Grooved Barrel Chambers in Firearmssnizz100% (6)
- Ostfront Quickfire PDFDocument14 pagesOstfront Quickfire PDFRyan YangNo ratings yet
- Corbin Technical Bulletin Volume 1Document38 pagesCorbin Technical Bulletin Volume 1aikidomoyses50% (2)
- Elements of An API 653 Tank InspectionDocument4 pagesElements of An API 653 Tank Inspectioncamasa2011No ratings yet
- TM9-1985-3, German Explosive Ordnance - Projectiles & Fuzes - 1953 PDFDocument280 pagesTM9-1985-3, German Explosive Ordnance - Projectiles & Fuzes - 1953 PDFhodhodhodsribdNo ratings yet
- Chapter Iii Ammunitions/CartridgesDocument8 pagesChapter Iii Ammunitions/CartridgesEy GrailNo ratings yet
- Garrison Artillery Drill Volume I - 1899Document269 pagesGarrison Artillery Drill Volume I - 1899cjnjr1No ratings yet
- Cartridge CaseDocument3 pagesCartridge Caseangyll agaledNo ratings yet
- TM 9-350 155-Mm Gun M2, Carriage M1 and M1A1, Gun Mount M13, Heavy Carriage Limber, Etc 1945Document251 pagesTM 9-350 155-Mm Gun M2, Carriage M1 and M1A1, Gun Mount M13, Heavy Carriage Limber, Etc 1945RobertLockie100% (1)
- PGK - Precision Guidance KitDocument2 pagesPGK - Precision Guidance KithdslmnNo ratings yet
- API 650 Tank Design 1foot MethodDocument4 pagesAPI 650 Tank Design 1foot Methodjakjak67% (3)
- Ammo Glossary PDFDocument27 pagesAmmo Glossary PDFIsidoro SanchezNo ratings yet
- FM 6-40 1945: Field Artillery GunneryDocument467 pagesFM 6-40 1945: Field Artillery GunneryThomas Conroy-Runyon100% (1)
- Parts of The Cartridge CaseDocument4 pagesParts of The Cartridge CaseAda Dukes100% (1)
- Marksmanship 2nd ModuleDocument7 pagesMarksmanship 2nd Modulejenny sansanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter IvDocument5 pagesChapter IvCherry A. ArcioNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics - 6Document7 pagesForensic Ballistics - 6Catherine AcedoNo ratings yet
- Forc106 - Module 6Document9 pagesForc106 - Module 6kimberlyn odoñoNo ratings yet
- Notes in Forensic Ballistics Mapfiles: The AmmunitionDocument10 pagesNotes in Forensic Ballistics Mapfiles: The AmmunitionZenwel PaulaNo ratings yet
- Chapter IiiDocument4 pagesChapter IiiCherry A. ArcioNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics Chapter 4Document16 pagesForensic Ballistics Chapter 4Ricci Earl Lauron100% (1)
- Forensic Ballistics Topic:: Bullet & Cartridge CaseDocument27 pagesForensic Ballistics Topic:: Bullet & Cartridge CasedenverboyboyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AmmunitionDocument11 pagesChapter 2 AmmunitionGabriel Sta Maria100% (1)
- Chapter 4 AmmunitionDocument32 pagesChapter 4 AmmunitionRonilo Padrogado NicolasNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument20 pagesReportjaylou taboriteNo ratings yet
- Yllana Bay View College: Balangasan District Pagadian CityDocument9 pagesYllana Bay View College: Balangasan District Pagadian CityElla BanlasanNo ratings yet
- Ammunition Report Wps OfficeDocument6 pagesAmmunition Report Wps OfficeBrielle Shai CruzNo ratings yet
- Group 2 AmmunitionDocument21 pagesGroup 2 AmmunitionJohn Noel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Ammunition Legal Definition of AmmunitionDocument7 pagesAmmunition Legal Definition of AmmunitionHanna Sobreviñas AmanteNo ratings yet
- This Page Is Basically An Illustrated Glossary of Cartridge Types. I Hope It Answers A Few Basic QuestionsDocument54 pagesThis Page Is Basically An Illustrated Glossary of Cartridge Types. I Hope It Answers A Few Basic QuestionsÁdám MajorNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument7 pagesForensic BallisticsLove Bella Mae AstilloNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics Module 7Document12 pagesForensic Ballistics Module 720-0383.dizorNo ratings yet
- Week5 AmmunitionDocument6 pagesWeek5 Ammunitionruui chizakuraNo ratings yet
- GunshotDocument19 pagesGunshotRizky IkwanNo ratings yet
- Firearm Ammunition and Cartridge CasesDocument5 pagesFirearm Ammunition and Cartridge CasesDomingo John-h Wyler CainoyNo ratings yet
- Forc106 - Module 4 NewDocument8 pagesForc106 - Module 4 Newkimberlyn odoñoNo ratings yet
- Practical No 8Document2 pagesPractical No 8Asim MemonNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument8 pagesForensic BallisticsJoshua D None-NoneNo ratings yet
- WOUND BALLISTICS ExamDocument143 pagesWOUND BALLISTICS ExamGUILAY, KEVIN MARK F.No ratings yet
- Cartridge CaseDocument2 pagesCartridge CaseLOVELY TRAZONANo ratings yet
- Ammunition: Forensic BallisticsDocument2 pagesAmmunition: Forensic BallisticsHaimelien De LimosNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics (BIGWAS)Document19 pagesForensic Ballistics (BIGWAS)KARLVINNo ratings yet
- Forc106 - Module 4 NewDocument21 pagesForc106 - Module 4 Newkimberlyn odoñoNo ratings yet
- Forensic Ballistics 2Document2 pagesForensic Ballistics 2john acostaNo ratings yet
- Ballistics PowerPointDocument42 pagesBallistics PowerPointSamira AbdoNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 AmmunitionsDocument7 pagesChapter-3 AmmunitionsJohn Calvin CalimNo ratings yet
- Forensic BallisticsDocument23 pagesForensic BallisticsCristiana Jsu DandanNo ratings yet
- Galano, Gio S. Bs - Criminology Echo - 2 Pe Crim 4Document3 pagesGalano, Gio S. Bs - Criminology Echo - 2 Pe Crim 4JL HUFANONo ratings yet
- What Is Forensic Ballistics?Document26 pagesWhat Is Forensic Ballistics?Maaya MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- IATG 06.30 Storage and Handling v.2Document18 pagesIATG 06.30 Storage and Handling v.2DOC LABNo ratings yet
- 76mm-Naval-Ammunition 3 WebDocument2 pages76mm-Naval-Ammunition 3 WebKhant Zaw HeinNo ratings yet
- AFEO Bulletin 12Document28 pagesAFEO Bulletin 12cpt_suzukiNo ratings yet
- Field Artillery Journal - Jan 1915Document271 pagesField Artillery Journal - Jan 1915CAP History Library100% (2)
- Afghanistan Ordnance ID Guide Complete Low Res - 18 Aug 2004Document472 pagesAfghanistan Ordnance ID Guide Complete Low Res - 18 Aug 2004Yewendim FentaNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Cartridge CaseDocument4 pagesParts of The Cartridge CaseAda Dukes100% (1)
- Base Fuze Activation Plate Thickness Minimums Versus Impact Obliquity by Nathan Okun (7/6/2008)Document3 pagesBase Fuze Activation Plate Thickness Minimums Versus Impact Obliquity by Nathan Okun (7/6/2008)Curtis BrownNo ratings yet
- Projectile and Mortar PartsDocument2 pagesProjectile and Mortar PartsGeorgios AnastasopoulosNo ratings yet
- Guide To Deactivating Warfare ItemsDocument8 pagesGuide To Deactivating Warfare Itemskate mclean100% (1)
- UW3 Welds Ranking From ASME VIII Div 1Document1 pageUW3 Welds Ranking From ASME VIII Div 1dextermindNo ratings yet