Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Separation Thecniques
Separation Thecniques
Uploaded by
tatangahumanaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Separation Thecniques
Separation Thecniques
Uploaded by
tatangahumanaCopyright:
Available Formats
2 .
S e pa r at i o n T e c h n i q u e s Name & Surname Class
Direction for Learning
Zahra, B.Ed(Hons), St. Albert The Great College
Mark the following Statements as Before After
Lessons Lessons
True (T), False (F), or Unsure (U)
Boiling is a separation technique
Water can be obtained from a salt solution by evaporation
Salt can be obtained from a salt solution by evaporation
Sublimation is a separation technique
Filtration is used to obtain an insoluble solid from its mixture with a
liquid
The solid collected by filtration is called a filtrate
Water and alcohol can be separated by fractional distillation
Water and oil can be separated by fractional distillation
Water and oil are separated using a separating funnel
Fractional distillation can be used to obtain hydrogen and oxygen ele-
ments from pure water
GJ
Dyestuffs are separated by chromatography
A substance that boils at –20°C is a gas at room temperature
Separation Techniques pg. 1 GJ Zahra B.Ed (Hons)
2.1 Mixtures
Mixtures are formed when two or more substances are mixed together without a chemical reaction.
In this case the substances can be separated using physical separating techniques.
When substances react chemically to form new compounds, such compounds cannot be divided by
the separation techniques discussed in this topic. They can only be separated by high temperatures
or electric currents.
Filtration
Filtration is used to separate an
insoluble solid from a liquid. Such a
mixture is called a suspension.
To separate this type of mixture, a filter
paper is used. A filter paper contains
holes which are big enough to allow the
liquid molecules to pass through but not
the solid particles.
The solid collected in the filter paper is
called the residue.
The liquid collected in the container is
called the filtrate.
A conical flask is preferred to collect the
filtrate because it is less likely to tip over
and the slanting walls make splashing
difficult and swirling the liquid easy.
Examples of mixtures separated by filtration:
Separation Techniques pg. 2 GJ Zahra B.Ed (Hons)
Evaporation
Evaporation is used to separate a soluble
solid from a liquid. Such a mixture is called a
solution.
In a solution, the solid is called the solute
and the liquid the solvent.
The mixture is heated in an evaporating dish
or an evaporating basin.
The solid collected in is called the evaporate.
The solvent is lost.
To collect heat sensitive substances (usually
crystals), heating is stopped when a little
solvent is remaining and the solute is let to
crystallize by itself.
Instead of direct heating on a flame, a water
bath can be used for more gentle heating.
Examples of mixtures separated by evaporation:
Sublimation
Sublimation is used to separate a solid that
sublimes from one that does not.
The subliming vapour is turned back to solid
on a cold surface.
Examples of mixtures separated by sublimation:
Separation Techniques pg. 3 GJ Zahra B.Ed (Hons)
Distillation
Distillation is used to obtain both solvent
and solute from a solution
The evaporated solvent is passed through a
condenser so that it condenses back into a
liquid.
The collected liquid is called the distillate.
The water in the condenser flows from top
to bottom so that all of the inner tube is
surrounded with water.
A thermometer is placed above the solution
so that the temperature of the vapour only
is read.
Examples of mixtures separated by distillation
Separating Funnel
This apparatus is used to separate to
immiscible liquids.
The mixture is put in the separating funnel
and let to separate. The tap of the funnel is
opened so that the lower liquid is collected
in a suitable container.
Examples of mixtures separated using a separating
funnel
Separation Techniques pg. 4 GJ Zahra B.Ed (Hons)
Fractional Distillation
Fractional distillation is used to separate two miscible liquids with different boiling points.
A fractionating column provides ‘obstacles’ for the vapours so that these are better separated.
The thermometer reads the temperature of the vapour passing through the condenser.
When one substance has been collected, the temperature reading will begin to rise. At this point the
container collecting the distillate must be changed in order to collect the second distillate in a clean
container.
Examples of mixtures separated by fractional distillation:
Separation Techniques pg. 5 GJ Zahra B.Ed (Hons)
Chromatography
Chromatography is used to separate soluble
dyestuffs.
A drop or two of the substance if put on a
chromatogram.
The chromatogram is placed in a jar with a
suitable solvent.
As the solvent is absorbed by the
chromatogram, it carries the soluble parts of
the dyestuff with it. The most soluble parts
move further up the chromatogram.
Different solvents give different results.
Examples of mixtures separated by chromatography:
Gas Mixtures
Gas/gas mixtures where one gas liquefies
easily can be passed through a U-tube
submerged in ice salt.
Where water vapour needs to be removed,
the mixture is passed through a drying agent
such as calcium chloride.
In industry, gas/gas mixtures are liquefied
and then fractionally distilled. This is how air
is separated in a process called fractional
distillation of liquid air.
Examples of mixtures a gas/gas mixture than can be
separated in this way.
Separation Techniques pg. 6 GJ Zahra B.Ed (Hons)
You might also like
- t3 SC 837 Separating Mixtures Cut and Stick Activity Sheet - Ver - 1Document3 pagest3 SC 837 Separating Mixtures Cut and Stick Activity Sheet - Ver - 1nesrine boufaden100% (1)
- Taipei 101Document19 pagesTaipei 101Shikha VermaNo ratings yet
- Sedimentation Is A Process by Which Heavier Impurities in A LiquidDocument1 pageSedimentation Is A Process by Which Heavier Impurities in A LiquidZaifel PacillosNo ratings yet
- Blue GenchemDocument2 pagesBlue Genchemmasillamakon3No ratings yet
- Ch07 Separation TechniquesDocument13 pagesCh07 Separation TechniquesFauzan AkbarNo ratings yet
- Methods of SeparationDocument2 pagesMethods of SeparationAjay LakshmananNo ratings yet
- WLP Science q1 w7 LandscapeDocument17 pagesWLP Science q1 w7 LandscapeJayral PradesNo ratings yet
- NSC U4 Matter. (Part Ii)Document10 pagesNSC U4 Matter. (Part Ii)Amaia TeranNo ratings yet
- Properties of Matter and Separating MixturesDocument3 pagesProperties of Matter and Separating MixtureskeziahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry MixturesDocument2 pagesChemistry MixturesmarleypootsNo ratings yet
- Upper Final-Practice Questions - April 2023 Ans KeyDocument14 pagesUpper Final-Practice Questions - April 2023 Ans KeyVi NgôNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures 1: Name ClassDocument3 pagesSeparating Mixtures 1: Name ClassAdtNo ratings yet
- SCI-100 LESSON PLAN FERNANDEZ WEEK 2 SodapdfDocument7 pagesSCI-100 LESSON PLAN FERNANDEZ WEEK 2 Sodapdfmichaelfernandez38060No ratings yet
- Chemistry Handout 1 REF #: 001: Separation Methods and TechniquesDocument7 pagesChemistry Handout 1 REF #: 001: Separation Methods and TechniquesNaomi JohnsonNo ratings yet
- WLP Science q1 w7w8 LandscapeDocument13 pagesWLP Science q1 w7w8 LandscapeJayral PradesNo ratings yet
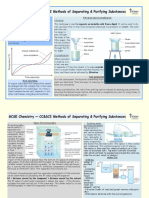
- Science Year 09 CC2 Methods of Separating and Purifying SubstancesDocument3 pagesScience Year 09 CC2 Methods of Separating and Purifying Substancesheidi elleithyNo ratings yet
- SEPARATION METHODS-I BY K.N.S.SWAMI - pdf476Document44 pagesSEPARATION METHODS-I BY K.N.S.SWAMI - pdf476Usman KhanNo ratings yet
- Separating TechniqueDocument2 pagesSeparating TechniqueJannat JeetNo ratings yet
- Methods and EquipmentDocument8 pagesMethods and EquipmentChristianNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures-1Document4 pagesSeparating Mixtures-1kareen.nelsonNo ratings yet
- Methods of Separating MixturesDocument21 pagesMethods of Separating MixturesMonica Morales MaañoNo ratings yet
- l4 Separating TechniquesDocument17 pagesl4 Separating Techniquesapi-616504906No ratings yet
- Separation of Substances (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer QuestionsDocument3 pagesSeparation of Substances (G6) : Handout I. Short Answer Questionsdon shiphrahNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument2 pagesSeparating MixturesAbigail MarianoNo ratings yet
- Separation Technique - Pharm Eng IDocument43 pagesSeparation Technique - Pharm Eng Ihakita86No ratings yet
- Separation of MixturesDocument25 pagesSeparation of MixturesYumie YamazukiNo ratings yet
- Separation of MixturesDocument52 pagesSeparation of MixturesEdgarVincentCharlesSalazarNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Guide To Types of MixturesDocument14 pagesA Comprehensive Guide To Types of MixturesMichelle SantosNo ratings yet
- Unit: 3 States of Matter Topic: Separation of Solution: Vocabulary WordsDocument2 pagesUnit: 3 States of Matter Topic: Separation of Solution: Vocabulary WordsNabila AzizNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument6 pagesSeparating Mixturescristopherlerma1No ratings yet
- 2024 - Science - Y1 - PPT2 - Separation Tech - Magnet, Using Solvent and FiltrationDocument21 pages2024 - Science - Y1 - PPT2 - Separation Tech - Magnet, Using Solvent and Filtrationcate.yim11No ratings yet
- Chem 1 Lesson 1. Properties of Matter and Separaion Techniques PDFDocument8 pagesChem 1 Lesson 1. Properties of Matter and Separaion Techniques PDFKyle Erika SayconNo ratings yet
- Filtration Is A Method To Separate The Components Of: Answer Key)Document2 pagesFiltration Is A Method To Separate The Components Of: Answer Key)Gauri BansalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry-Revision NotesDocument19 pagesChemistry-Revision NoteshadiaNo ratings yet
- Mixtures, Solutions & Chemical Processes Solution, Suspension & ColloidsDocument2 pagesMixtures, Solutions & Chemical Processes Solution, Suspension & ColloidsmhadzNo ratings yet
- Chemistry CompletedDocument24 pagesChemistry CompletedEltonNo ratings yet
- 2 - Elements Compounds and MixturesDocument13 pages2 - Elements Compounds and MixturesKhin Yadanar KyawNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Metode PemisahanDocument43 pagesPengantar Metode PemisahanMili APRILIANo ratings yet
- Separating Solids From LiquidsDocument4 pagesSeparating Solids From LiquidsRizal RusydiNo ratings yet
- Gravity Separation Lecture 5Document16 pagesGravity Separation Lecture 5Syazwan ShafriNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument4 pagesGeneral ChemistryCara Loriz TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Experimental - Techniques - 2 2Document58 pagesExperimental - Techniques - 2 2Winnie LeeNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us Pure NotesDocument9 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pure NotesRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Matter and Its PropertiesDocument45 pagesMatter and Its PropertiesJade AliyahNo ratings yet
- Methods - of - Separating - MixturesDocument18 pagesMethods - of - Separating - MixturesNomar MercinesNo ratings yet
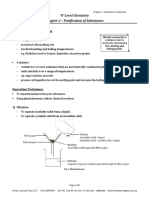
- Chapter 2 - Purification of SubstancesDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - Purification of SubstancesChristelle Ng Li Xuan (Student)No ratings yet
- Separation Techniques Revision CardDocument1 pageSeparation Techniques Revision Cardagentdog175No ratings yet
- Separation Funnel: ChemistryDocument9 pagesSeparation Funnel: ChemistryRhea FrancisNo ratings yet
- Class9 TH Chapter 2Document7 pagesClass9 TH Chapter 2knramya18No ratings yet
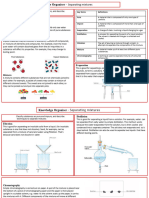
- Https://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//7e Knowledge Organiser PFRDocument1 pageHttps://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//7e Knowledge Organiser PFRAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- MixturesDocument25 pagesMixturesJoma Guerra ina moNo ratings yet
- Revising ChemistryDocument11 pagesRevising ChemistryMyat Thaw MhuuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Separation TechniquesDocument7 pagesLecture 3 Separation TechniquesÖzlem GülcenNo ratings yet
- Study Material - Separation MethodsDocument7 pagesStudy Material - Separation MethodsSahil NarkhedeNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us Pure? Separation TechniquesDocument15 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pure? Separation TechniquesAradhya RaiNo ratings yet
- Separation C.W. NotesDocument4 pagesSeparation C.W. NotesMeenakumari sankarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Week1 HandoutsDocument5 pagesChemistry Week1 HandoutsmeijigodwindepedroNo ratings yet
- Handout Lesson 41Document2 pagesHandout Lesson 41Rukhshanda NaazNo ratings yet
- Oil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandOil and Water Won't Mix and Other Mixture Separation Techniques - Chemistry Book for Kids 8-10 | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- AI For Business Final - CompressedDocument52 pagesAI For Business Final - CompressedAdhi NaNo ratings yet
- DB Managment Ch7 ProblemsDocument6 pagesDB Managment Ch7 ProblemsJuan Manuel Garcia NoguesNo ratings yet
- Clinker Cooler BalanceDocument8 pagesClinker Cooler BalancecemsavantNo ratings yet
- Separador Electromagnetico 2400 EriezDocument4 pagesSeparador Electromagnetico 2400 EriezVictor MoralesNo ratings yet
- Standard Controls 2. Rich Controls 3. Validation Controls 4. Databind ControlsDocument26 pagesStandard Controls 2. Rich Controls 3. Validation Controls 4. Databind ControlsAli RajpootNo ratings yet
- Flushing Oil Flooded Rotary Screw Air Compressors Procedure enDocument2 pagesFlushing Oil Flooded Rotary Screw Air Compressors Procedure enSergiSerrano100% (1)
- 11 WeirDocument32 pages11 WeirGray Fiore Fullbuster100% (1)
- Energy Resources and Electricity Generation MSDocument5 pagesEnergy Resources and Electricity Generation MSMangesh RahateNo ratings yet
- R7220402 Control SystemsDocument1 pageR7220402 Control SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Grain Drying and Dryers: Agricultural Mechanization For Sustainable Farming System Course 2004Document71 pagesGrain Drying and Dryers: Agricultural Mechanization For Sustainable Farming System Course 2004RamilArtates100% (2)
- Akcelerometar Tip 4534-BDocument4 pagesAkcelerometar Tip 4534-BDragan LazicNo ratings yet
- Ms0750 Vanguard 3-Cylinder Ohv LC Gasoline Briggs & StrattonDocument132 pagesMs0750 Vanguard 3-Cylinder Ohv LC Gasoline Briggs & StrattonKenn Ferro80% (5)
- LCD Grafico 128x64 t6963cDocument19 pagesLCD Grafico 128x64 t6963cEngenharia Eletrica Uniube UdiNo ratings yet
- Investigating The Performance of Various Channel Estimation Techniques For Mimo-Ofdm Systems Using MatlabDocument10 pagesInvestigating The Performance of Various Channel Estimation Techniques For Mimo-Ofdm Systems Using MatlabLawrence AveryNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes Intended Learning Outcomes Topic Assessment References Time TableDocument3 pagesLearning Outcomes Intended Learning Outcomes Topic Assessment References Time TableGerlie V. ArribaNo ratings yet
- Analysis Design of Multistorey Building PDFDocument124 pagesAnalysis Design of Multistorey Building PDFnap_carino100% (2)
- Field RoboticsDocument70 pagesField RoboticsSkanda SwaroopNo ratings yet
- Print Hello World #Include #Include Void Main (Printf (" Hello World") Getch )Document30 pagesPrint Hello World #Include #Include Void Main (Printf (" Hello World") Getch )AstitvaTyagiNo ratings yet
- Reaserch ProjectDocument55 pagesReaserch ProjectSeid AragawNo ratings yet
- Lelm 111Document7 pagesLelm 111Raging PhoenixNo ratings yet
- CS109B Quiz Directions Sign The PledgeDocument7 pagesCS109B Quiz Directions Sign The PledgeK. M. Junayed AhmedNo ratings yet
- XXXHJ BVCXCBNDocument10 pagesXXXHJ BVCXCBNLB AbderrahmaneNo ratings yet
- APAC - Literature - Coating - Epoxy Resin & Hardeners For Coating Selector Guide PDFDocument10 pagesAPAC - Literature - Coating - Epoxy Resin & Hardeners For Coating Selector Guide PDFSumanta RoyNo ratings yet
- Tracing A Number: //CELLID// // LACDocument7 pagesTracing A Number: //CELLID// // LACMahamadou Ousseini BarkiréNo ratings yet
- 10 1021@ie000063qDocument11 pages10 1021@ie000063qjuan diegoNo ratings yet
- Secury Module XPSAC5121Document4 pagesSecury Module XPSAC5121juan ochoaNo ratings yet
- Methanation of SyngasDocument7 pagesMethanation of SyngasGabriela Campos DávilaNo ratings yet
- Sim CCDocument8 pagesSim CCLivya GeorgeNo ratings yet
- PDF Digital - Decoder Encoder PDFDocument39 pagesPDF Digital - Decoder Encoder PDFAchrizNo ratings yet