Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Https://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//7e Knowledge Organiser PFR
Uploaded by
Amaya Ali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageOriginal Title
https%3A%2F%2Fd1c0fc7ib89kee.cloudfront.net%2Fuploads%2Fattachment%2Ffile%2Fdbdeddf7f73b7a040ab996105cf221ba%2F7E-Knowledge-Organiser-PFR.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageHttps://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//7e Knowledge Organiser PFR
Uploaded by
Amaya AliCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
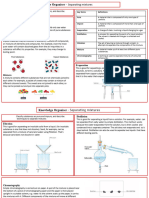
Describes a substance that 4.
Chromatography When a substance changes
Soluble
7E Mixtures and can dissolve in a liquid. Used to separate Condenses from its gas state into its
The total mass of a solution is Chromatography substances dissolved in a liquid state.
Separation the same as the mass of the A single substance that does
Conservation mixture.
dissolved substance plus the A concentrated dot of a not have anything else in it.
of Mass
mass of the liquid at the mixtures is placed at the Pure (Pure water only contains
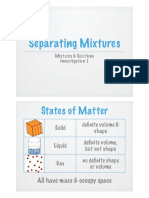
1. Mixtures
start. bottom of special water and no dissolved
Two or more substances solutes)
A solution that contains so chromatography paper.
Mixture jumbled together but not
much dissolved solute that Paper The bottom of the paper
joined together. Saturated
no more solute can dissolve Chromatography is dipped into a solvent
A mixture of a solid and liquid, in it. (such as water). As the
where the solid bits are heavy
Suspension The amount of a substance solvent moves up the Distillation
enough to settle out if the
that dissolves in a particular paper is carries the Apparatus
mixture is left to stand.
Solubility solvent at a particular dissolved substances.
A mixture of a solid, liquid or temperature to make a A solution that contains a
gas in a solid, liquid or gas saturated solution.
Colloid large amount of solute
where the substances do not Concentrated
dissolved in a small
settle out if left to stand. 3. Evaporation amount of solvent. Energy from the Sun is used
Spread out without settling When a liquid changes into a to evaporate salty/dirty
The results of
Dispersed out, such as the bits in a gas. Can be used to separate Solar Still water which is then
Evaporation chromatography such as
colloid. a liquid from the solid condensed, forming
a dried piece of paper for
Cannot be seen through- dissolved in it. pure/clean water.
Opaque Chromatogram paper chromatography
colloids are opaque / cloudy. Sodium The scientific name for table showing when the
When a substance has Chloride salt that we use on our food.
Solution dissolved solids have
dissolved in a liquid. When sodium chloride is been separated. Lesson Memorised?
Light can pass through and it Rock Salt found in thick layers of rock Different substances in a
Transparent can be seen through- solutions underground. mixture are carried at 1. Mixtures
are transparent. Can be dug up or mined. How different speeds,
Something through which a Water can be pumped into chromatography depending on how
Filter liquid is passed to remove layers of salt underground,
2. Solutions
works soluble they are, which
suspended pieces of solid. dissolving the sodium separates them out from
Extracting 3. Evaporation
chloride which is then each other.
2. Solutions Rock Salt
pumped to the surface and
The liquid in which a heated to evaporate the 5. Distillation 4. Chromatography
Solvent substance dissolves to make water, leaving behind sodium Separating water from the
a solution. chloride. Desalination salts in salty/sea water to
The substance that has 5. Distillation
When there is liquid turning produce fresh drinking water.
Solute dissolved in a liquid to make into a gas in all parts of a The process of separating a
a solution. Boiling
liquid- creates bubbles of gas liquid from a mixture by
When a substance breaks up in the liquid. Distillation evaporating the liquid and
into such tiny pieces in a The temperature at which a then condensing it to be
Dissolve Boiling Point
liquid that it can no longer be liquid boils. collected.
seen and forms a solution. Steam Water as a gas.
You might also like
- Separating Mixtures & Solutions Investigation 1Document11 pagesSeparating Mixtures & Solutions Investigation 1Roberto FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Examples Colloids: SubstanceDocument4 pagesExamples Colloids: SubstanceISABELITANo ratings yet
- PDF Document 2Document18 pagesPDF Document 2wyf69b6fhsNo ratings yet
- Solutions Booklet 2Document30 pagesSolutions Booklet 2api-546418402No ratings yet
- Is Matter Pure?Document8 pagesIs Matter Pure?Aarti JainNo ratings yet
- Mixtures, Solutions & Chemical Processes ExplainedDocument2 pagesMixtures, Solutions & Chemical Processes ExplainedmhadzNo ratings yet
- Keywords INORGANIC CHEMISTRYDocument9 pagesKeywords INORGANIC CHEMISTRYMARK BRIAN FLORESNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around us Pure_ _ Short NotesDocument4 pagesIs Matter Around us Pure_ _ Short Notessusabhan5dasNo ratings yet
- Chemical Formulas and MixturesDocument4 pagesChemical Formulas and MixturesCarmina DuldulaoNo ratings yet
- Physics - MatterDocument28 pagesPhysics - MatterDamimi 21No ratings yet
- Mixtures and Separations - Lecture #2Document28 pagesMixtures and Separations - Lecture #2victoriaNo ratings yet
- 13.2 Solutions and Their PropertiesDocument10 pages13.2 Solutions and Their PropertiesLore WheelockNo ratings yet
- Solutions ReadingDocument7 pagesSolutions Readingapi-189616674No ratings yet
- Chapter-2 - IS MATTER AROUND US PUREDocument25 pagesChapter-2 - IS MATTER AROUND US PURESATYAM RATHOURNo ratings yet
- CIE Igcse: CHEMISTRY//9093Document2 pagesCIE Igcse: CHEMISTRY//9093Dinara DzhakishovaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation On Separating TechDocument9 pagesEvaluation On Separating TechEssie KutisariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Separation Techniques - PPTX - 1Document49 pagesChapter 3 Separation Techniques - PPTX - 1Esraa BahaaNo ratings yet
- General ChemistryDocument4 pagesGeneral ChemistryCara Loriz TrinidadNo ratings yet
- When stress is placed upon a systemDocument6 pagesWhen stress is placed upon a systemZoren Jan CachoNo ratings yet
- Homogeneous Solution PropertiesDocument2 pagesHomogeneous Solution PropertiesDavid CruzNo ratings yet
- Solutes and Solvents ExplainedDocument1 pageSolutes and Solvents ExplainedMarjorie RedonaNo ratings yet
- Solutions: Properties and Solubility: Nat Sci 3 General ChemistryDocument22 pagesSolutions: Properties and Solubility: Nat Sci 3 General ChemistryAngelo Bon BalmesNo ratings yet
- Lo 8 ChemDocument27 pagesLo 8 ChemSpidy MoveNo ratings yet
- HandoutsDocument4 pagesHandoutsMaria Sahara FregilNo ratings yet
- Solubility Factors That Affect How Much Solute DissolvesDocument19 pagesSolubility Factors That Affect How Much Solute DissolvesPankaj JindamNo ratings yet
- Y7 Separating MixturesDocument2 pagesY7 Separating Mixturesellen mae GonatoNo ratings yet
- Resource Notes MixturesDocument4 pagesResource Notes MixturesAatikahNo ratings yet
- What Is The MatterDocument12 pagesWhat Is The MatterMeena SharmaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Module 3 ChemDocument7 pagesReviewer Module 3 Chemidieh ligNo ratings yet
- Separating Mixtures 1: Name ClassDocument3 pagesSeparating Mixtures 1: Name ClassAdtNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of A Pure SubstancesDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of A Pure SubstancesDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- C1: THE PARTICULATE NATURE OF MATTERDocument19 pagesC1: THE PARTICULATE NATURE OF MATTERhadiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Innovation SkylineDocument28 pagesChemistry: Innovation SkylineAbo Alphotoh GamingNo ratings yet
- Igcse Chemistry Revision Final!!Document126 pagesIgcse Chemistry Revision Final!!sohaila ibrahim100% (1)
- Science LessonsDocument8 pagesScience LessonsAnita PoshNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Pure Substances Year 8Document20 pagesMixtures and Pure Substances Year 8b2.dakurahNo ratings yet
- Chemistry textbook chapter on mixtures and pure substancesDocument14 pagesChemistry textbook chapter on mixtures and pure substancesHazel Penix Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter # 06: Solutions (Topic Wise Questions)Document10 pagesChapter # 06: Solutions (Topic Wise Questions)husain aliNo ratings yet
- Separate Mixtures Using PropertiesDocument3 pagesSeparate Mixtures Using PropertiesJenmar HemmingsNo ratings yet
- Separating MixturesDocument2 pagesSeparating MixturesAbigail MarianoNo ratings yet
- Mixtures and Separations-Lecture#1Document15 pagesMixtures and Separations-Lecture#1victoria0% (1)
- Module 2 SolutionDocument2 pagesModule 2 SolutionLJ Valdez100% (1)
- Science Lessons 3 To 6 (Autosaved)Document24 pagesScience Lessons 3 To 6 (Autosaved)Rodgen GerasolNo ratings yet
- Revising ChemistryDocument11 pagesRevising ChemistryMyat Thaw MhuuNo ratings yet
- Experimental techniques for measuring and separating mixturesDocument58 pagesExperimental techniques for measuring and separating mixturesWinnie LeeNo ratings yet
- PHYSICAL PHARMACY (MIDTERM COVERAGEDocument10 pagesPHYSICAL PHARMACY (MIDTERM COVERAGEMary Loise LimaNo ratings yet
- Science Year 09 CC2 Methods of Separating and Purifying SubstancesDocument3 pagesScience Year 09 CC2 Methods of Separating and Purifying Substancesheidi elleithyNo ratings yet
- Mixtures GuideDocument5 pagesMixtures GuideSusan BrowneNo ratings yet
- Jaydeep Tadvi Chemistry ProjectDocument10 pagesJaydeep Tadvi Chemistry ProjectNilesh DamorNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us PureDocument13 pagesIs Matter Around Us PureNANDITA NAYAK BNo ratings yet
- The Types and Energy of SolutionsDocument4 pagesThe Types and Energy of Solutionschem recordingsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12-SolutionsDocument32 pagesChapter 12-SolutionsNada MeselhyNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us Pure NotesDocument9 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pure NotesRajesh Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- Is Matter Around Us Pure - NotesDocument20 pagesIs Matter Around Us Pure - NotesRajveer KaushalNo ratings yet
- 8 Mixtures and Solutions (Revised)Document44 pages8 Mixtures and Solutions (Revised)Janna May ManliguezNo ratings yet
- 2 - Elements Compounds and MixturesDocument13 pages2 - Elements Compounds and MixturesKhin Yadanar KyawNo ratings yet
- Three States of MatterDocument2 pagesThree States of MatterWinner's AssociationNo ratings yet
- NOTES FOR SCIENCE 7 LPsDocument2 pagesNOTES FOR SCIENCE 7 LPsJink MargateNo ratings yet
- Lab Math Lec-MidtermsDocument43 pagesLab Math Lec-MidtermsMerra VenzuelaNo ratings yet
- The Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandThe Big Chemistry Book on Solutions - Chemistry for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
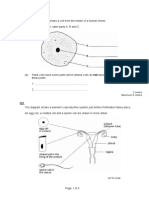
- Male Reproductive System and Pregnancy ExplainedDocument2 pagesMale Reproductive System and Pregnancy ExplainedAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Https://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//reproduction Exam QuestionDocument8 pagesHttps://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//reproduction Exam QuestionAmaya AliNo ratings yet
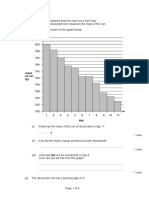
- Screenshot 2023-03-10 at 19.42.52 PDFDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-03-10 at 19.42.52 PDFAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells ComparedDocument2 pagesPlant and Animal Cells ComparedAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-01-03 at 01.50.29 PDFDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-01-03 at 01.50.29 PDFAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- How Russell Makes CoffeeDocument13 pagesHow Russell Makes CoffeeAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Human reproductive system and cell structure quizDocument3 pagesHuman reproductive system and cell structure quizAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- 1 MarkDocument9 pages1 MarkAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Https://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//workfortoday 13.12.2022Document4 pagesHttps://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//workfortoday 13.12.2022Amaya AliNo ratings yet
- Mire El 40Document12 pagesMire El 40JORGE IVAN CASTRO CASTRONo ratings yet
- Failure Analysis of Conveyor Pulley ShaftDocument12 pagesFailure Analysis of Conveyor Pulley ShafttuanNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Oil From Oil Cake by Soxhlet ExtractorDocument11 pagesExtraction of Oil From Oil Cake by Soxhlet Extractormahbub1332No ratings yet
- Respharma Company BrochureDocument7 pagesRespharma Company BrochureHiteshi Parekh100% (1)
- Data Faktur Apotik Mutiara InsaniDocument13 pagesData Faktur Apotik Mutiara Insaniapotek mutiarainsaniNo ratings yet
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-7Document8 pagesBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-7DikshantNo ratings yet
- Modern Chemistry Homework 9-6 AnswersDocument7 pagesModern Chemistry Homework 9-6 Answersffutcfrmg100% (1)
- Biologi K2Document16 pagesBiologi K2Nnmarziana NickNo ratings yet
- Phosphate HideoutDocument3 pagesPhosphate HideoutGreater Potential Tutoring100% (1)
- Atomic Structure NotesDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure NotesAayNo ratings yet
- Biogas-Repowering 0219 ENDocument16 pagesBiogas-Repowering 0219 ENArieWahyuWidodoNo ratings yet
- Soil Properties Influence on Dam DesignDocument27 pagesSoil Properties Influence on Dam DesignJulfikar KhanNo ratings yet
- (The Oily Press Lipid Library) Frederic Destaillats, Jean-Louis Sebedio, Fabiola Dionisi, Jean-Michel Chardigny - Trans Fatty Acids in Human Nutrition-Woodhead Publishing (2009)Document439 pages(The Oily Press Lipid Library) Frederic Destaillats, Jean-Louis Sebedio, Fabiola Dionisi, Jean-Michel Chardigny - Trans Fatty Acids in Human Nutrition-Woodhead Publishing (2009)Perpus StikesNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Atom and Periodic TablesDocument135 pagesStructure of The Atom and Periodic TablesCarol SoiNo ratings yet
- Iso 10540 1 2003Document9 pagesIso 10540 1 2003Jacky DoriaNo ratings yet
- Science 9 - Q2 - Mod3 - IONS-HOW-ARE-THEY-FORMED - VerFinalDocument23 pagesScience 9 - Q2 - Mod3 - IONS-HOW-ARE-THEY-FORMED - VerFinalAbel Emmanuel Solitario CabralesNo ratings yet
- AtomicStructureBasicConceptsofChemistry PDFDocument64 pagesAtomicStructureBasicConceptsofChemistry PDFSandhya PashamNo ratings yet
- The S - Block ElementsDocument1 pageThe S - Block ElementsRunjhunNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Xi: Short Questions and 20% Long QuestionsDocument3 pagesChemistry Xi: Short Questions and 20% Long QuestionsSyed Nabeel HassanNo ratings yet
- Method For Mercurous Nitrate Test For Copper I and Copper Alloys (Document4 pagesMethod For Mercurous Nitrate Test For Copper I and Copper Alloys (Mukesh kumarNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Study On Operating Conditions of 2 Ethylhexanol Operating ProcessDocument30 pagesAn Experimental Study On Operating Conditions of 2 Ethylhexanol Operating ProcessShay BlueNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.2 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction (Study Guide)Document22 pagesLesson 1.2 Intermolecular Forces of Attraction (Study Guide)Wilmark Rivera Official100% (2)
- Kondawar 2017 Solvent Free Glycerol TransesterifiDocument11 pagesKondawar 2017 Solvent Free Glycerol TransesterifiElisabeta StamateNo ratings yet
- Exolit AP 422Document3 pagesExolit AP 422محمد عزتNo ratings yet
- TRW 23925036 02Document9 pagesTRW 23925036 02Eddy GuerreroNo ratings yet
- State-of-the-Art Technologies For Separation of Azeotropic MixturesDocument24 pagesState-of-the-Art Technologies For Separation of Azeotropic MixturesNazir MoralesNo ratings yet
- Lec 1Document17 pagesLec 1Hadi H. HussenNo ratings yet
- Operation and Service Manual For Hermetic Sampler A.2: 0.5 LiterDocument36 pagesOperation and Service Manual For Hermetic Sampler A.2: 0.5 LiterGMNo ratings yet
- THERMAL PROPERTIES OF POLYMER (Update)Document38 pagesTHERMAL PROPERTIES OF POLYMER (Update)Vĩ Lê QuangNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration of Chemical EquationsDocument7 pagesStudent Exploration of Chemical EquationsDanitza RojasNo ratings yet