Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Male Reproductive System and Pregnancy Explained
Uploaded by
Amaya Ali0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesOriginal Title
https%3A%2F%2Fd1c0fc7ib89kee.cloudfront.net%2Fuploads%2Fattachment%2Ffile%2F6037918930ef1d97388377675fed5458%2F7B-Knowledge-Organiser-PFR.docx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesMale Reproductive System and Pregnancy Explained
Uploaded by
Amaya AliCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
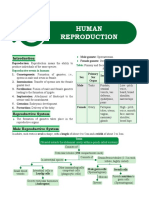
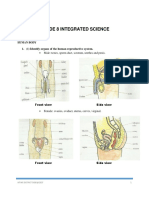
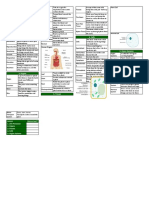
Male Reproductive System Egg Ultrasoun Produce images of foetus to
7B Sexual Cell d Scans check for problems.
Reproduction in Adaptations Alcohol, drugs, cigarette smoke
Harm to
Animals Baby
and viruses can pass through
placenta and harm foetus.
Premature Baby born small and early.
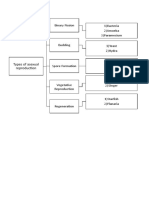
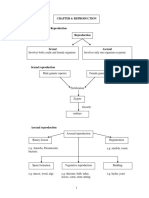
1. Animal Sexual Reproduction
Labour The act of giving birth.
The new organisms
Offspring 1. contractions start and cervix
produced by reproduction. Where the egg cells develop
Ovary begins to widen.
Sexual Reproduction that needs two and are released from.
2. amnion breaks and amniotic
Reproduction parents to produce offspring. Tube lined with cilia (tiny Stages of
Oviduct 3. Becoming Pregnant fluid leaves vagina.
Gametes Sex cells hairs). Giving
Sexual The erect penis is inserted 3. cervix at 10cm, stronger
Sperm Gamete that males make Where the baby will develop Birth
Uterus Intercourse into the vagina. contractions pushes baby
Egg Gamete that females make if the egg is fertilised.
Semen is pumped out of the through.
Sperm enters an egg cell and Ring of muscle between Ejaculation 4. Umbilical cord cut.
Cervix urethra.
Fertilisation nuclei fuse forming a uterus and vagina.
Vagina → sucked up through The placenta is passed out of
fertilised egg cell. Part that leads from the Route the Afterbirth
Vagina cervix → uterus → oviduct → the vagina- end of labour.
The sperm and egg cell meet cervix to the outside. sperm takes
External meets egg cell Produces milk for babies-
outside of the body. Female Reproductive System Mammary contains nutrients and
Fertilisation If fertilisation occurs the cell
e.g. fish Glands antibodies to protect from
starts to divide forming an
Internal The sperm and egg cell meet disease
Implantation embryo which will then sink
Fertilisation inside the body.
into the uterus lining. The
Large numbers of eggs are 5. Growing Up
Using woman is now pregnant.
produced because many get Sex Released by brain, tests &
External Amniotic Watery fluid to protect
washed away. The parents Hormones ovaries- start puberty.
Fertilisation Fluid growing embryo / foetus.
don’t look after their young. Changes to Voice deepens, shoulders
When males start to produce Bag containing the amniotic
Fewer egg cells produced Amnion Boys During widen, hair grows, testes/
Puberty sperm cells and egg cells in fluid.
Using because sperm is more likely Puberty penis grow, sperm produced.
female start to mature. Allows oxygen, food and
Internal to reach egg. The parents Changes to Breasts develop, hair grows,
Sperm Cell Adaptations water to be passed from
Fertilisation usually look after their Girls During hips widen, ovaries start to
mother’s blood into embryo’s
young. Puberty release eggs.
Placenta blood. Waste materials (like
Days 1-5: uterus lining lost
2. Reproductive Organs carbon dioxide) pass from
from body (menstruation)
Testes Where sperm cells are made. embryo’s blood into mother’s
Days 6-14: egg cell starts to
Bag of skin containing the blood.
Scrotum Menstrual mature and is released
testes. Umbilical Carries the embryo’s blood to
Cycle around day 14 (ovulation)
Sperm travels through here Cord and from the placenta.
Sperm Ducts Days 14+: egg cell swept
after leaving the testes. towards uterus, if not
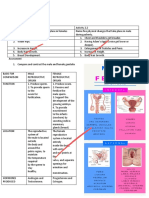
4. Gestation and Birth
Fluids are added to the fertilised cycle starts again.
Gestation The time from fertilisation until
Glands sperm- it is now called
Period birth.
semen.
The tube the semen leaves
When an embryo develops a Lesson Memorised?
Urethra Foetus full set of organs we call it a 1. Animal Sexual
the body through.
foetus (around 8 weeks).
Reproduction
2. Reproductive
Organs
3. Becoming Pregnant
4. Gestation & Birth
5. Growing Up
You might also like
- Esquema Unit 3 SciencesDocument4 pagesEsquema Unit 3 SciencesALBANo ratings yet
- Science Bab 4 (Subtopic Map)Document9 pagesScience Bab 4 (Subtopic Map)LEE SOON GUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- CR 010232Document20 pagesCR 010232kgothatso maleteNo ratings yet
- Science Bab 4 (Subtopic Map) (Second Version)Document8 pagesScience Bab 4 (Subtopic Map) (Second Version)LEE SOON GUAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Fa 3 e 1Document3 pagesFa 3 e 1Pahal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Understanding MenstruationDocument28 pagesUnderstanding Menstruationzannat khanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Rabbit (Final)Document9 pagesReproduction in Rabbit (Final)Tanzeem AnjumNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Lesson BioDocument3 pagesReproduction Lesson Biousha leninNo ratings yet
- t2 P 218 Sex and Relationships Education Menstruation Powerpoint - Ver - 12Document27 pagest2 P 218 Sex and Relationships Education Menstruation Powerpoint - Ver - 12ideatoon mediaNo ratings yet
- Class 8 Science: Reproduction in AnimalsDocument21 pagesClass 8 Science: Reproduction in AnimalsJ CNo ratings yet
- TWINKL Knowledge OrganiserDocument2 pagesTWINKL Knowledge OrganiserDearbhla HubbardNo ratings yet
- Science Lesson: With Teacher Aninda/Feny/Amal /lidaDocument9 pagesScience Lesson: With Teacher Aninda/Feny/Amal /lidaGIS Grade 5ANo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PresentationDocument6 pagesChapter 4 PresentationLhekha RaviendranNo ratings yet
- Reproduction NotesDocument2 pagesReproduction NotesNerminNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy A Young Persons GuideDocument16 pagesPregnancy A Young Persons GuideFridge FreezerNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Part3 HumanReproductionDocument27 pagesReproduction Part3 HumanReproductionbiology.alfonsinaNo ratings yet
- The Repoductive SystemDocument6 pagesThe Repoductive SystemIsabel CajamarcaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument79 pagesReproduction in Animalsmdudi558No ratings yet
- Reproduction in Animals - Class Notes - Pariksha AbhyasDocument78 pagesReproduction in Animals - Class Notes - Pariksha Abhyastechnoharshil201No ratings yet
- Animal Form and Function 2: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityDocument79 pagesAnimal Form and Function 2: School of Biotechnology, International UniversityThu AnhNo ratings yet
- Form 1 C4 Reproduction (Short Notes)Document9 pagesForm 1 C4 Reproduction (Short Notes)YuhannNo ratings yet
- 3q ScienceDocument5 pages3q Sciencemariefranchescadevelos.imcNo ratings yet
- STD 6 SCDocument42 pagesSTD 6 SCLokanayaki SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science 8 & 9 FinalDocument84 pagesIntegrated Science 8 & 9 FinalFrancis ShiliwaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction - S3AC - Actividades A Explicar - 2021Document50 pagesReproduction - S3AC - Actividades A Explicar - 2021Villaxx 05No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 SC Pt5Document19 pagesChapter 1 SC Pt5David ChangNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument103 pagesReproductionthejackal2014No ratings yet
- Sexual and Asexual ReproductionDocument3 pagesSexual and Asexual ReproductionTrisha MarwahaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in AnimalsDocument5 pagesReproduction in Animalsmokshithakapoor657No ratings yet
- MCHN 3RD LectDocument9 pagesMCHN 3RD LectZahNo ratings yet
- ReproductionDocument10 pagesReproductionSalesNo ratings yet
- Frog Reproductive SystemDocument13 pagesFrog Reproductive Systemkaiden.g.lambertNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction: Gametogenesis to GestationDocument19 pagesHuman Reproduction: Gametogenesis to GestationSantosh JoshiNo ratings yet
- 3rd Quarter Science Periodical Test NotesDocument13 pages3rd Quarter Science Periodical Test Notesmichael enriquezNo ratings yet
- G7-Chapter 10-Lesson 3Document9 pagesG7-Chapter 10-Lesson 3archurbaNo ratings yet
- Topic 17: ReproductionDocument29 pagesTopic 17: ReproductionEva SidhaniNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 - Reproduction (Science Form 1)Document13 pagesCHAPTER 3 - Reproduction (Science Form 1)w pNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemERIC ASAMAMLEH KLEMEHNo ratings yet
- Male Reproductive Organ and Female Reproductive SystemDocument3 pagesMale Reproductive Organ and Female Reproductive SystemLisette LaoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet About Reproduction - RevisionDocument5 pagesWorksheet About Reproduction - RevisionISMAYILOV IlyasNo ratings yet
- La Fecu: La Reproduccion Sexual en Los AnimalesDocument1 pageLa Fecu: La Reproduccion Sexual en Los AnimalesAbedias Olivares LlancaNo ratings yet
- Continuity: Beings TheirDocument12 pagesContinuity: Beings TheirAmoNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science 8 & 9 FinalDocument54 pagesIntegrated Science 8 & 9 FinalKasman Kasonde MumbaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Reproductive System (Anatomy)Document7 pagesIntroduction To Reproductive System (Anatomy)Hamza MalikNo ratings yet
- Reproduction and Development: BIOLOGY: Today and TomorrowDocument60 pagesReproduction and Development: BIOLOGY: Today and Tomorrowmaine pamintuanNo ratings yet
- Integrated Science 8 & 9 Final PDFDocument54 pagesIntegrated Science 8 & 9 Final PDFAnthony Mabaso SichaliNo ratings yet
- Huma JoshDocument17 pagesHuma JoshBenny AgassiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction: The Perpetuation of LifeDocument3 pagesReproduction: The Perpetuation of LifeXyy MallariNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - MCN MaternalDocument20 pagesModule 2 - MCN MaternalChristine DuqueNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemGoal Digger Squad VlogNo ratings yet
- Human reproduction and development explainedDocument5 pagesHuman reproduction and development explainedsalmasomaNo ratings yet
- Human Reproductive SystemsDocument120 pagesHuman Reproductive SystemsYasseen AshrafNo ratings yet
- Homework #1 answers key stages fertilizationDocument3 pagesHomework #1 answers key stages fertilizationIbrahim ShanaaNo ratings yet
- Level of Organization Sample ActivityDocument1 pageLevel of Organization Sample ActivityKay AbawagNo ratings yet
- Class Notes Grade 7Document3 pagesClass Notes Grade 7Gerard LawNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Goat Reproduction: Animal ScienceDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Goat Reproduction: Animal Sciencekung fuNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Humans Final RevisionDocument28 pagesReproduction in Humans Final RevisionziadmelagamyNo ratings yet
- Puberty and reproductive system comparisonDocument3 pagesPuberty and reproductive system comparisonPura Joshua Gregory50% (2)
- Human ReproductionDocument41 pagesHuman ReproductionMmabatho VilakaziNo ratings yet
- Https://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//7e Knowledge Organiser PFRDocument1 pageHttps://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//7e Knowledge Organiser PFRAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Https://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//reproduction Exam QuestionDocument8 pagesHttps://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//reproduction Exam QuestionAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-03-10 at 19.42.52 PDFDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-03-10 at 19.42.52 PDFAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-01-03 at 01.50.29 PDFDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-01-03 at 01.50.29 PDFAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Cells ComparedDocument2 pagesPlant and Animal Cells ComparedAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- 1 MarkDocument9 pages1 MarkAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- How Russell Makes CoffeeDocument13 pagesHow Russell Makes CoffeeAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Human reproductive system and cell structure quizDocument3 pagesHuman reproductive system and cell structure quizAmaya AliNo ratings yet
- Https://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//workfortoday 13.12.2022Document4 pagesHttps://d1c0fc7ib89kee - Cloudfront.net/uploads/attachment/file//workfortoday 13.12.2022Amaya AliNo ratings yet
- OC Set B NEWDocument18 pagesOC Set B NEWmatrixtrinityNo ratings yet
- Activity On The Menstrual CycleDocument3 pagesActivity On The Menstrual CycleElaine BaratitaNo ratings yet
- Gyna Endocrinology DR Nadine 2021Document16 pagesGyna Endocrinology DR Nadine 2021Community Round3 G1No ratings yet
- (M3-MAIN) Unpacking The SelfDocument329 pages(M3-MAIN) Unpacking The SelfAngelo PayodNo ratings yet
- NEET Reproductive HealthDocument24 pagesNEET Reproductive HealthDip KcNo ratings yet
- Maternal & Child NursingDocument10 pagesMaternal & Child Nursingnokolip100% (2)
- Health8 Q2 M6 1Document12 pagesHealth8 Q2 M6 1Mar BadajosNo ratings yet
- Handbook 16-1-23Document52 pagesHandbook 16-1-23Janani M GowdaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Obj 3.9Document37 pagesModule 3 - Obj 3.9Nashawn BrownNo ratings yet
- REVALIDA EXAM 200 Answers With RationaleDocument17 pagesREVALIDA EXAM 200 Answers With Rationalexaileenx100% (1)
- Taking A Gynaecological HistoryDocument21 pagesTaking A Gynaecological Historyasif_siddiqui_2100% (1)
- Biology: Anterior Pituitary HormonesDocument12 pagesBiology: Anterior Pituitary Hormoneserika12767% (3)
- 12th Biology NCERT Microassignments All Chapters - FinalDocument38 pages12th Biology NCERT Microassignments All Chapters - Finalasdwaad0% (2)
- MODULE 5 (GEC 1: The Physical and Sexual Self) Lesson 5: The Physical and Sexual SelfDocument20 pagesMODULE 5 (GEC 1: The Physical and Sexual Self) Lesson 5: The Physical and Sexual SelfNovie Viernes100% (1)
- The Essential Phases of the Menstrual CycleDocument17 pagesThe Essential Phases of the Menstrual CyclePauline Yves IyaNo ratings yet
- f1 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocument22 pagesf1 Chapter 4 ReproductionshshshchinNo ratings yet
- 12 TH Study MaterialDocument63 pages12 TH Study MaterialAkash VigneshwarNo ratings yet
- Biochemical Investigation of Infertile Couple-My PresentationDocument91 pagesBiochemical Investigation of Infertile Couple-My PresentationOlukoyejo OluwaboriNo ratings yet
- Helping Fertility, by The Book: The Essential Fertility Plan For Healthy Pregnancy and Clearing Blocked Fallopian TubesDocument69 pagesHelping Fertility, by The Book: The Essential Fertility Plan For Healthy Pregnancy and Clearing Blocked Fallopian TubesJames Akibon100% (1)
- SOAL BAHASA INGGRIS TENTANG MENARCHEDocument2 pagesSOAL BAHASA INGGRIS TENTANG MENARCHENADIANo ratings yet
- Essential Knowledge About Hormonal ImplantsDocument21 pagesEssential Knowledge About Hormonal ImplantsazifadewiatasyaNo ratings yet
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome PcosDocument28 pagesPolycystic Ovary Syndrome PcosYosef Pratama Bangun100% (1)
- Vaginal BleedingDocument8 pagesVaginal BleedingMaria Monica Alcantara MedenillaNo ratings yet
- Obg MCQS PDFDocument11 pagesObg MCQS PDFPreeti ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cycle BekantanDocument8 pagesOvarian Cycle BekantanzhaifaNo ratings yet
- Variations in Lipid Levels According To Menstrual Cycle Phase Clinical ImplicationsDocument11 pagesVariations in Lipid Levels According To Menstrual Cycle Phase Clinical ImplicationsCatherina AileenNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Tuberculosis Health TeachingDocument3 pagesPulmonary Tuberculosis Health Teachinggenellemaarte100% (1)
- LP Menstrual CycleDocument3 pagesLP Menstrual CycleKaren Joy LendayaoNo ratings yet
- 02 - IRAOvulation Induction For TheDocument11 pages02 - IRAOvulation Induction For TheHartanto LieNo ratings yet
- Breasts A To ZDocument42 pagesBreasts A To Zalex1413No ratings yet