Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Schema Notes
Schema Notes
Uploaded by
Nandita Asthana SankerCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Schema Notes
Schema Notes
Uploaded by
Nandita Asthana SankerCopyright:
Available Formats
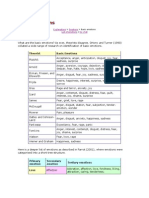
Needs of a child
1. Attachment and safety 2. Freedom to express needs
3. Develop competence and independence 4. Play 5. Realistic boundaries
Modes : three types - Child, parent, coping
Child modes
A. Vulnerable Child Mode is associated with depressed or anxious feelings such as shame, loneliness,
anxiety, sadness, or threat.
1. Abandonment & instability 2. Social isolation
2. Trust 4. Emotional deprivation 5. Defectiveness & Shame
B. Angry or impulsive Child Mode In this Mode one usually feels rage, anger, impulsivity, or defiance.
Impulsive behaviors appear when someone acts out of the moment without considering the possible
negative consequences of his or her actions
1. Angry child – sharp words - 2. Rage – intense and out of control
3. Defiance – when autonomy is not respected 4. Impulsivity 5. Spoilt behavior & lack of discipline
C Happy Child Mode. a healthy Mode: one feels curious and playful, and takes easygoing pleasure in
games and activities
1. Curiousity 2. playfulness
Feelings associated with each mode
Vulnerable Child Angry or Impulsive Happy Child Mode
Mode Child Mode
Anxiety Irritated Playfulness
•• Sadness •• Rage •• Easiness
•• Loneliness •• Anger •• Curiosity
•• Despair •• Impulsivity •• Fun
•• Helplessness •• Defiance •• Lightheartedness
•• Shame •• Stubbornness •• Safety
•• Abandonment •• Lack of discipline •• Confident
•• Dependence •• Spoilt
•• Abused
•• Humiliated
Parent Modes
1. Demanding parent
2. Guilt inducing
Parentification
Vicarious learning
3. Punitive parent mode
Coping modes
Surrender
Avoidant
Typical Avoidant Behavior
Patterns
1. •• Avoidance in a narrow sense. Staying away from difficult situations, avoiding particular tasks.
2. •• Distraction. Computer games, excessive Internet use, watching movies, loud music, non-stop
working, excessive participation in sports.
3. •• Stimulation. Overeating, watching porn, gambling, risky sports.
4. •• Weakening perception. Unpleasant feelings are avoided by drinking alcohol or using drugs.
5. •• Moaning and grumbling. Monotonous, stereotyped
6. moaning, grumbling, complaining; blaming others for everything. Frequently these people do not really
seem to suffer or to be really angry. It’s more that their usual habit is to grumble and complain.
7. •• Low expectations. It’s another form of avoidance not to set yourself any goals – then you don’t feel
disappointed by encountering problems reaching them…
Over compensate
Narcissistic arrogance. These people present themselves as brilliant and superior
Paranoid control. very suspicious of others. They believe that they are being taken advantage
of, so they seek to protect themselves against attacks.
Obsessive control. Sometimes people who actually feel insecure insist on telling others what to do.
They take strong control of a situation to arrange things “in the right way.”
Attention-seeking. Attention-seeking behavior was formerly called “hysterical.” These people force
everyone to treat them as the center of attention.
Box 5.1: Features of the Healthy
Adult Mode
•• “Healthy ego functioning”
•• Realistic judgment of situations, conflicts, relationships,
yourself, and other people
•• Little problems do not trigger overwhelming negative
emotions
•• You sense both your own feelings and needs and those
of other people
•• You can balance your needs with the needs of others
•• You can make commitments, take responsibilities, and
comply to your duties
•• You find constructive solutions for problems
•• You enjoy adult pleasures and interests (sports, culture,
sex, etc.)
You might also like
- Me and My Feelings A Kids Guide To Understanding and Expressing Themselves by Vanessa Allen MEd NBCTDocument113 pagesMe and My Feelings A Kids Guide To Understanding and Expressing Themselves by Vanessa Allen MEd NBCTCassandra100% (4)
- Healthy and Unhealthy Relationships Ameerah AidrusDocument39 pagesHealthy and Unhealthy Relationships Ameerah Aidrusmasudur rahman100% (1)
- Robert Plutchiks Psychoevolutionary Theory of Basic EmotionsDocument1 pageRobert Plutchiks Psychoevolutionary Theory of Basic Emotionsperalozac123100% (4)
- Defense Mechanism 2022Document33 pagesDefense Mechanism 2022Majd HusseinNo ratings yet
- Understanding Codependency: How to Overcome Abuse, Addiction, Trauma and Shaming to Live a Peaceful LifeFrom EverandUnderstanding Codependency: How to Overcome Abuse, Addiction, Trauma and Shaming to Live a Peaceful LifeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Borderline and Histrionic Personality DisordersDocument38 pagesBorderline and Histrionic Personality DisordersSahel100% (1)
- Human Behavior and VictimologyDocument53 pagesHuman Behavior and VictimologySevilla Joenard91% (11)
- Felt Sense ExercisesDocument11 pagesFelt Sense ExercisesNandita Asthana Sanker50% (2)
- True Self - Shame, Trauma, Narcissism, & Your True Self: Presented by David Tian, PH.DDocument20 pagesTrue Self - Shame, Trauma, Narcissism, & Your True Self: Presented by David Tian, PH.DJohannes Hansen100% (2)
- Remedy For Negative EmotionsDocument2 pagesRemedy For Negative Emotionspkpal1No ratings yet
- Child AbuseDocument16 pagesChild AbuseSreenitha Mandari100% (1)
- Basic EmotionsDocument3 pagesBasic Emotionssajidobry_847601844No ratings yet
- Sibling Conflict - For ParentsDocument44 pagesSibling Conflict - For ParentsNIST Ele ICT DepartmentNo ratings yet
- Self Awareness: Knowing One's Own Attitudes-Opinion Feelings - Emotion Motives - Purpose Desires - NeedsDocument58 pagesSelf Awareness: Knowing One's Own Attitudes-Opinion Feelings - Emotion Motives - Purpose Desires - Needswintoday01No ratings yet
- List of 14 Schema ModesDocument4 pagesList of 14 Schema ModesmentationNo ratings yet
- Novena Prayer For Our Dear DepartedDocument3 pagesNovena Prayer For Our Dear DepartedMecelNarteBancale65% (17)
- Emotional Freedom Self QuizDocument4 pagesEmotional Freedom Self QuizPremNo ratings yet
- The Bully, The Bullied, and The BystanderDocument33 pagesThe Bully, The Bullied, and The BystanderHRCNo ratings yet
- Interactive Color Code Slide ShowDocument47 pagesInteractive Color Code Slide ShowNovira Maya Sari100% (1)
- Defining Challenging Behavior by Milkyas SolomonDocument52 pagesDefining Challenging Behavior by Milkyas SolomonVerity SplendourNo ratings yet
- Erik Eriksons Theory of Psychosocial DevelopmentDocument49 pagesErik Eriksons Theory of Psychosocial DevelopmentCardiel Padua100% (1)
- Job Discription SampleDocument10 pagesJob Discription SampleNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Condolence ExamplesDocument15 pagesCondolence ExamplesadatNo ratings yet
- Anger Management: Presented By: Lolita V. Bucot RGCDocument54 pagesAnger Management: Presented By: Lolita V. Bucot RGCResty FloresNo ratings yet
- WierzbickaDocument47 pagesWierzbickaCroitoru DanielNo ratings yet
- The Permission Wheel Hawkes L PDFDocument8 pagesThe Permission Wheel Hawkes L PDFNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- A08 - The Anxious Personality - NotesDocument2 pagesA08 - The Anxious Personality - NotesMinh Anh DangNo ratings yet
- Self From The Perspectives of Psychology: Prof. Cherry CostalesDocument23 pagesSelf From The Perspectives of Psychology: Prof. Cherry CostalesAllyson DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Major Problems Faced by Teenagers2.0Document15 pagesMajor Problems Faced by Teenagers2.0MokshanandNo ratings yet
- Perkembangan KepribadianDocument33 pagesPerkembangan KepribadianGhea RifanaNo ratings yet
- Theories of PersonalityDocument34 pagesTheories of PersonalityShelender KumarNo ratings yet
- Abpsych TestDocument18 pagesAbpsych TestGian Francis TancioNo ratings yet
- A Parent'S Guide To The Child Protection SystemDocument50 pagesA Parent'S Guide To The Child Protection SystemKenotNotsniwOnaromNo ratings yet
- ABUSEDocument1 pageABUSEMary Belle OrtegaNo ratings yet
- PMSSD 2 Topic 1Document54 pagesPMSSD 2 Topic 1Jonathan CarretasNo ratings yet
- Group 1. The Self FromPsychological Perspective. Acain Caña GuanzonDocument17 pagesGroup 1. The Self FromPsychological Perspective. Acain Caña Guanzonricopactor56No ratings yet
- 2020 Adoption 101 Class OneDocument22 pages2020 Adoption 101 Class OneKavi rajputNo ratings yet
- GriefDocument54 pagesGriefAytülKTürerNo ratings yet
- Child Protection - Safety PresentationDocument48 pagesChild Protection - Safety Presentationjaja c.No ratings yet
- Soulless PsychopathDocument9 pagesSoulless PsychopathedwinNo ratings yet
- Teen PPT PresentationDocument18 pagesTeen PPT PresentationSantosh YadavNo ratings yet
- Avoidant PersonalityDocument8 pagesAvoidant PersonalityHazel VakhariaNo ratings yet
- Youth Depression: Lorna Martin Lormartin@gov - Mb.caDocument25 pagesYouth Depression: Lorna Martin Lormartin@gov - Mb.caBanasthali StudentNo ratings yet
- Psychoanalytical Theory PDFDocument26 pagesPsychoanalytical Theory PDFAjju SKNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry SlidesDocument323 pagesPsychiatry SlidesSukumar SubramaniNo ratings yet
- 02.2 Psychosocial Development Theory EriksonDocument21 pages02.2 Psychosocial Development Theory EriksonARIENNE JANICAH FRIA FABENo ratings yet
- Personality Dis PSTDocument79 pagesPersonality Dis PSTMonika JosephNo ratings yet
- Emotional Intelligence PPT 2Document23 pagesEmotional Intelligence PPT 2Harari Management and Kaizen Institute (HMKI)No ratings yet
- Cyber Bullying PresentationDocument21 pagesCyber Bullying PresentationJoão Pedro MarquesNo ratings yet
- 1) Distorted Thinking Patterns 2) Problematic Emotional Responses 3) Over-Or Under-Regulated Impulse Control 4) Interpersonal DifficultiesDocument38 pages1) Distorted Thinking Patterns 2) Problematic Emotional Responses 3) Over-Or Under-Regulated Impulse Control 4) Interpersonal Difficultiesnico ValenzonaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 PersonalityDocument24 pagesLesson 1 PersonalityEugine RioNo ratings yet
- Emotional IntelligenceDocument26 pagesEmotional IntelligenceNishpa prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Attachment Difficulties in Schools:: What Might Happen, Why and How To Handle ItDocument2 pagesAttachment Difficulties in Schools:: What Might Happen, Why and How To Handle ItAnghel Roxana MihaelaNo ratings yet
- Personality DisordersDocument11 pagesPersonality DisordersPIH SHTNo ratings yet
- Theories of Growth and DevelopmentDocument72 pagesTheories of Growth and DevelopmentCHONANo ratings yet
- Psyc1013 Lesson 5Document56 pagesPsyc1013 Lesson 5LEXIZZZNo ratings yet
- Alfred AdlerDocument4 pagesAlfred AdlerLourdes Jane SongkipNo ratings yet
- How To Enhance Childs Self EsteemDocument2 pagesHow To Enhance Childs Self EsteemOyrania AndreopoulouNo ratings yet
- UTS OutputDocument4 pagesUTS Outputlyka vidalNo ratings yet
- Anxiety WorkbookDocument20 pagesAnxiety WorkbookWanda FschraNo ratings yet
- Dear, Where Are You?: Nurathirah BT Shamsuddin - Nurhanis BT Zamshah - Nurul Izni BT IshakDocument19 pagesDear, Where Are You?: Nurathirah BT Shamsuddin - Nurhanis BT Zamshah - Nurul Izni BT IshakSylvia WongNo ratings yet
- Karen HorneyDocument30 pagesKaren HorneyRhaine EstebanNo ratings yet
- Socioemotional Development 112Document40 pagesSocioemotional Development 112KikoNo ratings yet
- Winning The Game of Fear WorkbookDocument6 pagesWinning The Game of Fear WorkbookJames DesulmaNo ratings yet
- Psy CHP-3Document30 pagesPsy CHP-3Nurhanisha AinaNo ratings yet
- Healthy Ways To Cope With StressDocument5 pagesHealthy Ways To Cope With StressAlexandra NovaNo ratings yet
- Parenting StylesDocument22 pagesParenting StylesHASAN ABDUL KOHARNo ratings yet
- Name: (Optional) : - AgeDocument6 pagesName: (Optional) : - AgeShaira Rehj RiveraNo ratings yet
- Here Are The Steps: 1. Ask Your Clients To Identify A Specific Traumatic Event From Their Past. The Instructions ForDocument4 pagesHere Are The Steps: 1. Ask Your Clients To Identify A Specific Traumatic Event From Their Past. The Instructions ForNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Project Work - Competency Mapping - CPCD WorkshopDocument23 pagesProject Work - Competency Mapping - CPCD WorkshopNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Certified Learning & Development Manager: Project at Week 1 For ParticipantsDocument3 pagesCertified Learning & Development Manager: Project at Week 1 For ParticipantsNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- JEA and BARS For Administration and Automation ProfileDocument14 pagesJEA and BARS For Administration and Automation ProfileNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Counselling Course OutlineDocument1 pageCounselling Course OutlineNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- JD - HR Team Section 1: Project Summary I. Objective of The ProjectDocument2 pagesJD - HR Team Section 1: Project Summary I. Objective of The ProjectNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- International Labour Organization (ILO) and The Asian Development Bank There Have Been As Much AsDocument1 pageInternational Labour Organization (ILO) and The Asian Development Bank There Have Been As Much AsNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- CTM - Diiferential CompetencyDocument3 pagesCTM - Diiferential CompetencyNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Competency Mapping Project - Quality Manager - Priya FDocument12 pagesCompetency Mapping Project - Quality Manager - Priya FNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Competency Mapping ProjectDocument8 pagesCompetency Mapping ProjectNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Tia Invitation FinalDocument2 pagesTia Invitation FinalNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Workshops, Courses, SeminarsDocument1 pageWorkshops, Courses, SeminarsNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Things I Love About My Daddy - TiaDocument2 pagesThings I Love About My Daddy - TiaNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Competency MappingDocument6 pagesAssignment - Competency MappingNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Journalism NotesDocument16 pagesJournalism NotesNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Strategy Map - Hotel Industry - Vimal ColinDocument5 pagesStrategy Map - Hotel Industry - Vimal ColinNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Education Industry in IndiaDocument7 pagesEducation Industry in IndiaNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Fashion WarsDocument20 pagesFashion WarsNandita Asthana SankerNo ratings yet
- Living in Two Worlds - Children S Experiences After The - 2018 - Journal of PediDocument8 pagesLiving in Two Worlds - Children S Experiences After The - 2018 - Journal of PediRio DikiNo ratings yet
- Scheff, T - Social Components in Depression, (2001) 64 Psychiatry 212Document13 pagesScheff, T - Social Components in Depression, (2001) 64 Psychiatry 212Sonja OsmanovićNo ratings yet
- Necessity of Sadness Draft 4Document6 pagesNecessity of Sadness Draft 4api-241786723No ratings yet
- Rhetorical Analysis RevisedDocument9 pagesRhetorical Analysis RevisedGuillermo CabreraNo ratings yet
- Characters Inside OutDocument5 pagesCharacters Inside OutLeah RoseNo ratings yet
- Inside Out - Per DevDocument7 pagesInside Out - Per DevJesse MirandaNo ratings yet
- Freedom From SadnessDocument11 pagesFreedom From SadnessmalsrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Anger WorksheetsDocument13 pagesAnger WorksheetsNISHANo ratings yet
- Assignment 1: Movie Review "Inside-Out"Document2 pagesAssignment 1: Movie Review "Inside-Out"Hira MadniNo ratings yet
- ISHPAL CHHABRA - 22 - 01 - 2020 - Mindvalley - Report PDFDocument11 pagesISHPAL CHHABRA - 22 - 01 - 2020 - Mindvalley - Report PDFIshpal chhabraNo ratings yet
- Karlle Louis P. Obviar - S11-04Document2 pagesKarlle Louis P. Obviar - S11-04Karlle ObviarNo ratings yet
- Essay About Happiness and SadnessDocument2 pagesEssay About Happiness and SadnessLuna RuthNo ratings yet
- Necessity of Sadness Draft 1Document6 pagesNecessity of Sadness Draft 1api-241786723No ratings yet
- Happiness - Sadness EssayDocument2 pagesHappiness - Sadness EssayLizbeth Morocho MorochoNo ratings yet
- MADRSDocument4 pagesMADRSGonzalo GVNo ratings yet
- Pelakor TM 4Document24 pagesPelakor TM 4devi afifahNo ratings yet
- Film Review of Inside Out (2016)Document1 pageFilm Review of Inside Out (2016)Marielle NabareteNo ratings yet
- The Art of Letting Go Stop Overthinking Stop Negative Spirals and Find Emotional Freedom The Path To Calm Book 13Document170 pagesThe Art of Letting Go Stop Overthinking Stop Negative Spirals and Find Emotional Freedom The Path To Calm Book 13Damayanti SinagaNo ratings yet
- Sissela Bok - Exploring Happiness - From Aristotle To Brain Science-Yale University Press (2010)Document224 pagesSissela Bok - Exploring Happiness - From Aristotle To Brain Science-Yale University Press (2010)MAROUANE AbdelkaderNo ratings yet
- Damasio (2000)Document8 pagesDamasio (2000)yukos300100% (4)
- Inside Out AnalystsDocument2 pagesInside Out Analystsapi-538562000No ratings yet
- What Are Grief and Loss?Document4 pagesWhat Are Grief and Loss?TommyNo ratings yet
- Tomo Ii - InglesDocument37 pagesTomo Ii - InglesAriana TelleNo ratings yet