Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2
2
Uploaded by
Kimchhorng Hok0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 page2
2
Uploaded by
Kimchhorng HokCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
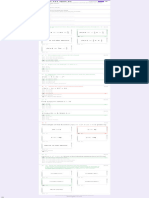
_______ 10. Receivable j.
Deposit made and recorded by the
depositor but not yet received on
the bank statement.
_______ 11. Accounts Receivable k. Report that explains the difference
between the book (company)
balance of cash and the cash
balance reported on the bank
statement, for purposes of
computing the adjusted cash
balances.
_______ 12. Notes Receivable l. Are short term, highly liquid
investment assets, readily
convertible to a known cash.
_______ 13. Direct write-off method m. The most liquid of all assets that
include currency, coins, and checks
deposited to the bank.
_______ 14. Allowance method n. Consists of the policies and
procedures managers used to
protect assets. Ensure reliable
accounting, promote efficient
operations and urge adherence to
company policies.
_______ 15. Aging of Accounts Receivable o. Are assets that are physically
consumed when used.
_______ 16. Plant Assets p. Amounts received in advance from
customers for future products or
services.
_______ 17. Depreciation q. Value based on a company’s
historical financial results.
_______ 18. Straight-line Method r. Charges the same amount of
expense to each period of the
assets useful life.
_______ 19. Units of Production Method s. Tangible long-lived assets used to
produce or sell products and
services.
_______ 20. Book Value t. Accounting for bad debts matches
the estimated loss from
uncollectible account receivable
against sales they helped produce.
_______ 21. Useful life u. A more formal credit agreement
with interest components.
_______ 22. Unearned Revenue v. An amount due from another party.
_______ 23. Intangible Assets w. Checks written (or drawn) by the
depositor, deducted on the
depositor’s record.
_______ 24. Natural Resources x. Small amount of cash in fund to pay
minor expenses; imprest system.
You might also like
- EOU-TEST-1-2-English For Business Studies - 3rd EditionDocument16 pagesEOU-TEST-1-2-English For Business Studies - 3rd EditionTô Duyên100% (1)
- Question 1: SolutionDocument15 pagesQuestion 1: Solutiondebate ddNo ratings yet
- First Summative Test-Business FinanceDocument3 pagesFirst Summative Test-Business FinanceRaul Cabanting100% (6)
- Accounting Test Bank - Bank ReconciliationDocument2 pagesAccounting Test Bank - Bank ReconciliationAyesha RGNo ratings yet
- Markel Corp (MKL) Analysis by Find - Me - ValueDocument38 pagesMarkel Corp (MKL) Analysis by Find - Me - ValueWall Street ConversationsNo ratings yet
- 2014 3016 Midterm Departmental ExamDocument14 pages2014 3016 Midterm Departmental ExamPatrick ArazoNo ratings yet
- Department of EducationDocument3 pagesDepartment of EducationAlvin Echano AsanzaNo ratings yet
- Exam 1sem 2019 Midterm BFDocument3 pagesExam 1sem 2019 Midterm BFWilson MoralesNo ratings yet
- Financial Management 1Document9 pagesFinancial Management 1Herdanto UtamaNo ratings yet
- Financial Analysis and Reporting Activity 6Document3 pagesFinancial Analysis and Reporting Activity 6Winelin TaroyNo ratings yet
- Acc106 p2 q2 Set A KDocument3 pagesAcc106 p2 q2 Set A KLeddie Bergs Villanueva VelascoNo ratings yet
- Pre and Post of Accounting 2Document14 pagesPre and Post of Accounting 2Nancy AtentarNo ratings yet
- Eou Test 1 - M4 - CTTTDocument10 pagesEou Test 1 - M4 - CTTTTuyền NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Eou Test 1 2 HP4CTTTDocument16 pagesEou Test 1 2 HP4CTTTTín HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Eou Test 1 2 HP4CTTTDocument13 pagesEou Test 1 2 HP4CTTTNHINo ratings yet
- Lab Posttest 1 - The Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemDocument1 pageLab Posttest 1 - The Accounting Equation and The Double Entry SystemRaymond PacaldoNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet and Statement of Cash FlowsDocument55 pagesBalance Sheet and Statement of Cash FlowsJayne Carly Cabardo100% (2)
- Fdnacct ReviewerDocument23 pagesFdnacct RevieweralyssaNo ratings yet
- Fdnacct ReviewerDocument23 pagesFdnacct RevieweralyssaNo ratings yet
- Review of Accounting Cycle - w97Document17 pagesReview of Accounting Cycle - w97Ding CostaNo ratings yet
- ACCT105 Accounting For Non Accounting MajorsDocument31 pagesACCT105 Accounting For Non Accounting MajorsG JhaNo ratings yet
- Acc 106 Receivable FinanceDocument2 pagesAcc 106 Receivable FinanceHeavenneNo ratings yet
- First Monthly Test in Fundamentals of ABM 2: I. Direction: Identify The Term Described in Each NumberDocument2 pagesFirst Monthly Test in Fundamentals of ABM 2: I. Direction: Identify The Term Described in Each Numbermanuel hipolitoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 4 ReviewerDocument14 pagesQuiz 4 ReviewerNaomi SyNo ratings yet
- Semi Quiz FM11Document3 pagesSemi Quiz FM11Mary Joy DayaoNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - External Financial Reporting - Balance Sheet and ValuationDocument12 pagesModule 1 - External Financial Reporting - Balance Sheet and ValuationPatricia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Sub-Innovative Financial Services Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Ty Bms Sem-ViDocument12 pagesSub-Innovative Financial Services Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Ty Bms Sem-Viarjun pradeepNo ratings yet
- Ifs Tybms Sem Vi Mcqs FinalDocument12 pagesIfs Tybms Sem Vi Mcqs FinalSudhakar Guntuka0% (1)
- Cfas - Chapter 8: Pas 1 - Presentation of Financial STATEMENTS (Statement of Financial Position)Document2 pagesCfas - Chapter 8: Pas 1 - Presentation of Financial STATEMENTS (Statement of Financial Position)agm25No ratings yet
- Finding The Financial FactsDocument2 pagesFinding The Financial Factsapi-509516948No ratings yet
- Key AnswerDocument6 pagesKey Answerpeter pakerNo ratings yet
- Prelim Exam-Banking and Financial Institution-March 2020Document4 pagesPrelim Exam-Banking and Financial Institution-March 2020Richard Oliver CortezNo ratings yet
- ACC106 P2 Q2 Set A KDocument2 pagesACC106 P2 Q2 Set A KShane QuintoNo ratings yet
- Amortized Cost Net Realizable Value Net Realizable Value Of: To The AcquisitionDocument1 pageAmortized Cost Net Realizable Value Net Realizable Value Of: To The AcquisitionAngela Mae N. AureoNo ratings yet
- Credit and Collections I. Identification (1 Point)Document2 pagesCredit and Collections I. Identification (1 Point)Aivan John CanadillaNo ratings yet
- ch12 PDFDocument30 pagesch12 PDFLê Chấn PhongNo ratings yet
- QTNH-C4 2Document35 pagesQTNH-C4 2Cao NganNo ratings yet
- Summative TEst EntrepDocument1 pageSummative TEst EntrepFretz Ael100% (1)
- TYBBI - Financial Reporting AnalysisDocument18 pagesTYBBI - Financial Reporting AnalysisNandhiniNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Acctg 1 Practice SetDocument3 pagesIntermediate Acctg 1 Practice SetMae Celine MarimonNo ratings yet
- Acc 111Document9 pagesAcc 111Rona Amor MundaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting ReviewerDocument48 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting ReviewerKeana Drew AysonNo ratings yet
- Chap1-4 INCDocument18 pagesChap1-4 INCVIRAY, CRISTIAN JAY V.No ratings yet
- FAR Practice MCQDocument17 pagesFAR Practice MCQBea PahuyoNo ratings yet
- 3 - Activities For ULO 7, 8, 9, 10 & 11Document8 pages3 - Activities For ULO 7, 8, 9, 10 & 11RJ 1No ratings yet
- D1Document13 pagesD1Anonymous bljN91No ratings yet
- Set C 4th Long Quiz Answer KeyDocument2 pagesSet C 4th Long Quiz Answer KeyRonah SabanalNo ratings yet
- Unit 11 Part IIDocument13 pagesUnit 11 Part IIИван БарановNo ratings yet
- Review 105 - Day 1 Theory of AccountsDocument13 pagesReview 105 - Day 1 Theory of AccountsMarites ArcenaNo ratings yet
- FINAL TEST DUM ExampleDocument8 pagesFINAL TEST DUM ExampleAryanie TlonaenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 Lending To Business Firms and Pricing Business LoansDocument33 pagesChapter 17 Lending To Business Firms and Pricing Business LoansTÂM PHẠM CAO MỸNo ratings yet
- Unittest 1 Fabm 1Document1 pageUnittest 1 Fabm 1wilhelmina romanNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Class Fabm 1Document4 pagesAsynchronous Class Fabm 1barrettacarlyn.22No ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Objective QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 10 Objective QuestionsjhouvanNo ratings yet
- PDFsam MergeDocument17 pagesPDFsam MergeStephanie RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Study Guide CH 12Document7 pagesStudy Guide CH 12Stephanie RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Business Finance 1st Quarter Examination 22-23Document3 pagesBusiness Finance 1st Quarter Examination 22-23Phegiel Honculada MagamayNo ratings yet
- Study Guide For Module 9 (Marketing)Document4 pagesStudy Guide For Module 9 (Marketing)mattheweberhard2No ratings yet
- QuickBooks Study GuideDocument9 pagesQuickBooks Study GuideKatrina EustaceNo ratings yet
- CPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionFrom EverandCPA Financial Accounting and Reporting: Second EditionNo ratings yet
- The Art of Persuasion: Cold Calling Home Sellers for Owner Financing OpportunitiesFrom EverandThe Art of Persuasion: Cold Calling Home Sellers for Owner Financing OpportunitiesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 BUSDocument6 pagesChapter 2 BUSKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Quiz #1Document1 pageQuiz #1Kimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- TowS 7 11 Analysis Group 2Document4 pagesTowS 7 11 Analysis Group 2Kimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Coffee Surveys-2Document2 pagesCoffee Surveys-2Kimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- 7eleven 151123165749 Lva1 App6891Document2 pages7eleven 151123165749 Lva1 App6891Kimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- ISSUU PDF DownloaderDocument44 pagesISSUU PDF DownloaderKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Coffee SurveysDocument2 pagesCoffee SurveysKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Ch9 ManualDocument4 pagesCh9 ManualKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- MakingConvenient7 ElevenDocument43 pagesMakingConvenient7 ElevenKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- ENGL - Assignment 4Document2 pagesENGL - Assignment 4Kimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- College Students' Perception On College Quality of Life: A Study On Constructivist-Grounded TheoryDocument6 pagesCollege Students' Perception On College Quality of Life: A Study On Constructivist-Grounded TheoryKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- KHM PresentationDocument3 pagesKHM PresentationKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 07 18 2023 23.36Document2 pagesCamScanner 07 18 2023 23.36Kimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Purchasing OrderDocument2 pagesPurchasing OrderKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Engl Comparisoncontrast Essays PresentationDocument28 pagesEngl Comparisoncontrast Essays PresentationKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Product Label (PDF) - 2Document1 pageProduct Label (PDF) - 2Kimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Product TemplateDocument4 pagesProduct TemplateKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- PV Beginning of Year PV End of Year PV Middle of YearDocument2 pagesPV Beginning of Year PV End of Year PV Middle of YearKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Vesta, Inc.: Bill To Ship To Invoice # 100 Invoice Date Due DateDocument2 pagesVesta, Inc.: Bill To Ship To Invoice # 100 Invoice Date Due DateKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- 1 Peng Sear 2Document1 page1 Peng Sear 2Kimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Mis GPDocument2 pagesMis GPKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Invoices 2Document1 pageInvoices 2Kimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- LookupDocument1 pageLookupKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Narrative EssayDocument2 pagesNarrative EssayKimchhorng HokNo ratings yet
- Signaling: 14.12 Game Theory Muhamet YildizDocument11 pagesSignaling: 14.12 Game Theory Muhamet Yildizgd3000No ratings yet
- Manufacturing Performance Improvement Through Lean Production-2009Document11 pagesManufacturing Performance Improvement Through Lean Production-2009Juan BarronNo ratings yet
- Inc42's 100 Unicorn Report 2022Document253 pagesInc42's 100 Unicorn Report 2022imrahulpasiNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory by Wiley Testbank 1Document87 pagesAuditing Theory by Wiley Testbank 1Liam Jacque LapuzNo ratings yet
- FPAC Part 1 Chapter 01Document72 pagesFPAC Part 1 Chapter 01Agnes BofillNo ratings yet
- Dole FaqsDocument22 pagesDole FaqsNoel DomingoNo ratings yet
- New - Delhi SouvenirDocument52 pagesNew - Delhi SouvenirDavid ThomasNo ratings yet
- Epm Course Outline 20 - 21 Bcom-BbaDocument2 pagesEpm Course Outline 20 - 21 Bcom-BbaIanNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship ProjectDocument25 pagesSummer Internship ProjectGAurav MeHareesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Economic Globalization: Poverty and InequalityDocument2 pagesEconomic Globalization: Poverty and InequalityGenerose UnayNo ratings yet
- The Great Debate On The Soviet Industria PDFDocument4 pagesThe Great Debate On The Soviet Industria PDFApollo MoirangthemNo ratings yet
- Sri Lanka Telecom PLCDocument2 pagesSri Lanka Telecom PLCclogebisluNo ratings yet
- Final Project 2017-18Document3 pagesFinal Project 2017-18Monali rautNo ratings yet
- 2012 Index of Economic FreedomDocument483 pages2012 Index of Economic FreedomJose Carbonell SanchezNo ratings yet
- Southwest Airlines AnalysisDocument6 pagesSouthwest Airlines Analysisdocmund100% (1)
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Employment - EditedDocument3 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Employment - Editedkimanthi samuelNo ratings yet
- Capital Mobility in Developing CountriesDocument41 pagesCapital Mobility in Developing CountriesEmir TermeNo ratings yet
- Flipkart Labels 01 Dec 2020 04 37Document1 pageFlipkart Labels 01 Dec 2020 04 37pgpm20 SANCHIT GARGNo ratings yet
- Unit I 12: Bank Subject: Ba5207 Marketing Management Sem / Year: Ii/IDocument10 pagesUnit I 12: Bank Subject: Ba5207 Marketing Management Sem / Year: Ii/IDhanya vijeeshNo ratings yet
- BUS 698 Course Career Path Begins Bus698dotcomDocument20 pagesBUS 698 Course Career Path Begins Bus698dotcomEssayest2No ratings yet
- Chapter - Iii Theoretical Framework of Financial Literacy and Financial Well-BeingDocument28 pagesChapter - Iii Theoretical Framework of Financial Literacy and Financial Well-Beingpooja shandilyaNo ratings yet
- Group 7Document11 pagesGroup 7Joshua AbogadieNo ratings yet
- MSBsDocument538 pagesMSBsEvangeline VillegasNo ratings yet
- Basel 1:: Tier-I Capital Tier-II CapitalDocument4 pagesBasel 1:: Tier-I Capital Tier-II CapitalRafiur RahmanNo ratings yet
- CLAW6031 International Financial Crime Problem Week 2, 2022Document2 pagesCLAW6031 International Financial Crime Problem Week 2, 2022yue xuNo ratings yet
- Prashant: ObjectiveDocument3 pagesPrashant: Objectiveprashant mujgelwarNo ratings yet
- Purchasing Manager or Sr. Buyer or Procurement Manager or DirectDocument2 pagesPurchasing Manager or Sr. Buyer or Procurement Manager or Directapi-121424087No ratings yet
- ProfileDocument2 pagesProfileThế Anh ĐàmNo ratings yet