0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views6 pagesUnderstanding PID Controller Functions
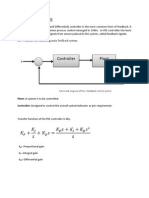
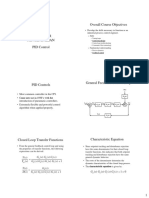
A PID controller continuously calculates an error value as the difference between a set point and a measured process variable and applies corrections based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms. Proportional control reduces rise time and steady state error, but can cause overshoot. Integral control eliminates steady state error but can cause oscillation. Derivative control anticipates error and increases stability, reducing overshoot and settling time.
Uploaded by
Tanvir Mahatab NadimCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views6 pagesUnderstanding PID Controller Functions
A PID controller continuously calculates an error value as the difference between a set point and a measured process variable and applies corrections based on proportional, integral, and derivative terms. Proportional control reduces rise time and steady state error, but can cause overshoot. Integral control eliminates steady state error but can cause oscillation. Derivative control anticipates error and increases stability, reducing overshoot and settling time.
Uploaded by
Tanvir Mahatab NadimCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd