0% found this document useful (0 votes)
307 views1 pageMedia and Information Literacy: Transmission Models
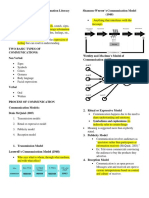
The document discusses various models of media and information literacy including Lasswell's communication model, Shannon-Weaver's model, and Westley and MacLean's model. It also covers characteristics of media literate citizens and information literate persons as well as different types of computer literacy and defines key terms such as communication and information.
Uploaded by
7xnc4st2g8Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
307 views1 pageMedia and Information Literacy: Transmission Models
The document discusses various models of media and information literacy including Lasswell's communication model, Shannon-Weaver's model, and Westley and MacLean's model. It also covers characteristics of media literate citizens and information literate persons as well as different types of computer literacy and defines key terms such as communication and information.
Uploaded by
7xnc4st2g8Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd