Controller
Er. Vinay Kumar
Department of Electronics Engineering
Kamla Nehru Institute of Technology, Sultanpur (U.P.)
vinaykumar@knit.ac.in
© 2022 Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
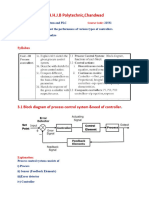
�Controller :
A controller is one which compares controlled values with the desired values and has a
function to correct the deviation produced.
A controller takes error input and generate suitable controlled signal in order to reduce the
over all error at output.
Error signal or Actuating signal
+ Controller M(s) Process
R(s) C(s)
– GC(s) G(s)
B(s)
H(s)
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Controller :
The important uses of the controllers are :
1. Controllers improve steady state accuracy by decreasing the steady state errors.
2. As the steady state accuracy improves, the stability also improves.
3. They also help in reducing the offsets produced in the system.
4. Maximum overshoot of the system can be controlled using these controllers.
5. They also help in reducing the noise signals produced in the system.
6. Slow response of the over damped system can be made faster with the help of these
controllers.
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
1) ON–OFF controller
2) Proportional controller
3) Derivative controller
4) Integral controller
5) Proportional Derivative (PD) controller
6) Proportional Integral (PI) controller
7) Proportional Integral Derivative (PID) controller
8) Output derivative feedback controller.
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
1) ON-OFF controller :
Output of the controller error is zero or one when input falls below a certain
predefined value the controller is turn off and when it increase beyond the certain
value the controller turn on.
Note:
The ON-OFF controller has a problem of chattering (sound) which is reduce by
introducing, the hysteresis in the characteristics of the controller that’s why their
application are limited.
Heating, cooling, speed controller, electric iron etc.
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
GP
2) Proportional controller : R(s) + E(s) M(s) n2 C(s)
Input KP Output
– s(s + 2n)
B(s)
H(s)
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
GP
R(s) + E(s) M(s) n2 C(s)
Input KP Output
– s(s + 2n)
B(s)
H(s)
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
3) Derivative Controller :
R(s) + E(s) M(s) 2n
Kds C(s)
– s(s+2n)
B(s)
Effect of Derivative Controller
i. The oscillation of the system is reduce it adds open loop zero at the origin of the s-plane.
ii. The stability of system improved.
Note : If the slope of the error signal known the output of the controller required in future can
be predicted, because of this characteristic. This controller is known as predictive controller.
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
4) Integral Controller :
R(s) + E(s) Ki M(s) 2n
C(s)
– s s(s+2n)
B(s)
Effect of Integral Controller
i. It increase the order and type of system by 1, since type number increase by one than steady
state error reduced.
ii. Since order of system increase, thus stability decrease.
iii. Band width of the system is reduces, thus SNR is improved.
iv. An integrator add open loop pole at origin there fore the effect of integrator is adding open loop
pole at origin.
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
5) Proportional + Derivative Controller :
KP
n
2
+ E(s) + M(s)
R(s) C(s)
– + s(s + 2n)
Kds
B(s)
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
Effect of Proportional + Derivative Controller :
KP
n
2
+ E(s) + M(s)
R(s) C(s)
– + s(s + 2n)
Kds
B(s)
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
6) Proportional + Integral Controller :
KP
Effect of PI Controller
2
+ E(s)
R(s) + M(s) n
C(s)
– Ki + s(s + 2n) i. It increase the type and order by 1 as order
B(s) s increase by 1 stability at system is reduced.
ii. As type is increase by one ess, bandwidth
are reduced and SNR is increases.
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
7) Proportional + Integral + Derivative (PID) Controller :
KP Effect of PID Controller
+ E(s) + M(s)
2
n
R(s) Kds C(s)
– ++ s(s + 2n) i. It add an open loop at origin and two open loop
B(s) Ki/s zero at the left half of s-plane.
ii. It increase the type of one, it improve transient
and steady state response of system.
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
8) Output Derivative Feedback Controller :
R(s) + E(s) + M(s) n
2 Effect
C(s)
– – s(s + 2n)
Kds
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Type of Controller :
8) Proportional + Derivative Controller :
KP
n
2
+ E(s) + M(s)
R(s) C(s)
– + s(s + 2n)
Kds
B(s)
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Significant or Dominant Pole (Roots) :
Concept : Among the finite pole zero of a system the pole near to the origin is called
significant pole or dominant pole. If distance between the significant pole and other
pole of the system is greater or equal to 5 times than they are called insignificant pole
otherwise they called significant pole.
× × ×
–3 –2 –1
Significant (near to origin)
Here non pole is insignificant but if a pole is found to be insignificant we can remove
the pole from transfer function of system, by doing so there will be hardly or no affect
at characteristic on the system.
Note : To remove the insignificant pole we always use time constant form.
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Significant or Dominant Pole (Roots) :
Example :
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved
�Significant or Dominant Pole (Roots) :
Example :
© 2022 | Er. Vinay Kumar, Department of Electronics Engineering, KNIT, Sultanpur. All rights reserved