0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesAsphalt Testing Equipment Overview
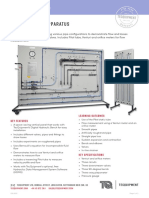
The document describes various laboratory equipment and devices used for testing materials, particularly in asphalt and soil analysis. Key tools include the Asphalt Stability Test Set, Triaxial Load Frame, and Universal Testing Machine, each serving specific functions related to stability, strength, and flow characteristics. Additionally, it outlines systems for studying fluid mechanics and hydraulic principles, emphasizing their importance in construction and engineering applications.
Uploaded by
imalazaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesAsphalt Testing Equipment Overview
The document describes various laboratory equipment and devices used for testing materials, particularly in asphalt and soil analysis. Key tools include the Asphalt Stability Test Set, Triaxial Load Frame, and Universal Testing Machine, each serving specific functions related to stability, strength, and flow characteristics. Additionally, it outlines systems for studying fluid mechanics and hydraulic principles, emphasizing their importance in construction and engineering applications.
Uploaded by
imalazaCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd