0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views23 pages2 Cerebral Cortex
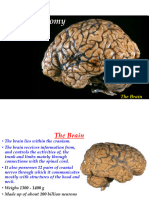
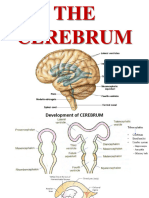
The document provides an overview of the cerebral cortex, detailing its organization, including the location of motor and sensory areas, and the components of the medial temporal lobe. It describes the functional organization of the cortex, highlighting areas related to language, sensory processing, and motor control, along with specific Brodmann areas. Additionally, it discusses the hippocampal formation and its intrinsic circuitry, emphasizing its role in memory and spatial navigation.
Uploaded by
بشار العباديCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views23 pages2 Cerebral Cortex
The document provides an overview of the cerebral cortex, detailing its organization, including the location of motor and sensory areas, and the components of the medial temporal lobe. It describes the functional organization of the cortex, highlighting areas related to language, sensory processing, and motor control, along with specific Brodmann areas. Additionally, it discusses the hippocampal formation and its intrinsic circuitry, emphasizing its role in memory and spatial navigation.
Uploaded by
بشار العباديCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd