Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mirtazapine
Uploaded by
JEn ValentosOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mirtazapine
Uploaded by
JEn ValentosCopyright:
Available Formats
VALENTOS, Jenshent Viniel R.
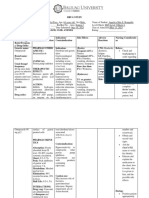
CA-12 DRUG STUDY Mirtazapine Generic name: Mirtazapine Brand Name :Remeron, Remeron RD (CA), Remeron Soltab, Zispin (UK) Pharmacologic class: Piperazinoazepine derivative Therapeutic class: Tetracyclic antidepressant Pregnancy risk category C Mechanism of Action: It is thought to work by blocking presynaptic alpha-2 adrenergic receptors that normally inhibit the release of the neurotransmitters norepinephrine (noradrenaline) and serotonin, thereby increasing active levels in the synapse. Mirtazapine also blocks post-synaptic 5-HT2 and 5-HT3 receptorsan action which is thought to enhance serotonergic neurotransmission while causing a low incidence of side effects.
Remeron Indications & Dosage: Tablets are indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder, and bipolar disorder with either depression or agitation. Contraindications Factors that prohibit its use include known hypersensitivity to tricyclic antidepressants, convulsive disorders, and prostatic hypertrophy. Its use is also contraindicated in patients who are in the recovery phase of a myocardial infarction. Side Effect/Adverse Reaction:
Body as a Whole: frequent: malaise, abdominal pain, abdominal syndrome acute; infrequent: chills, fever, face edema, ulcer, photosensitivity reaction, neck rigidity, neck pain, abdomen enlarged; rare: cellulitis, chest pain substernal. Cardiovascular System: frequent: hypertension, vasodilatation; infrequent: angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, bradycardia, migraine, hypotension; rare: atrial arrhythmia, , vascular headache, pulmonary embolus, cerebral ischemia, cardiomegaly, phlebitis, left heart failure. Digestive System: frequent: vomiting, anorexia; infrequent, nausea and vomiting, gum hemorrhage, stomatitis, colitis, liver function tests abnormal; rare: tongue discoloration, ulcerative stomatitis, salivary gland enlargement, increased salivation, intestinal obstruction, pancreatitis, aphthous stomatitis, cirrhosis of liver, gastritis, gastroenteritis, oral moniliasis, tongue edema. Endocrine System: rare: goiter, hypothyroidism. Hemic and Lymphatic System: rare: lymphadenopathy, leukopenia, petechia,anemia, thrombocytopenia, lymphocytosis, pancytopenia. Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders: frequent: thirst; infrequent: dehydration,weight loss; rare: gout, SGOT increased, healing abnormal, diabetes mellitus, hyponatremia. Musculoskeletal System: frequent: myasthenia, arthralgia; infrequent: arthritis, tenosynovitis; rare: pathologic fracture, osteoporosis fracture, bone pain,myositis, tendon rupture, arthrosis, bursitis. Nervous System: frequent: hypesthesia, apathy, depression, hypokinesia,vertigo, twitching, agitation, anxiety, amnesia, hyperkinesia, paresthesia;, infrequent: ataxia, delirium, delusions, depersonalization, dyskinesia, extrapyramidal syndrome, libido increased, coordination abnormal, dysarthria, hallucinations, manic reaction, neurosis, dystonia, hostility, reflexes increased, emotional lability Respiratory System: frequent: cough increased, sinusitis; infrequent: epistaxis,bronchitis, asthma, pneumonia; Skin and Appendages: frequent: pruritus, rash; infrequent: acne, e, dry skin, herpes simplex, alopecia. Special Senses: infrequent: eye pain, abnormality of lacrimation disorder, glaucoma, hyperacusis, ear pain, Urogenital System: frequent: urinary tract infection; infrequent: kidney calculus, cystitis, dysuria, urinary incontinence, urinary retention, vaginitis,hematuria, breast pain, amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, leukorrhea, impotence
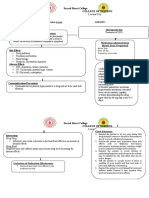
Patient monitoring: Monitor vital signs, especially for orthostatic hypotension. Assess neurologic status. Watch for weight gain caused by edema or increased appetite. Stay alert for urinary tract infection, sinusitis, and flulike symptoms. Monitor CBC with white cell differential. Stay alert for agranulocytosis. Watch for suicidal behavior or ideation (especially in child or adolescent). Patient teaching: Advise patient to take with food or milk to reduce GI upset. Tell patient he may crush conventional tablets if he can't swallow them whole. Instruct patient to take orally disintegrating tablet without water. Tell him to place it on tongue until it melts and to make sure tablet isn't broken. Tell patient to immediately report sore throat, fever, mouth sores, or other signs or symptoms of infection. Instruct patient (or parent) to immediately report suicidal thoughts or actions (especially in child or adolescent). Caution patient not to discontinue drug abruptly. Dosage must be tapered. If drug causes over sedation, tell patient to consult prescriber about taking entire daily dose at bedtime. Caution patient to avoid driving and other hazardous activities until he knows how drug affects concentration and alertness. Tell patient to avoid alcohol and to discuss herbal use with prescriber. Instruct patient to avoid exposure to excessive sunlight or sun lamps. Advise patient that therapeutic effects may take 2 to 3 weeks.
You might also like
- Zoloft Sertraline Drug CardDocument1 pageZoloft Sertraline Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- Zopiclone clinical worksheetDocument2 pagesZopiclone clinical worksheetMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- Venlafaxine XRDocument2 pagesVenlafaxine XRMichael KuzbytNo ratings yet
- DesyrelDocument1 pageDesyrelKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Olanzapine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesOlanzapine Drug Studyjohnlester_jlfNo ratings yet
- Drug Study HaldolDocument2 pagesDrug Study HaldolGracia EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug Studyunkown userNo ratings yet
- NAME OF DRUG NozinanDocument3 pagesNAME OF DRUG NozinanMill Jan CruzNo ratings yet
- RemeronDocument1 pageRemeronENo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyJezen SucalitNo ratings yet
- Tricyclic antidepressants overviewDocument2 pagesTricyclic antidepressants overviewAaLona RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Mesoridazine Drug StudyDocument5 pagesMesoridazine Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- CCMH Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCCMH Drug StudyJoy JarinNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acamprosate (Campral) and Bupropion)Document5 pagesDrug Study (Acamprosate (Campral) and Bupropion)kuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquilloDocument4 pagesDRUG-STUDY OmeprazoleIV AngelicaRonquillokarl eiron delos santosNo ratings yet
- Droperidol (Inapsine)Document1 pageDroperidol (Inapsine)ENo ratings yet
- Drug AnalysisDocument3 pagesDrug Analysiskristel_nicole18yahoNo ratings yet
- Drug Analysis in PsychDocument3 pagesDrug Analysis in PsychBryan Andrew GonzalesNo ratings yet
- TegretolDocument4 pagesTegretolianecunar100% (2)
- Nursing responsibilities for chlorpromazine administrationDocument3 pagesNursing responsibilities for chlorpromazine administrationkaycelyn jimenezNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Mebeverine Hydrochloride Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Assessment & Drug EffectsDocument4 pagesGeneric Name: Mebeverine Hydrochloride Mechanism of Action Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Nursing Responsibility Assessment & Drug EffectsNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- SeroquelDocument2 pagesSeroqueldanaNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazole Drug Study - Rhuby AbenojaDocument1 pageAripiprazole Drug Study - Rhuby AbenojaRHUBY ABENOJANo ratings yet
- CymbaltaDocument2 pagesCymbaltaENo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyjohnclement_dcNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam BiperidinDocument6 pagesAlprazolam BiperidinFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument3 pagesDRUG StudyArfe BaquinquitoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyKeanu ArcillaNo ratings yet
- HaloperidolDocument2 pagesHaloperidolMikz JocomNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Form TJDocument4 pagesDrug Study Form TJJasmin Santiago CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Citalopramhydrobromide CelexaDocument3 pagesCitalopramhydrobromide CelexaKristi Wray100% (1)
- Clozapine, Quetiapine, Biperiden, and Fluphenazine Drug StudyDocument6 pagesClozapine, Quetiapine, Biperiden, and Fluphenazine Drug StudyRegine Lorenzana Mey-AngNo ratings yet
- Drug Studies PsychDocument12 pagesDrug Studies PsychAnna Mendiola-BasbasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FluvoxamineDocument2 pagesDrug Study FluvoxamineAngeline de Gala0% (1)
- NCP Drug Study Final Paranoid SchizophreniaDocument11 pagesNCP Drug Study Final Paranoid SchizophreniaCherubim Lei DC FloresNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyzenNo ratings yet
- Mina Drug StudyDocument7 pagesMina Drug StudyChi Chaw Giselle HilarioNo ratings yet
- Valproate Uses, Dosing & Side EffectsDocument15 pagesValproate Uses, Dosing & Side EffectsdrdeuceNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyBadgal BazingaNo ratings yet
- Fluvoxamine MaleateDocument3 pagesFluvoxamine MaleateHilman Fitriaji Suganda PrawiraNo ratings yet
- Prescribed Fluanxol Depot dosage and administrationDocument4 pagesPrescribed Fluanxol Depot dosage and administrationHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Esophageal DiverticulaDocument13 pagesEsophageal DiverticulaShekaira B. SimsimNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonDocument6 pagesCASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonTiffany GordonNo ratings yet
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Document1 pageCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrug StudyBien EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Case Study - DrugsDocument4 pagesCase Study - DrugsYza DizaNo ratings yet
- New DS3Document3 pagesNew DS3dakieNo ratings yet
- Thioridazine hydrochloride for schizophrenia treatmentDocument1 pageThioridazine hydrochloride for schizophrenia treatmentGritoNo ratings yet
- Buspar (Buspirone)Document1 pageBuspar (Buspirone)ENo ratings yet
- AMITRIPTYLINEDocument2 pagesAMITRIPTYLINERPh Krishna Chandra JagritNo ratings yet
- Amitriptyline PDFDocument3 pagesAmitriptyline PDFscribdseewalNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyGail SantosNo ratings yet
- NCP PsychosisDocument3 pagesNCP PsychosisKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-is100% (1)
- Lithium Carbonate (Lithicarb, Quilonum SR) : Information For PatientsDocument2 pagesLithium Carbonate (Lithicarb, Quilonum SR) : Information For PatientsgavinbuzzNo ratings yet
- ChlorpromazineDocument1 pageChlorpromazineimthebossNo ratings yet
- TrihexyphenidylDocument7 pagesTrihexyphenidylfachsyarNo ratings yet
- CVA Drug StudyDocument51 pagesCVA Drug StudyKarel LuNo ratings yet
- C C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentDocument12 pagesC C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentEarl Tony TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Ranitidine Is Contraindicated in Patients With Known Hypersensitivity To The DrugDocument4 pagesRanitidine Is Contraindicated in Patients With Known Hypersensitivity To The DrugMohd HarizNo ratings yet
- Paracetamol Antipyretic and Analgesic GuideDocument7 pagesParacetamol Antipyretic and Analgesic GuideAnne Monique Moran OngjocoNo ratings yet